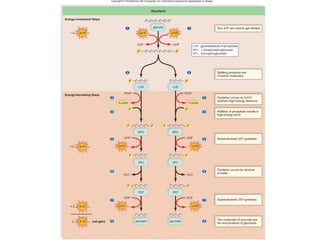
Cellular respiration involves the breakdown of glucose to release energy through a series of redox reactions. There are four stages: glycolysis, the preparatory reaction, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. These stages occur in both the cytoplasm and mitochondria, with oxygen as the final electron acceptor. The process generates approximately 38 ATP per glucose molecule through oxidative phosphorylation. When oxygen is limited, fermentation allows limited ATP production without oxygen.