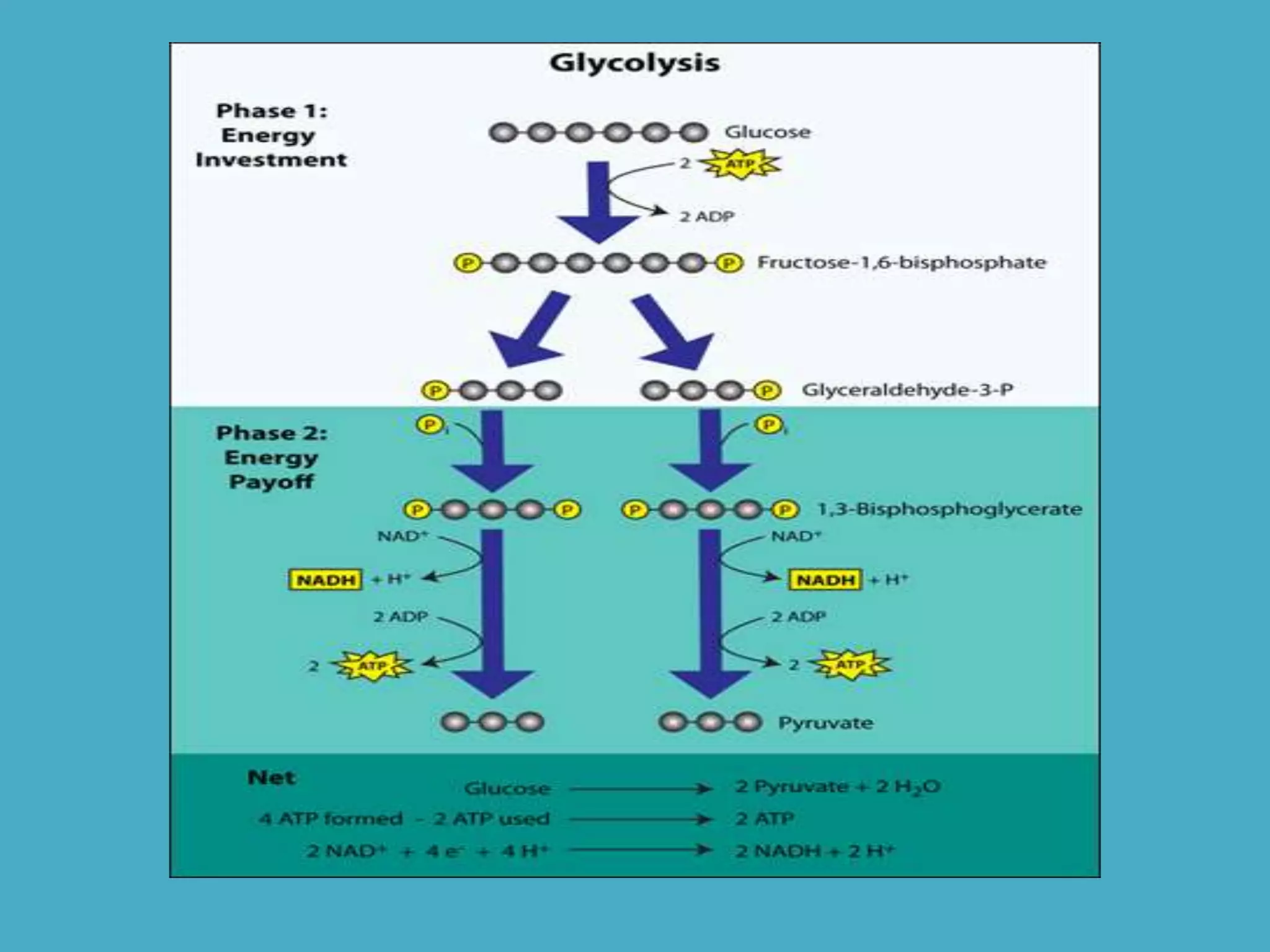
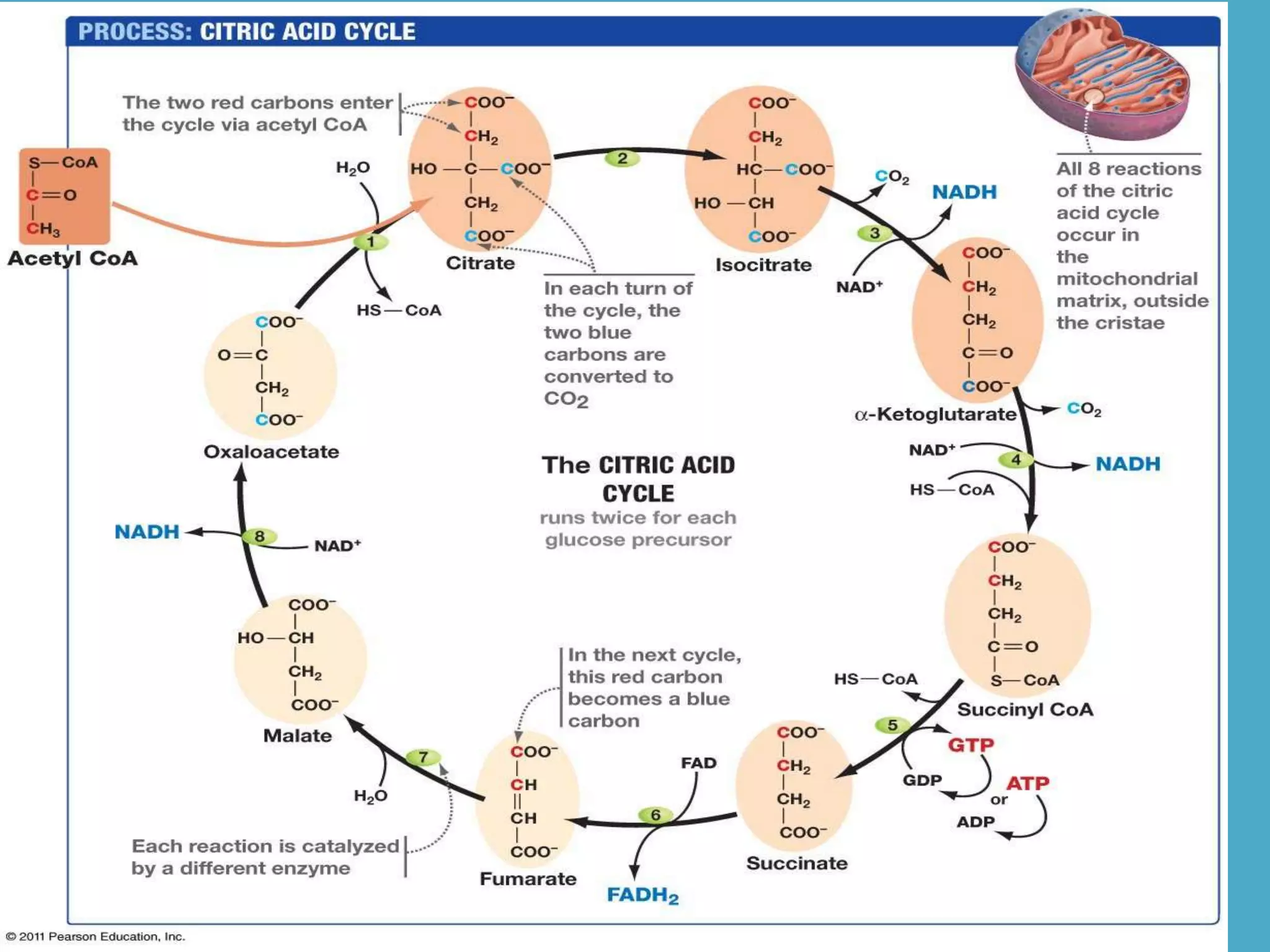
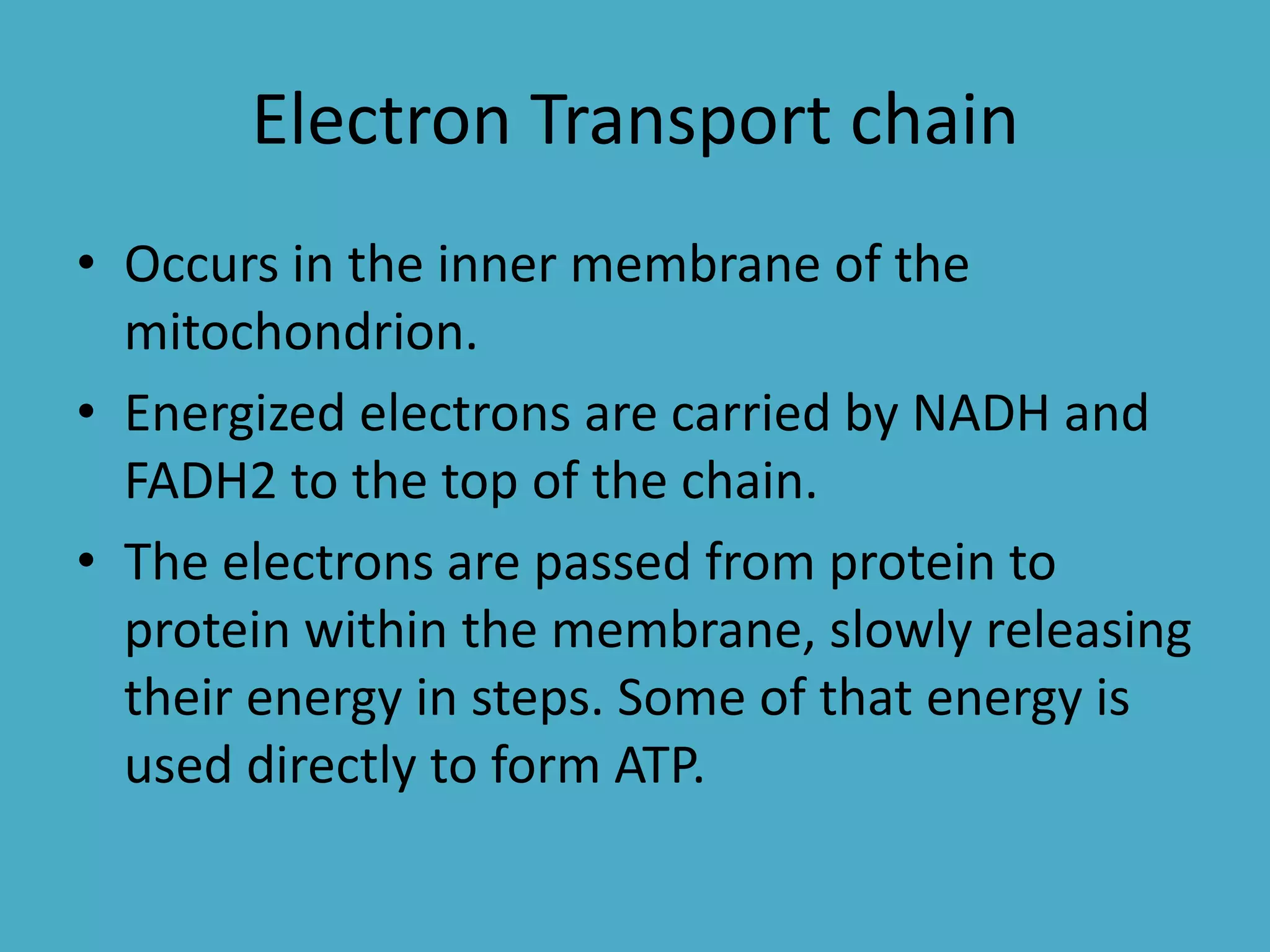
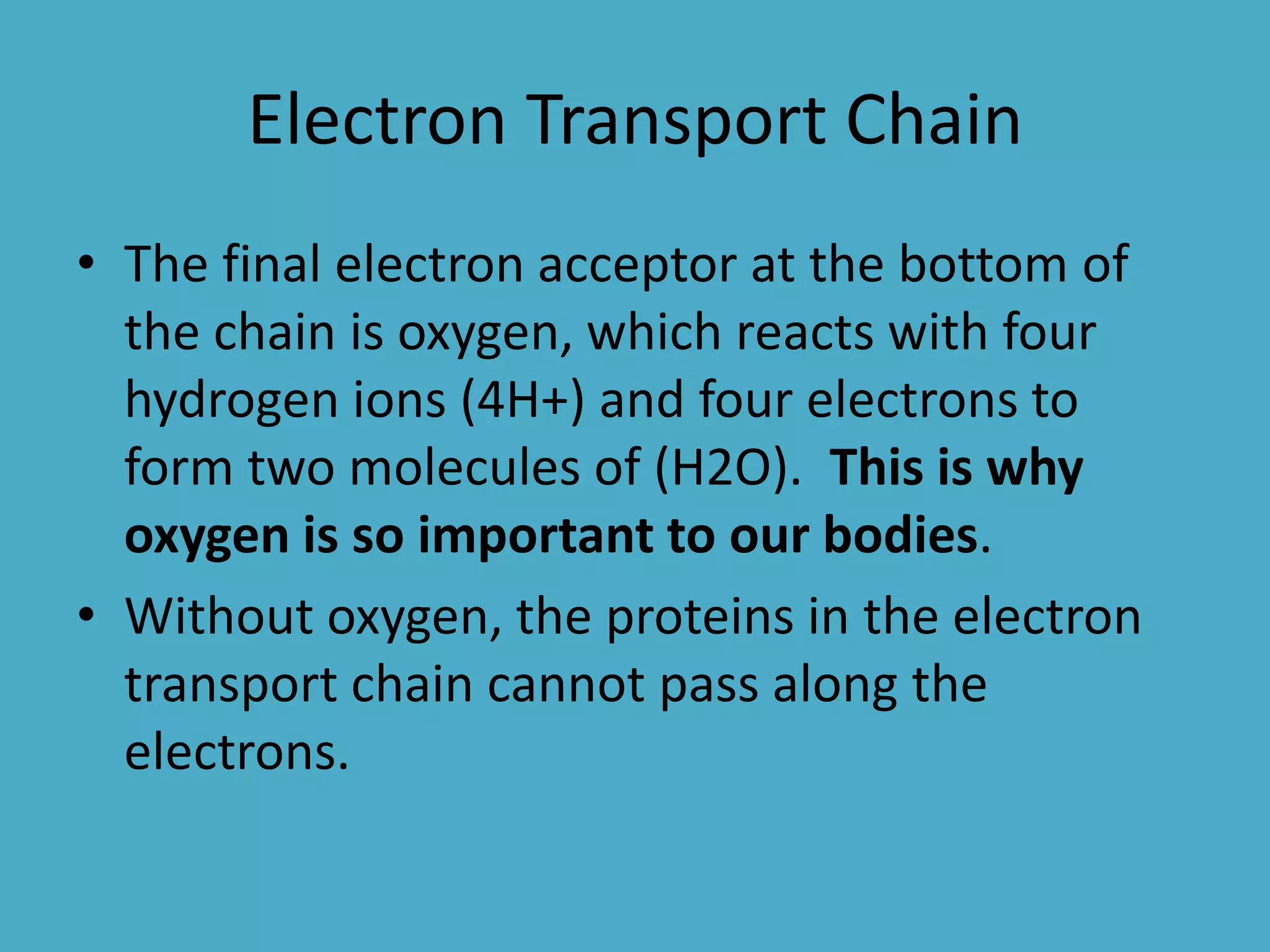
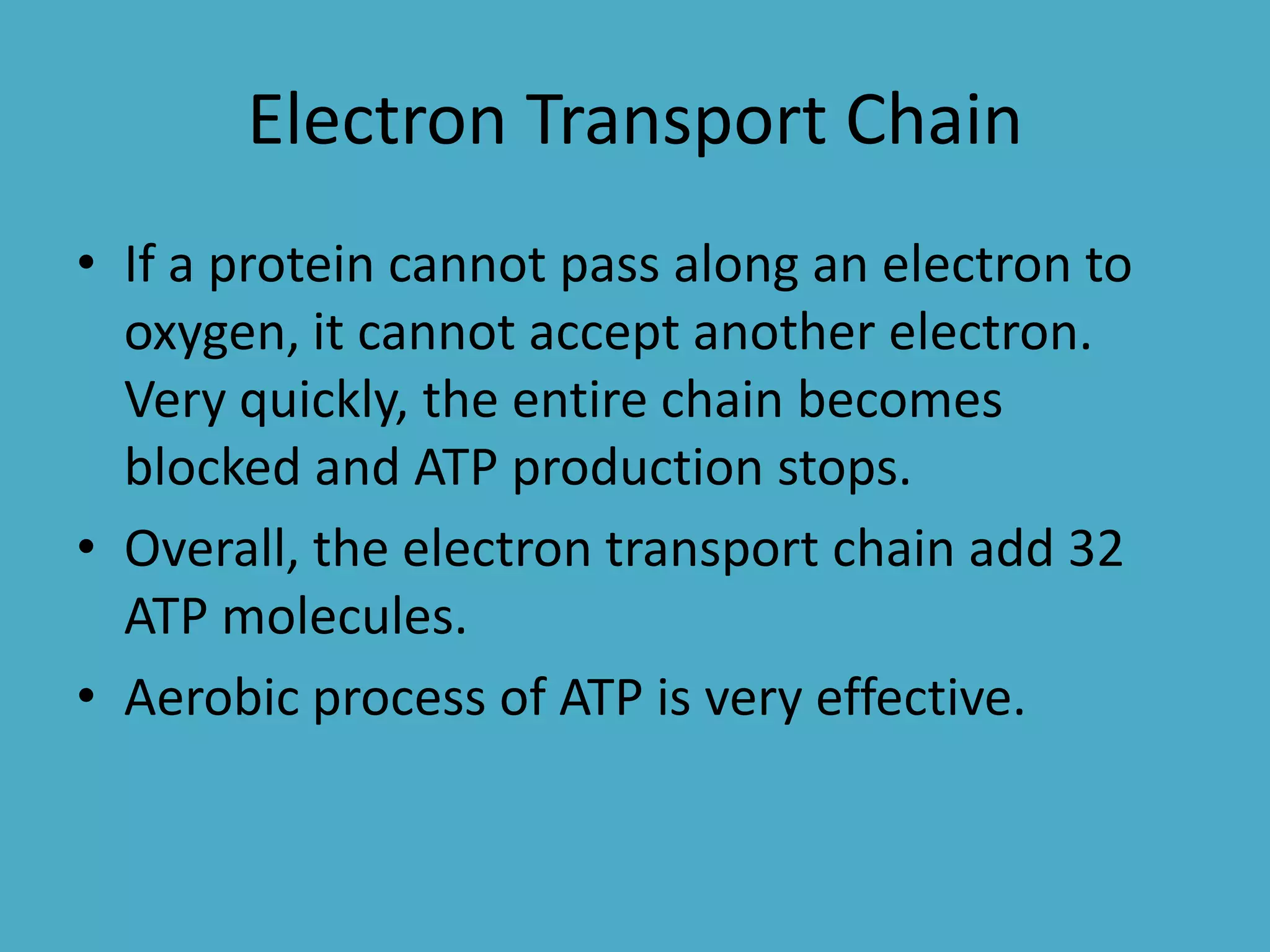
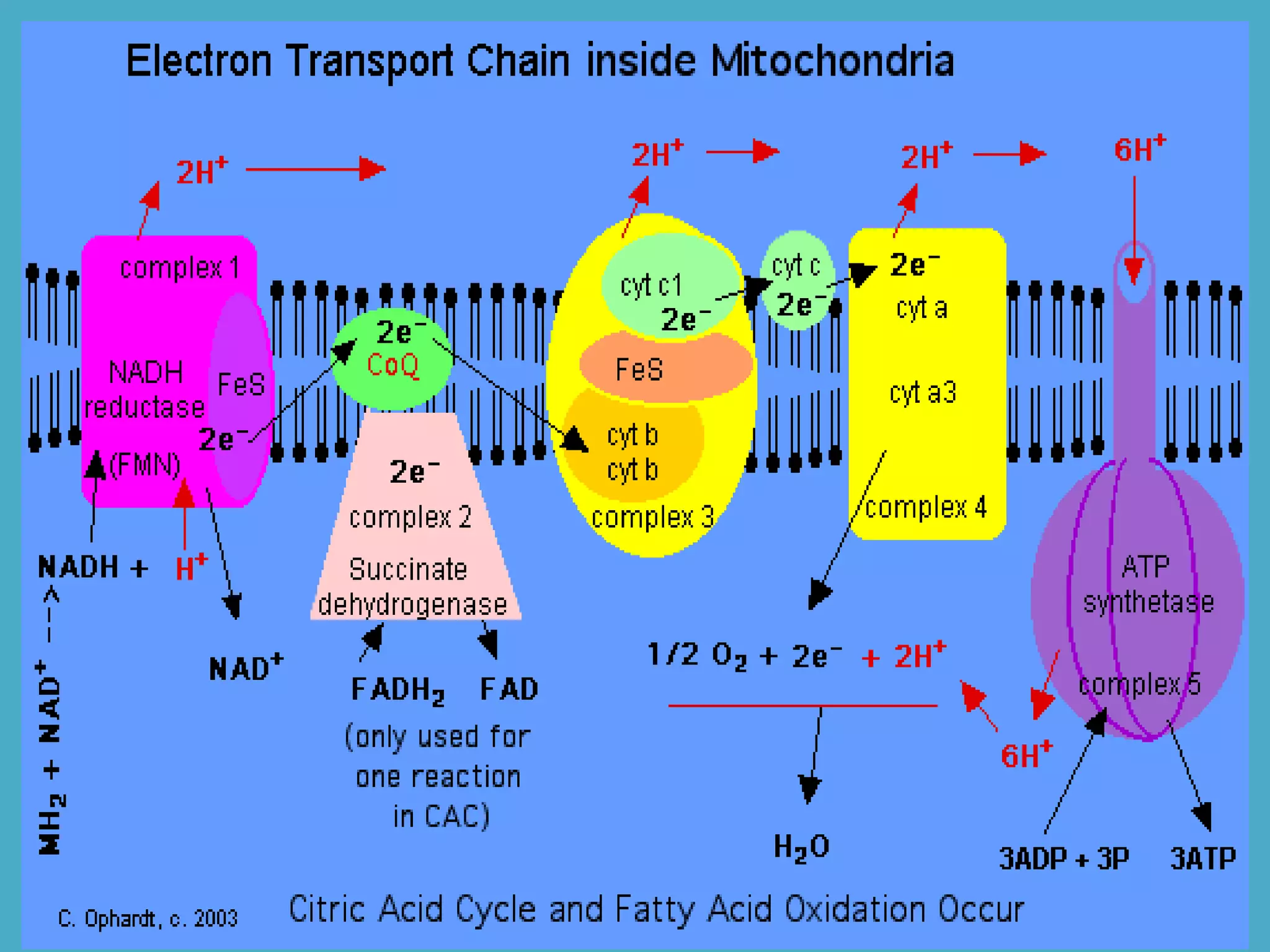
Cellular respiration has three main stages - glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain. Glycolysis breaks down glucose into pyruvic acid, producing a small amount of ATP. Pyruvic acid then enters the citric acid cycle in the mitochondria, producing more ATP and electron carriers. These electron carriers transport electrons through the electron transport chain, producing the most ATP through oxidative phosphorylation as electrons are transferred to oxygen as the final electron acceptor.