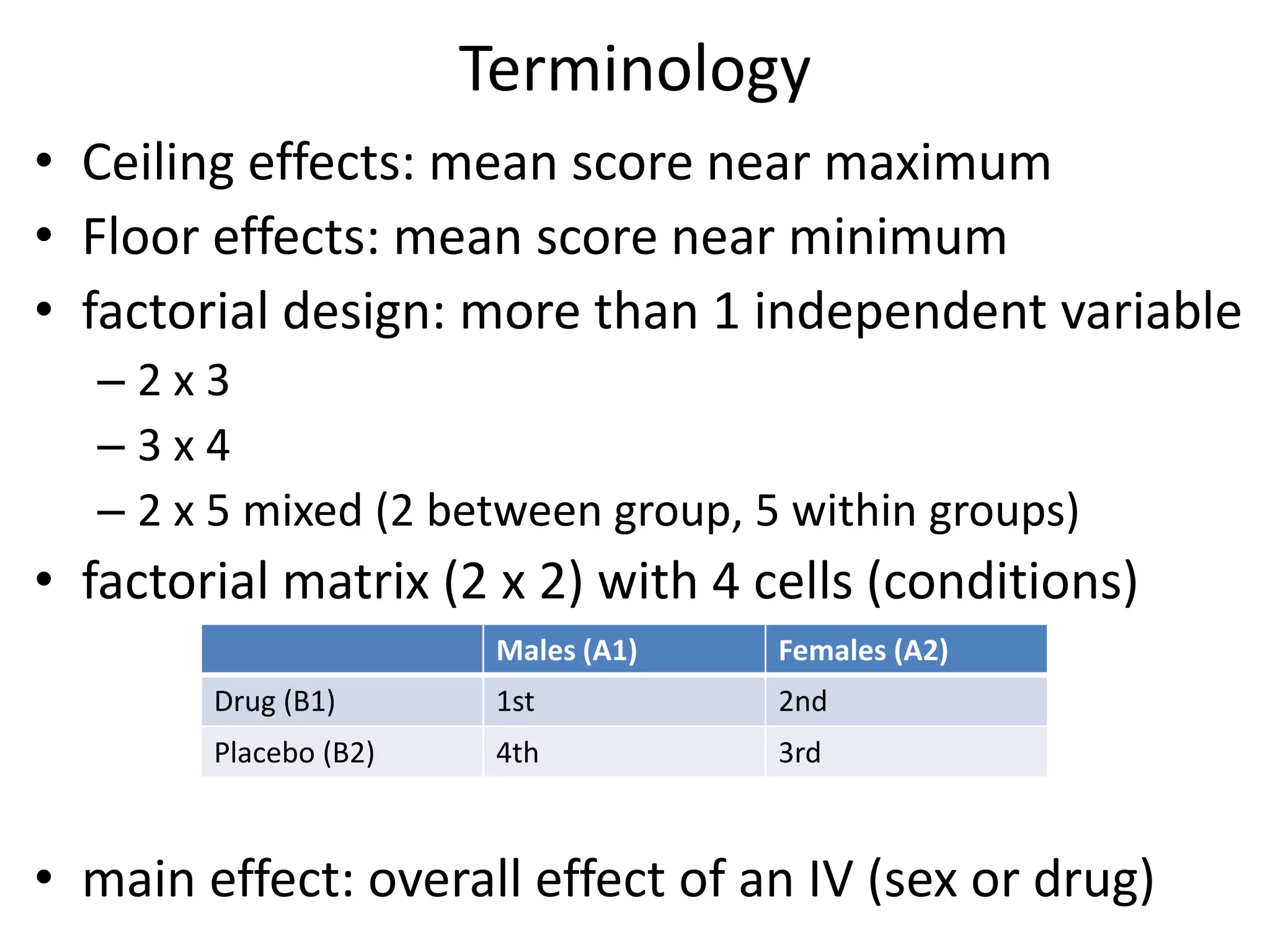
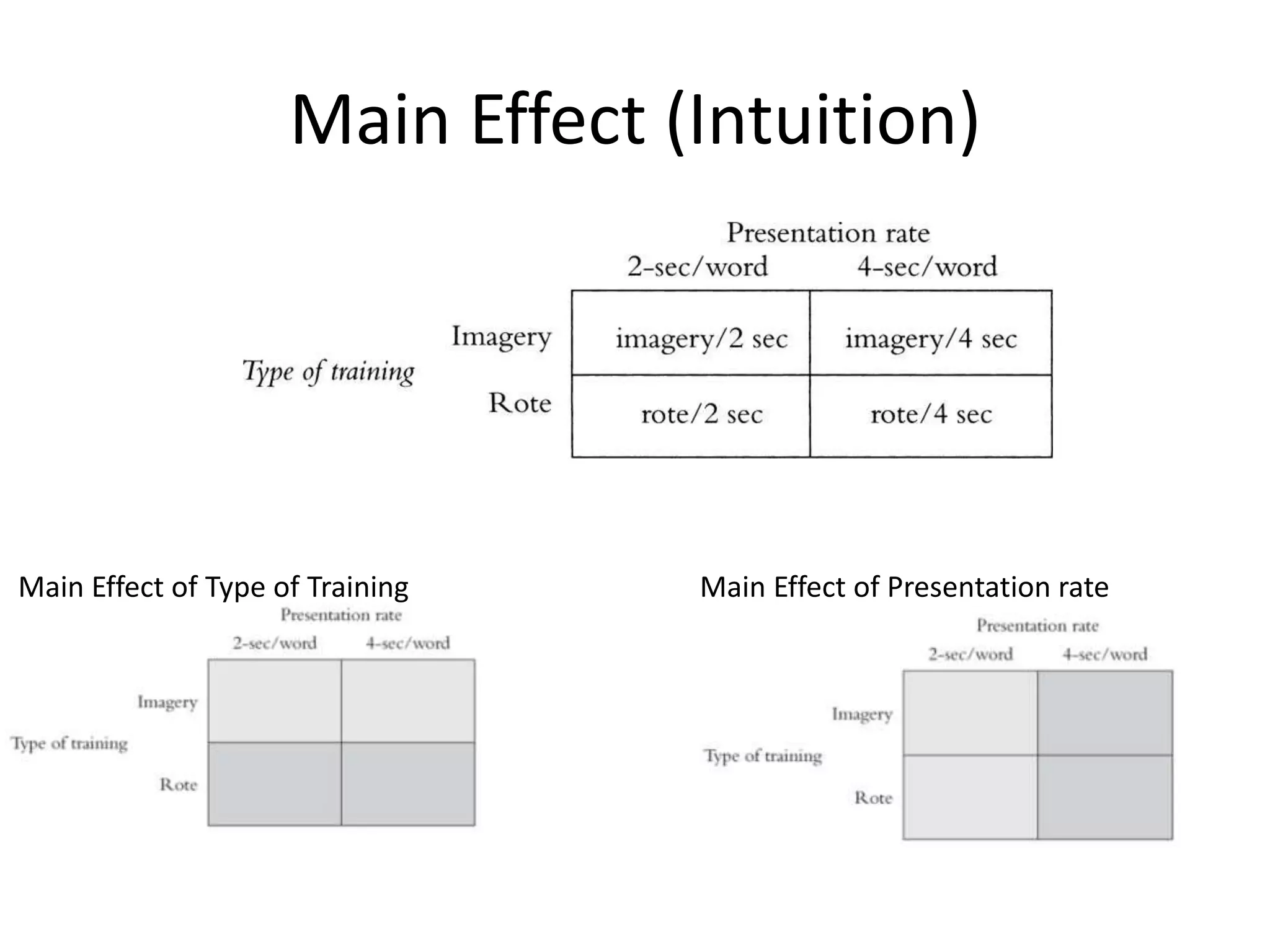
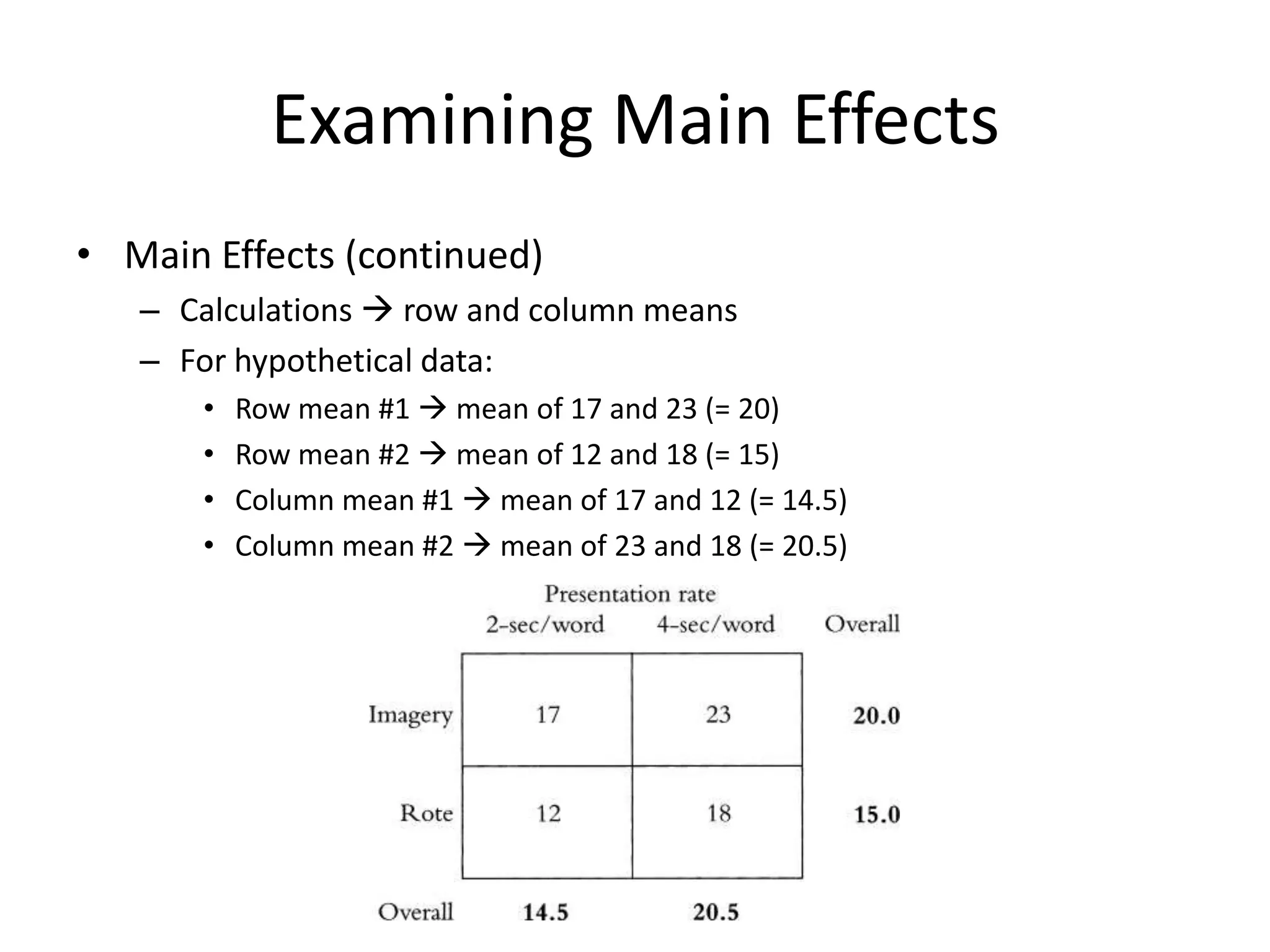
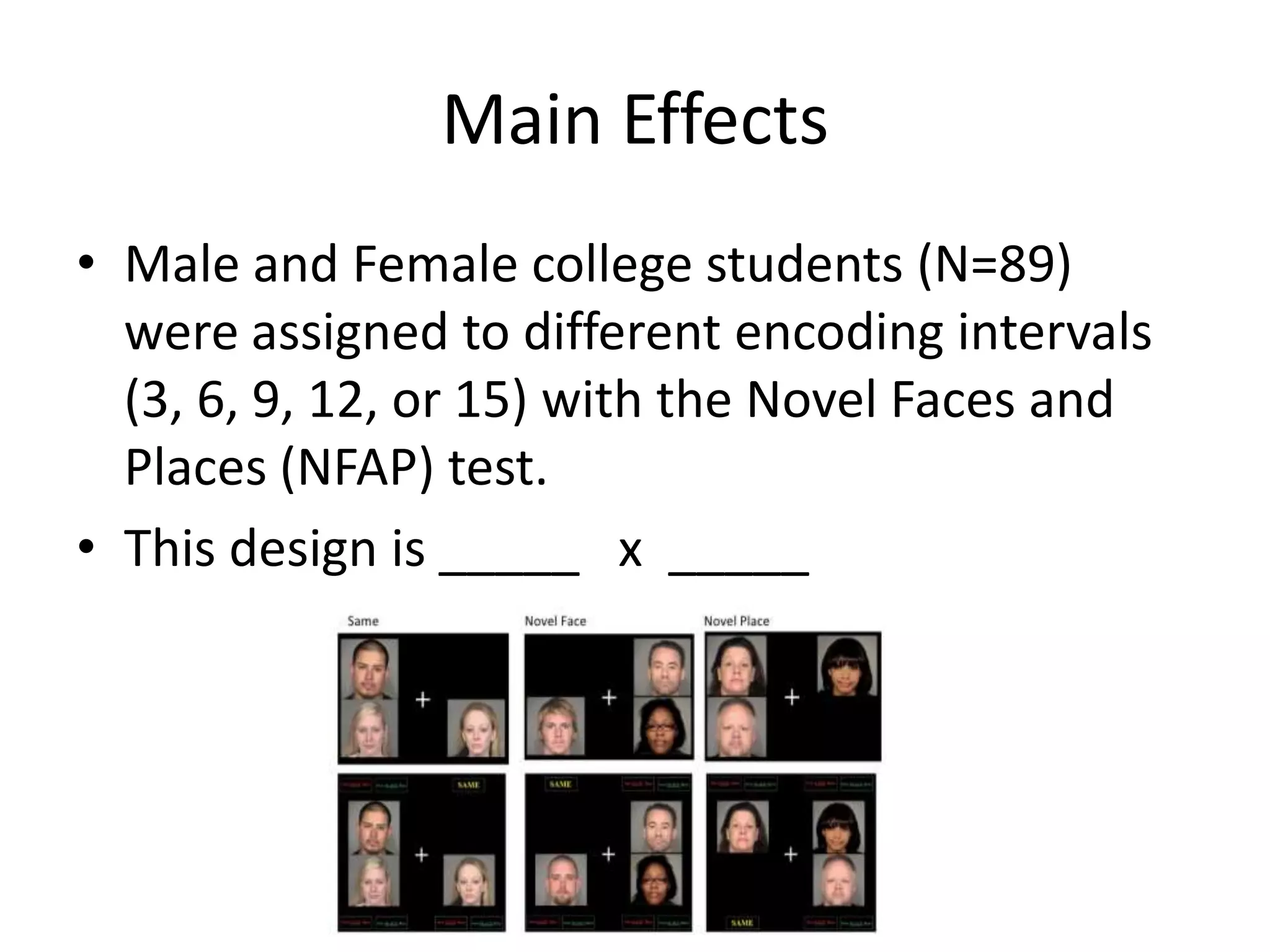
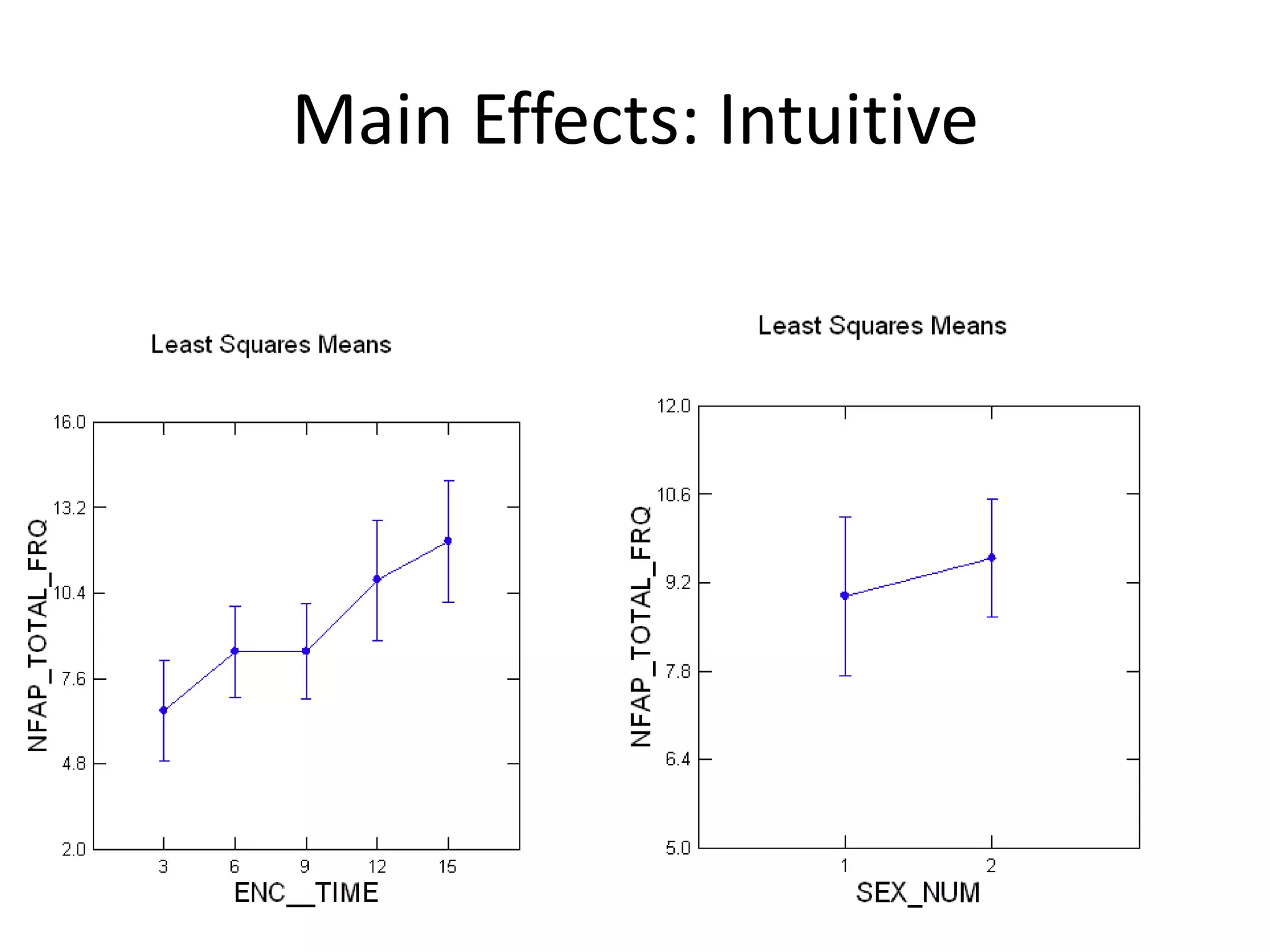
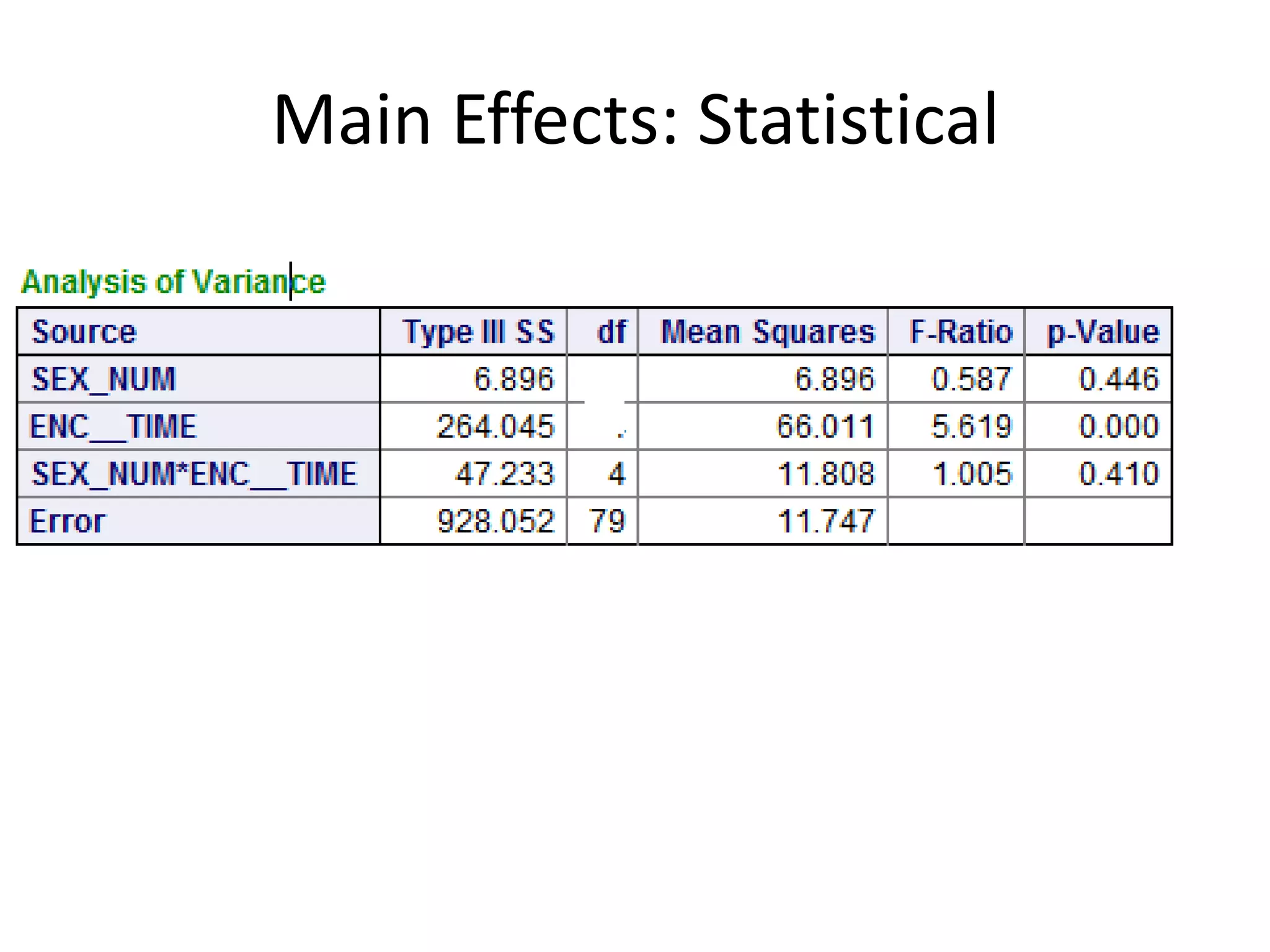
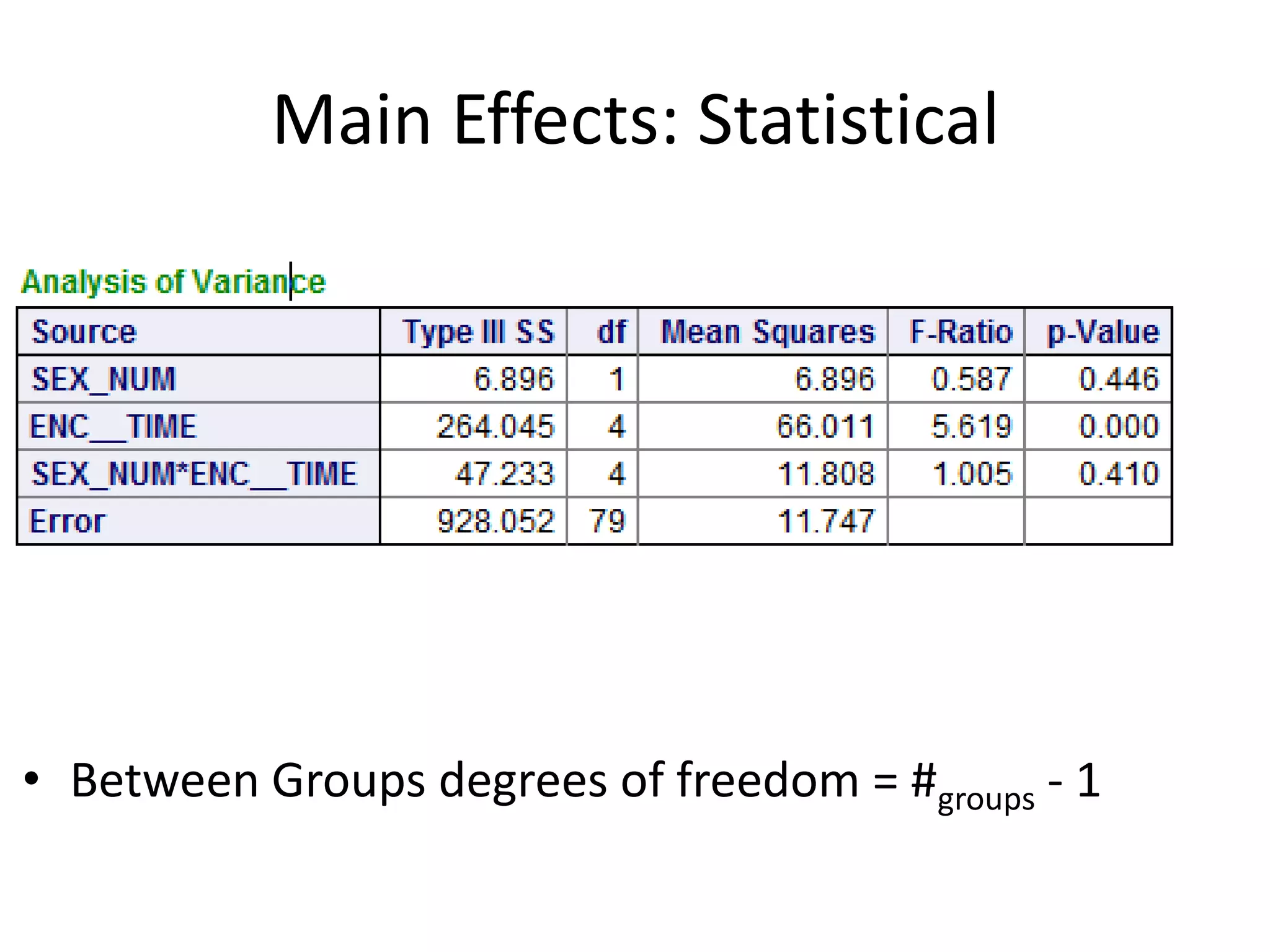
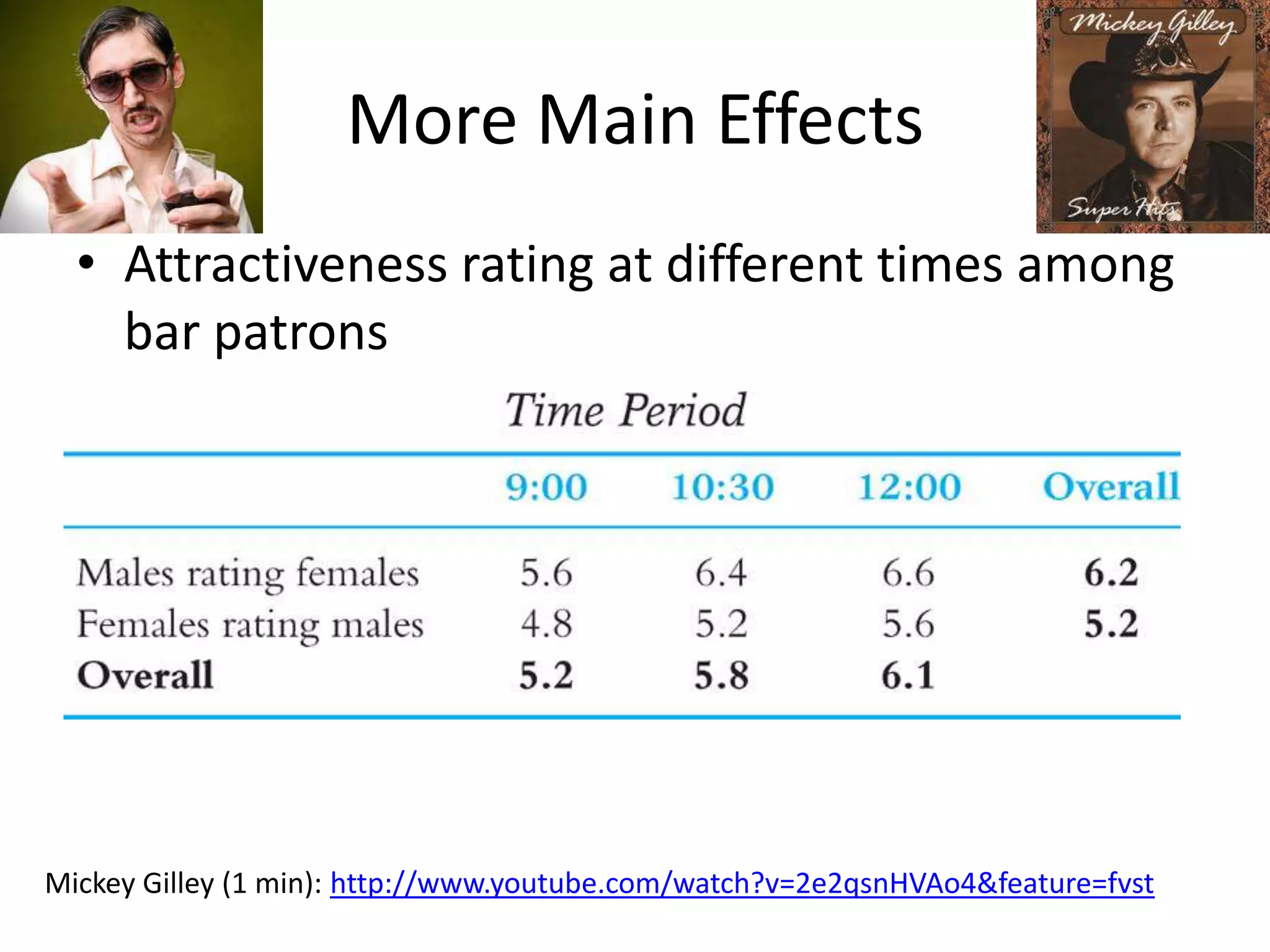
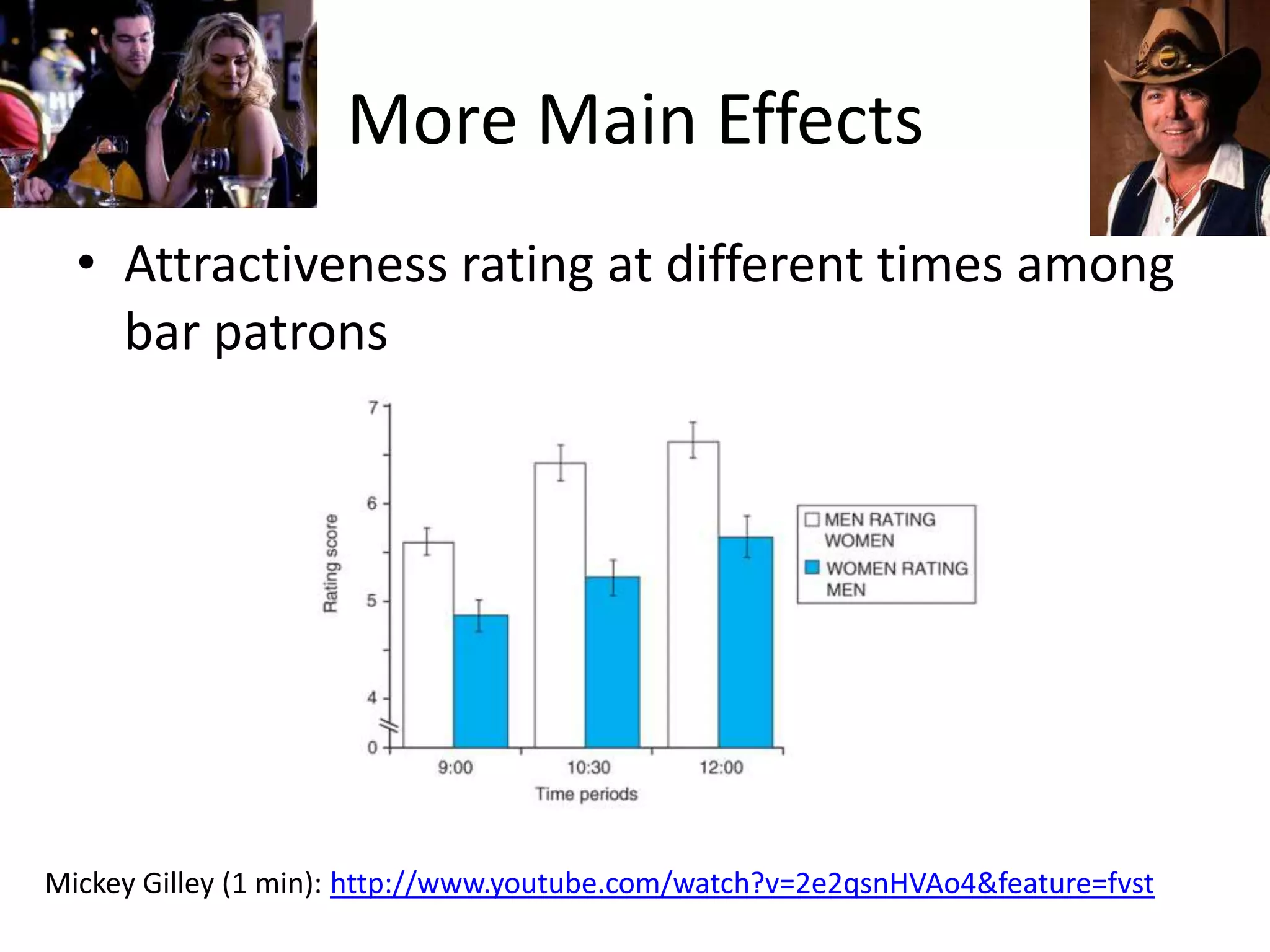
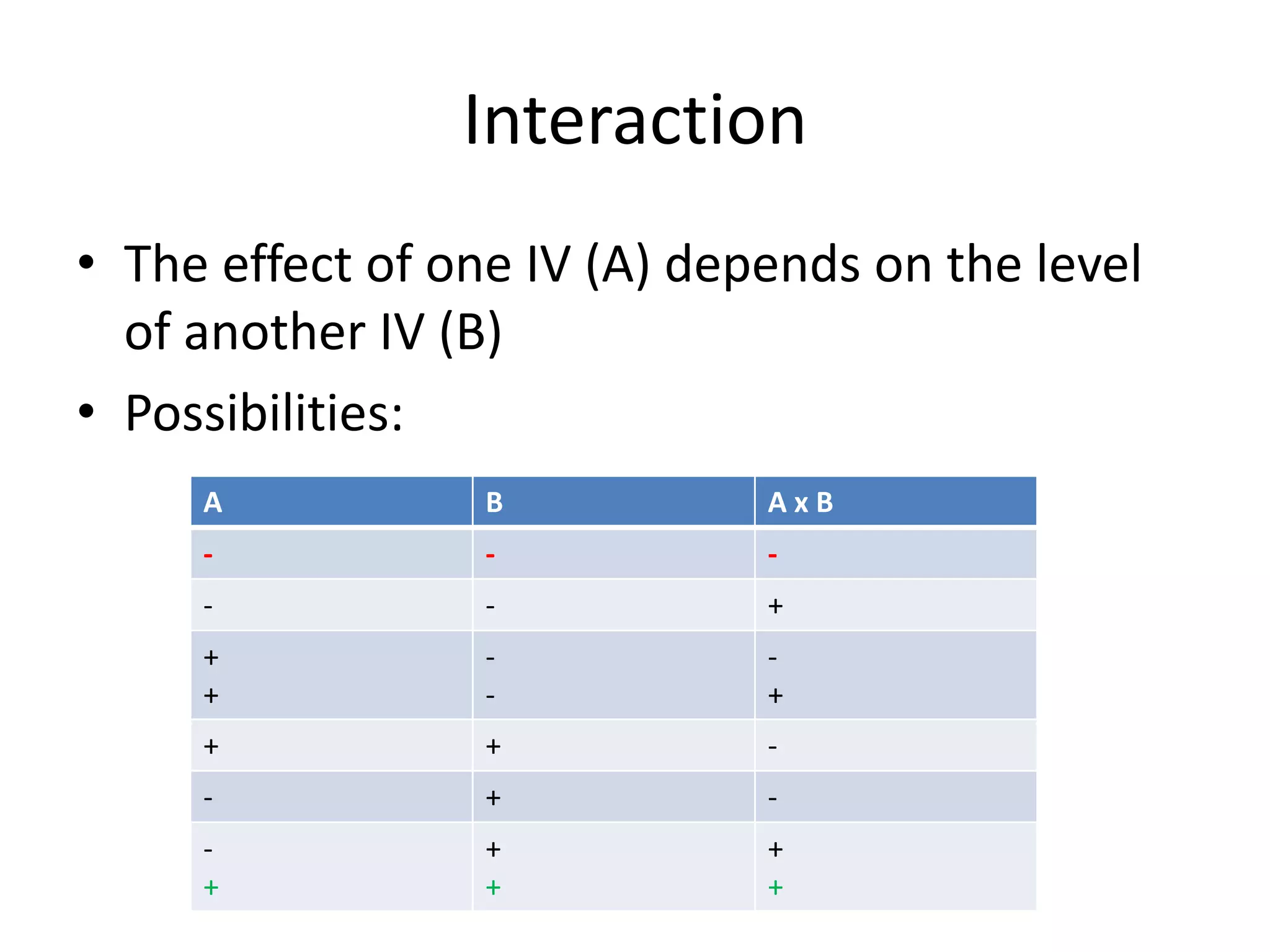
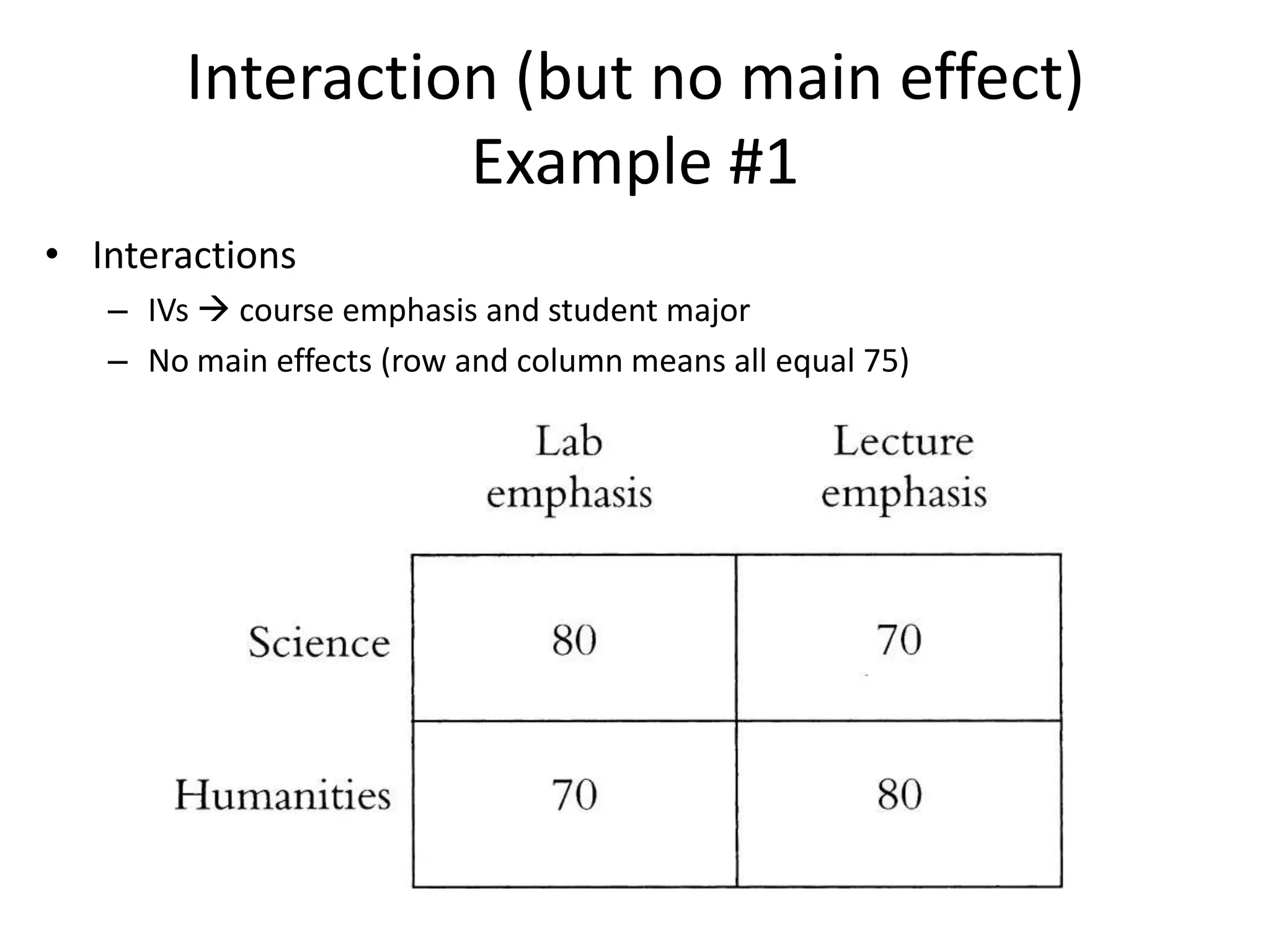
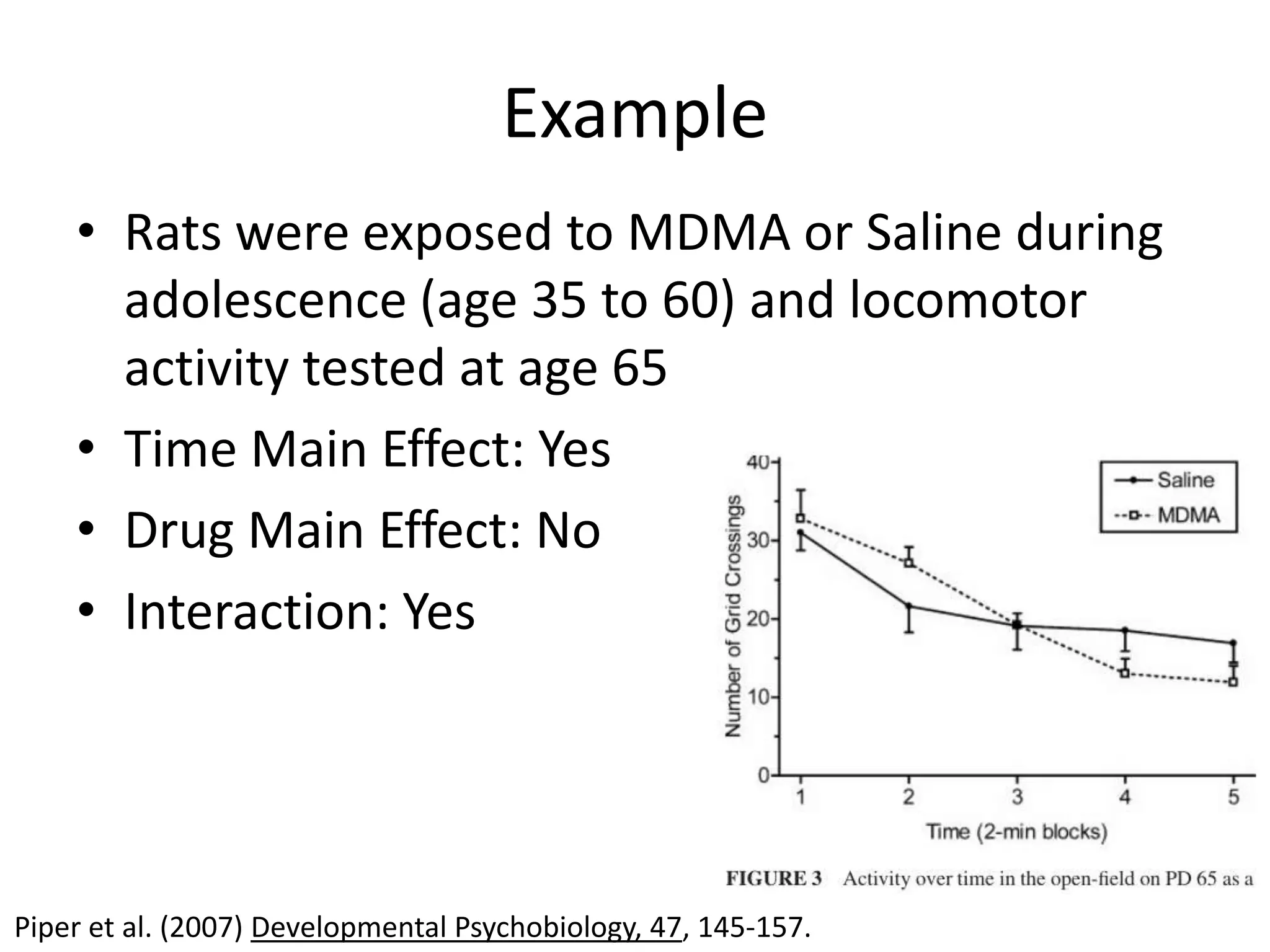
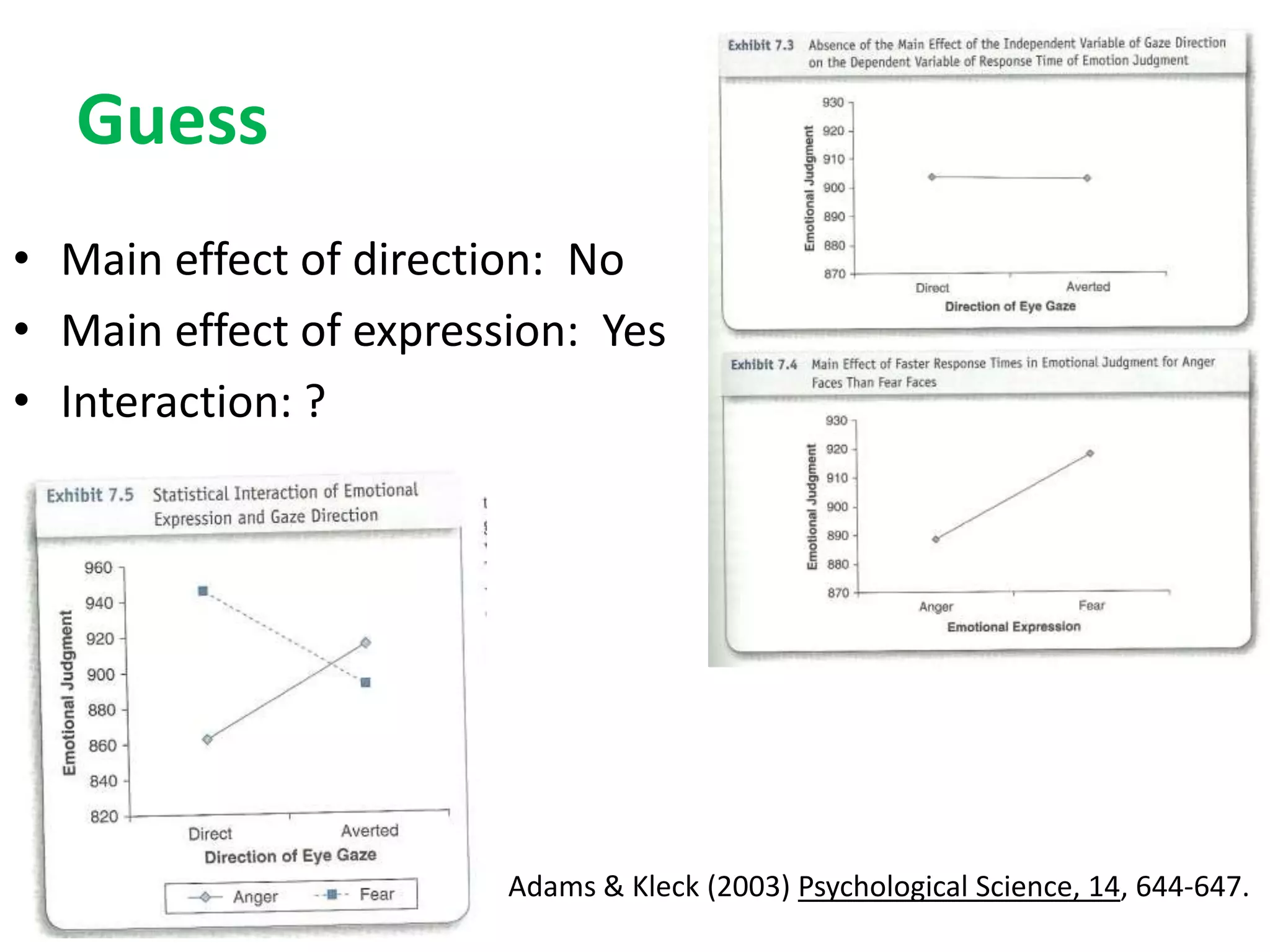
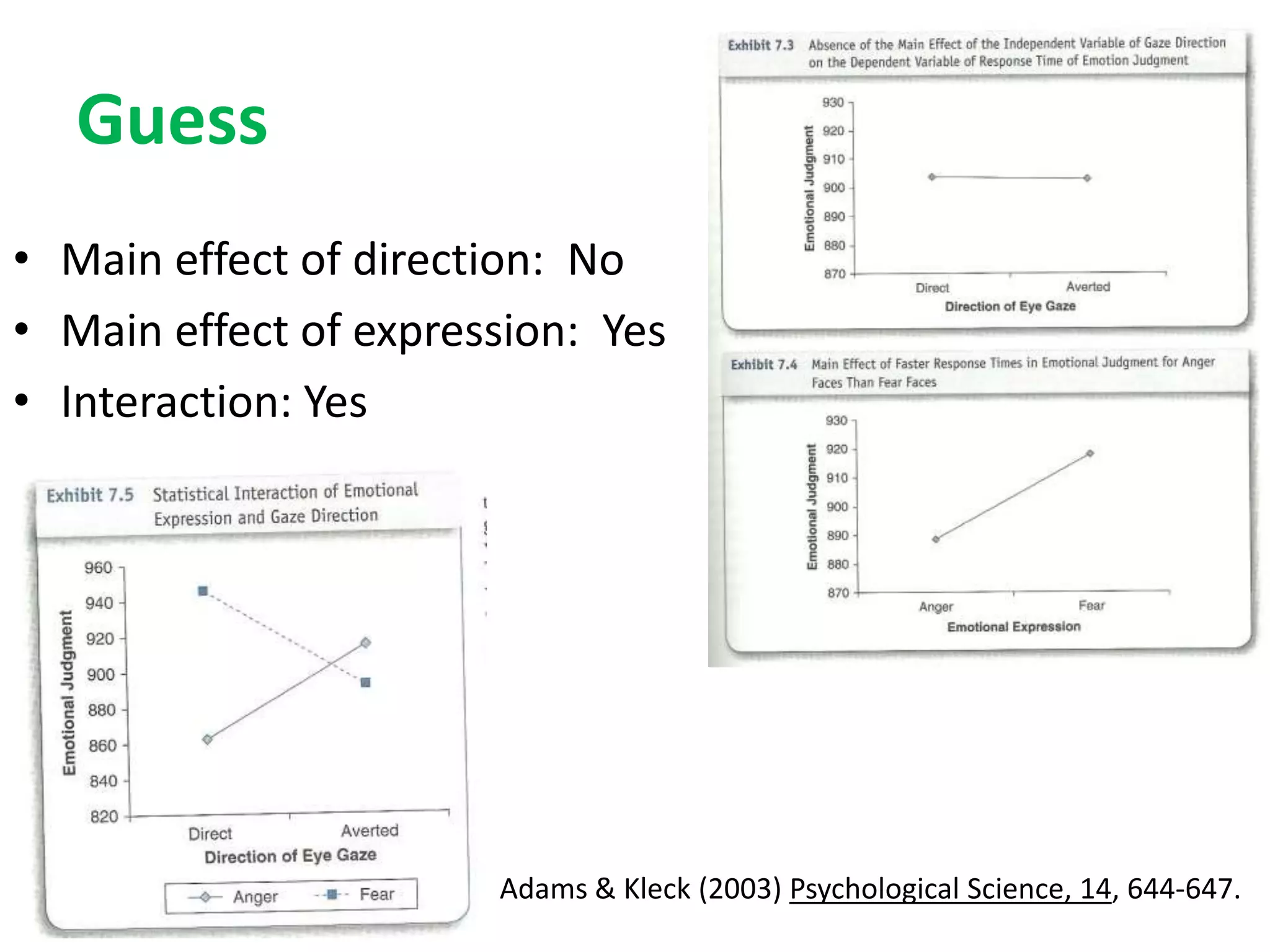
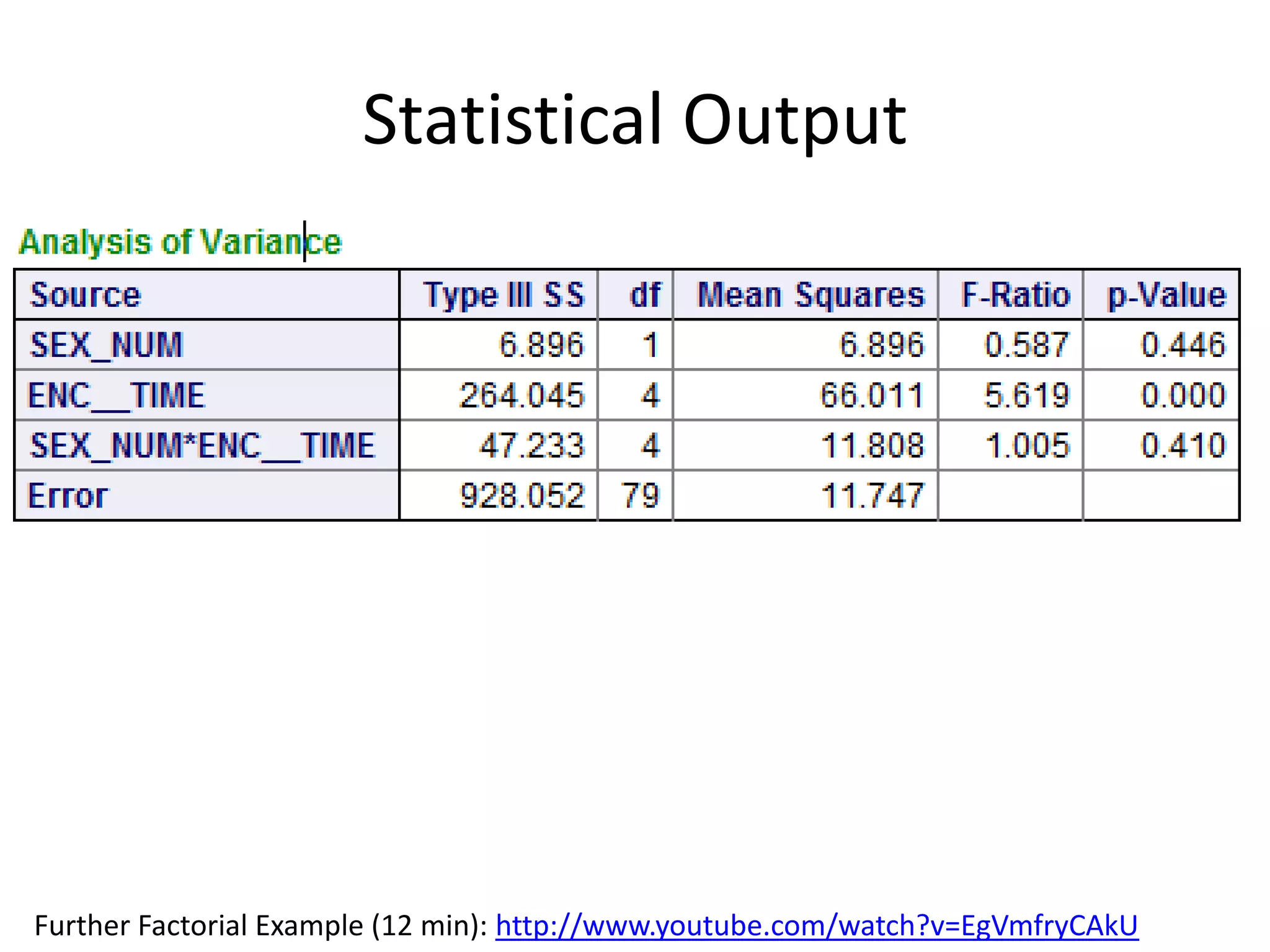
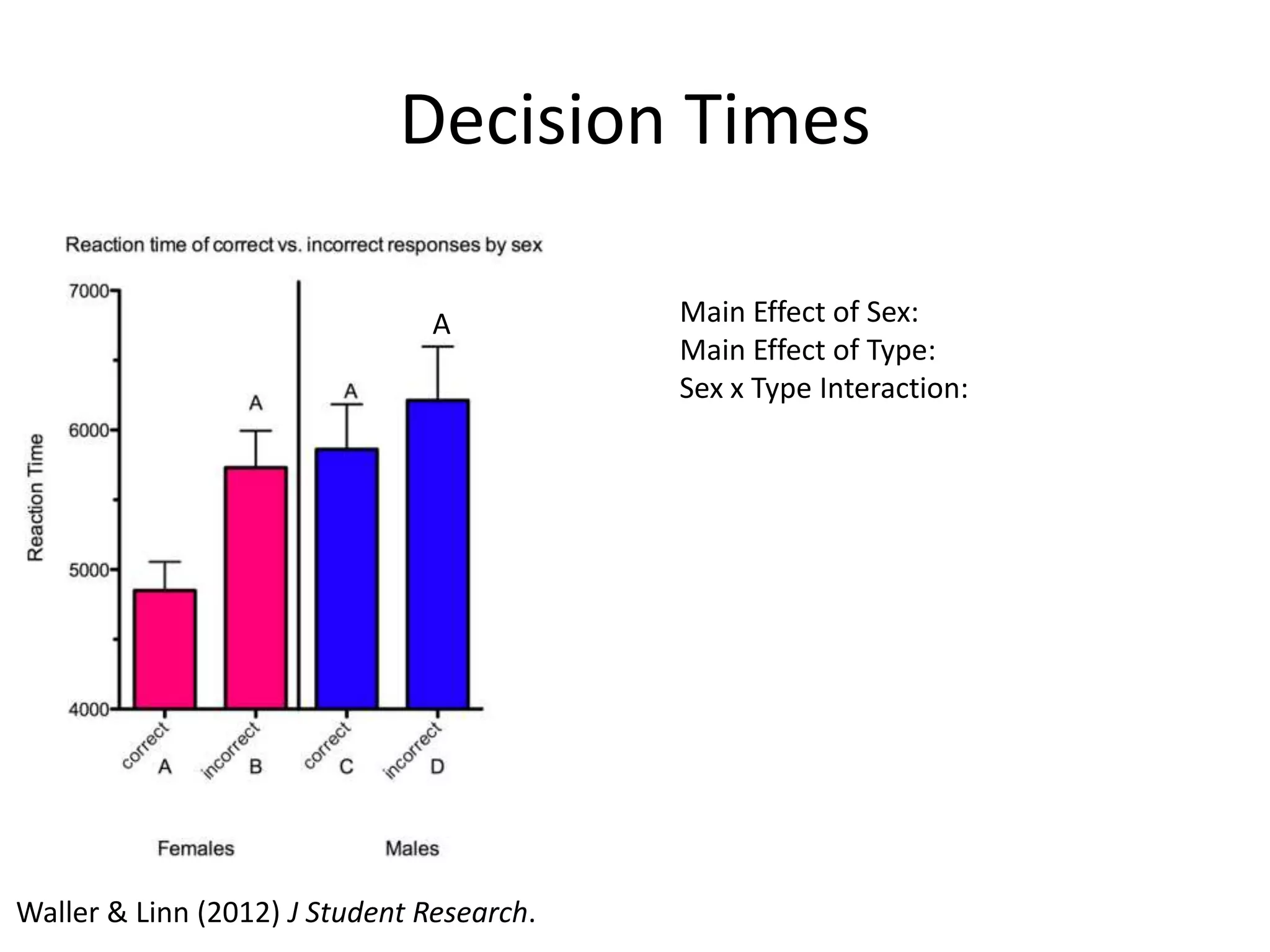
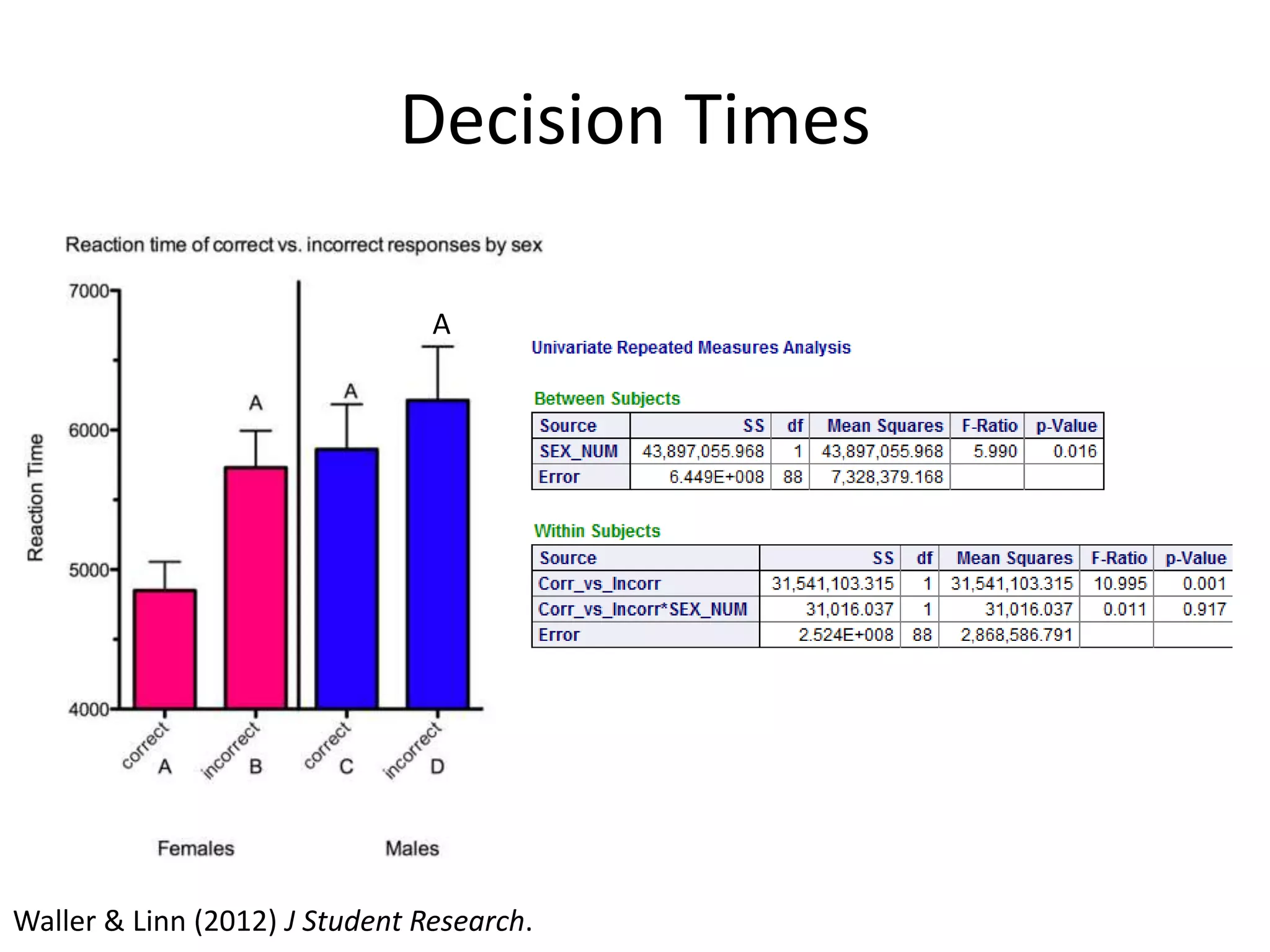
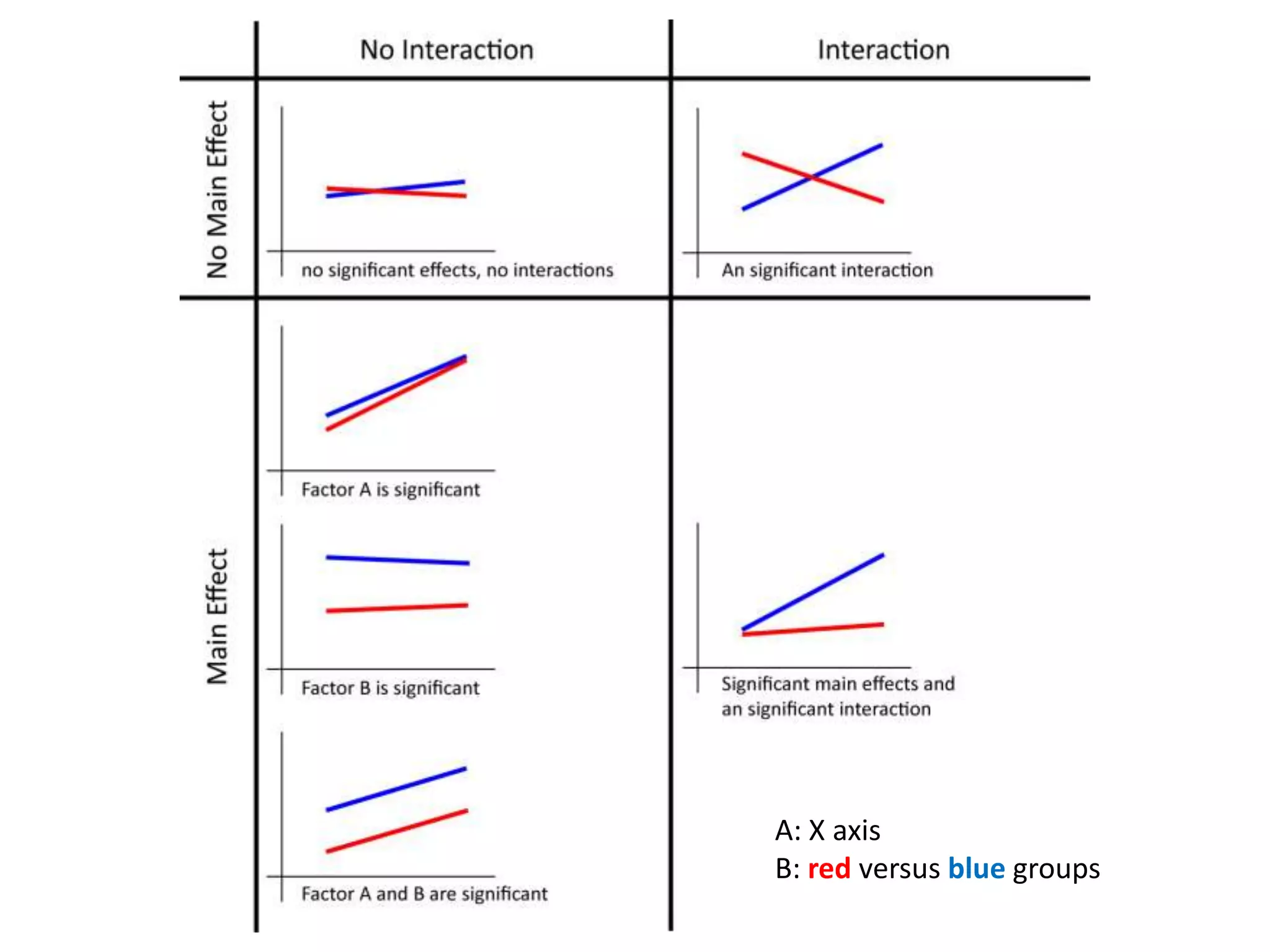
The document discusses factorial designs in research, focusing on main effects, interactions, and relevant terminology. It includes examples illustrating the calculation of main effects and how to interpret interactions between independent variables. The document also emphasizes data collection guidelines for conducting factorial studies.