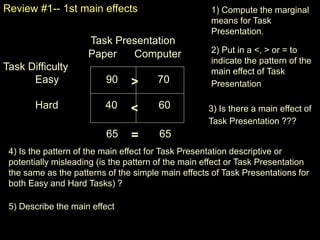
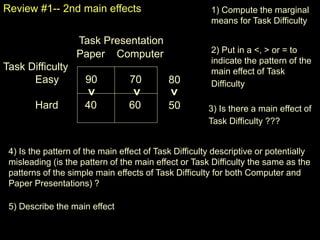
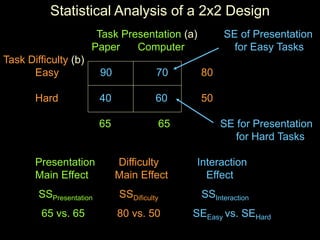
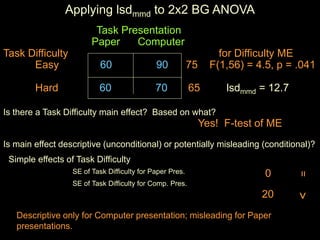
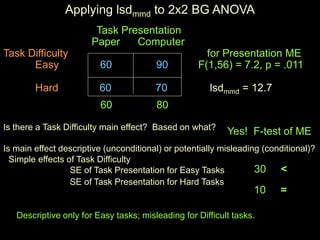
The document discusses statistical analysis of factorial designs, including 2x2 factorial designs. It covers reviewing interactions through examining simple effects and main effects. It also discusses kinds of factorial designs, including between-groups, within-groups, and mixed designs. Additionally, it provides examples of interpreting interactions and main effects, constructing F-tests, and using LSD to describe interactions by comparing cell means in 2x2 designs.



















![Effect Sizes for 2x2 BG Factorial designs
For Main Effects & Interaction (each w/ df=1)
r = [ F / (F + dferror)]
For Main Effects & Simple Effects
d = (M1 - M2 ) / Mserror
d²
r = ----------
d² + 4 (This is an “approximation formula”)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bgfactstat-220826052547-30addaa7/85/bgfact_stat-ppt-25-320.jpg)