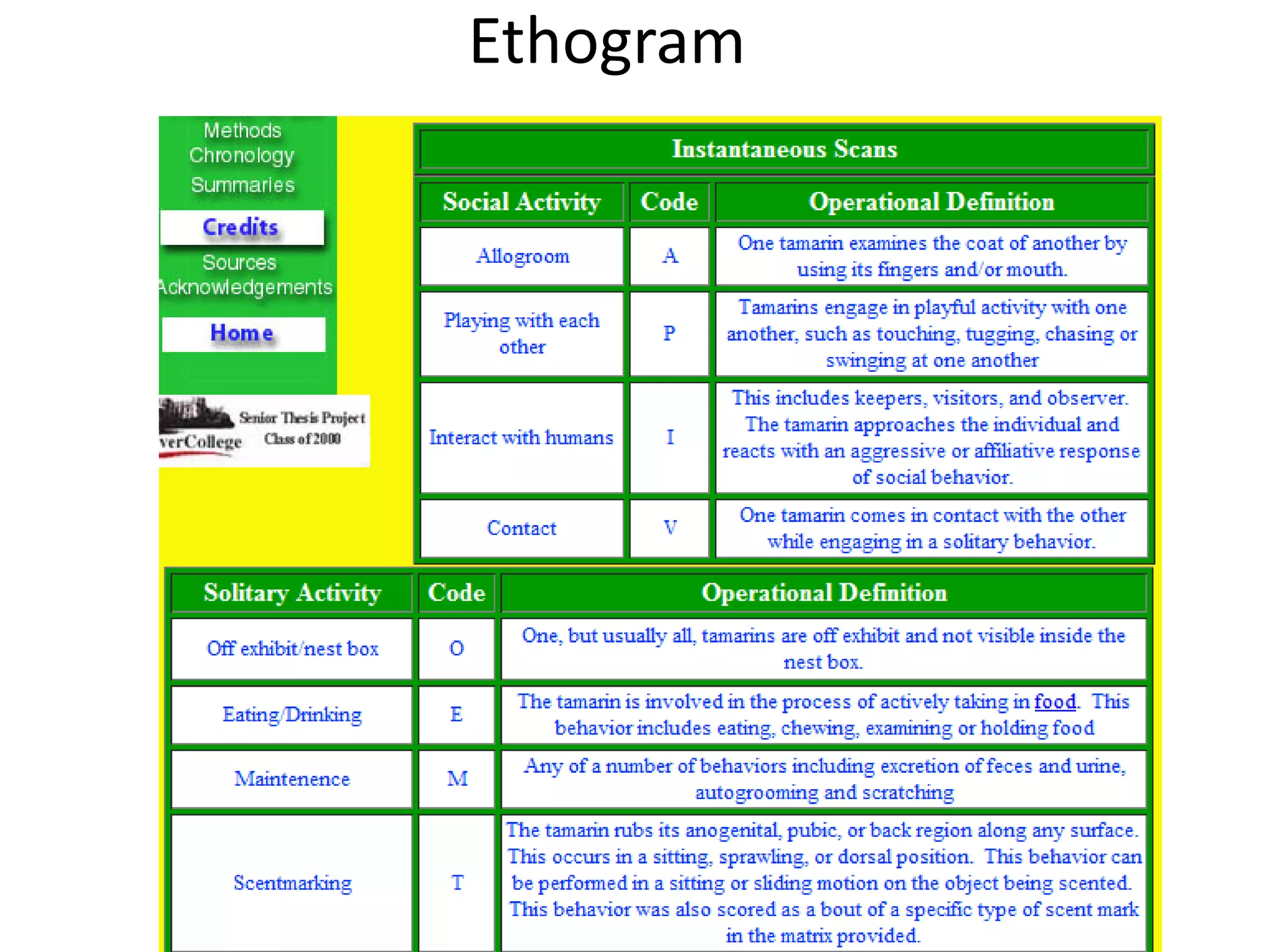
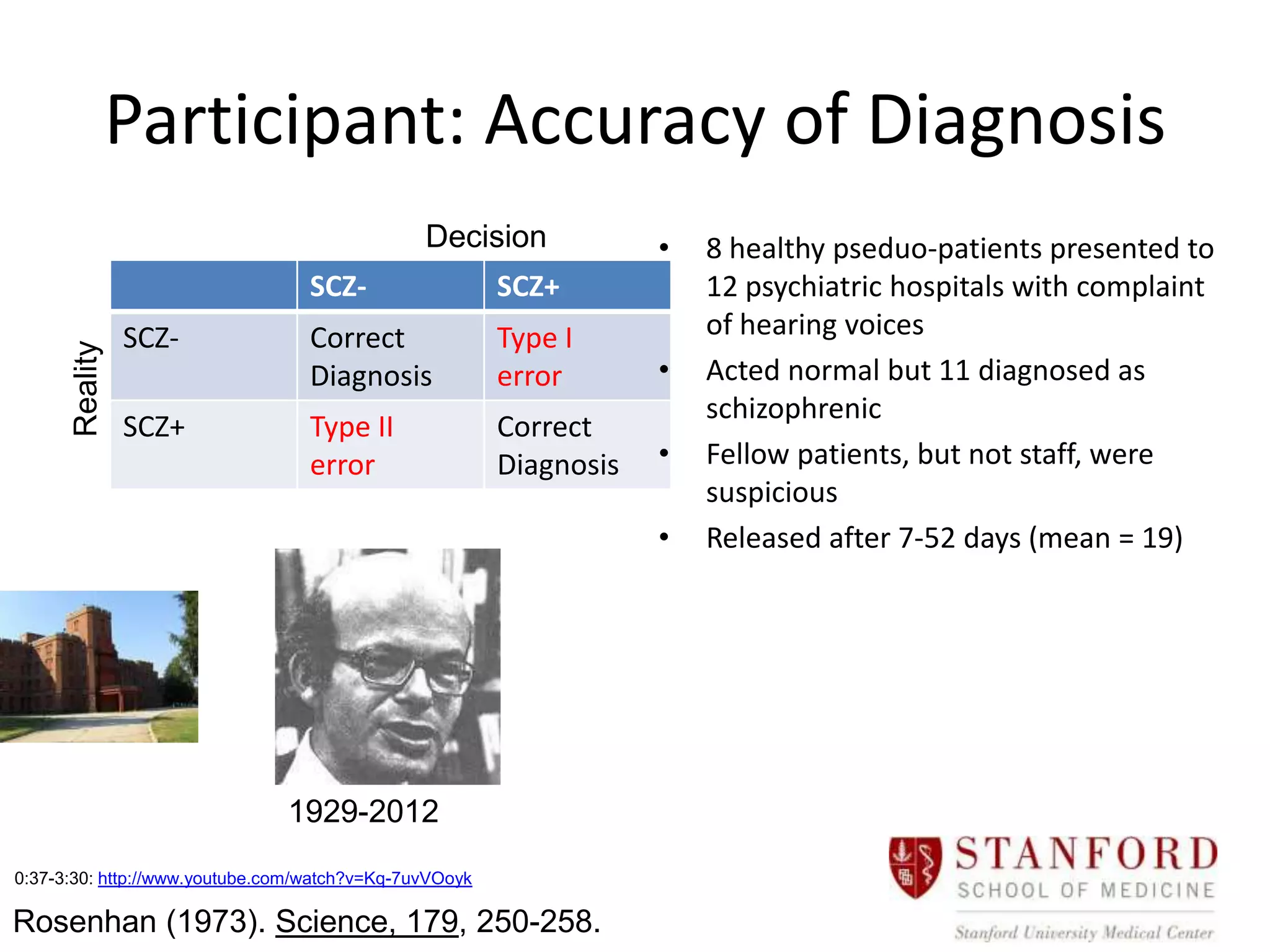
The document discusses observational research, highlighting two main types: naturalistic observation and participant observation, with examples from Jane Goodall's studies on chimpanzees and Robert Sapolsky's work on baboons. It also addresses challenges in observational research, such as observer bias, variable control, and participant reactivity. Additionally, it references a study by Rosenhan demonstrating diagnosis inaccuracies in psychiatric settings.