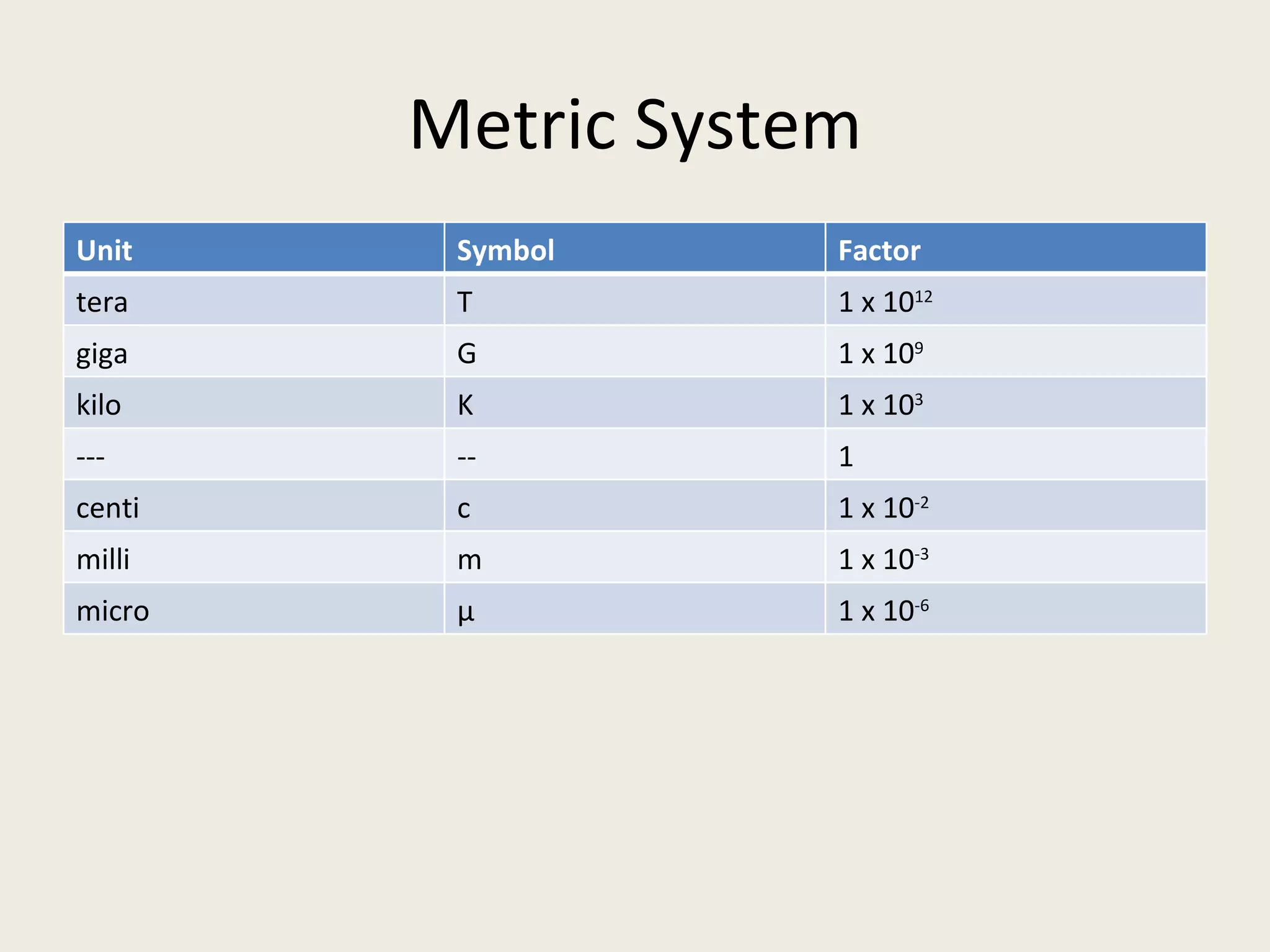
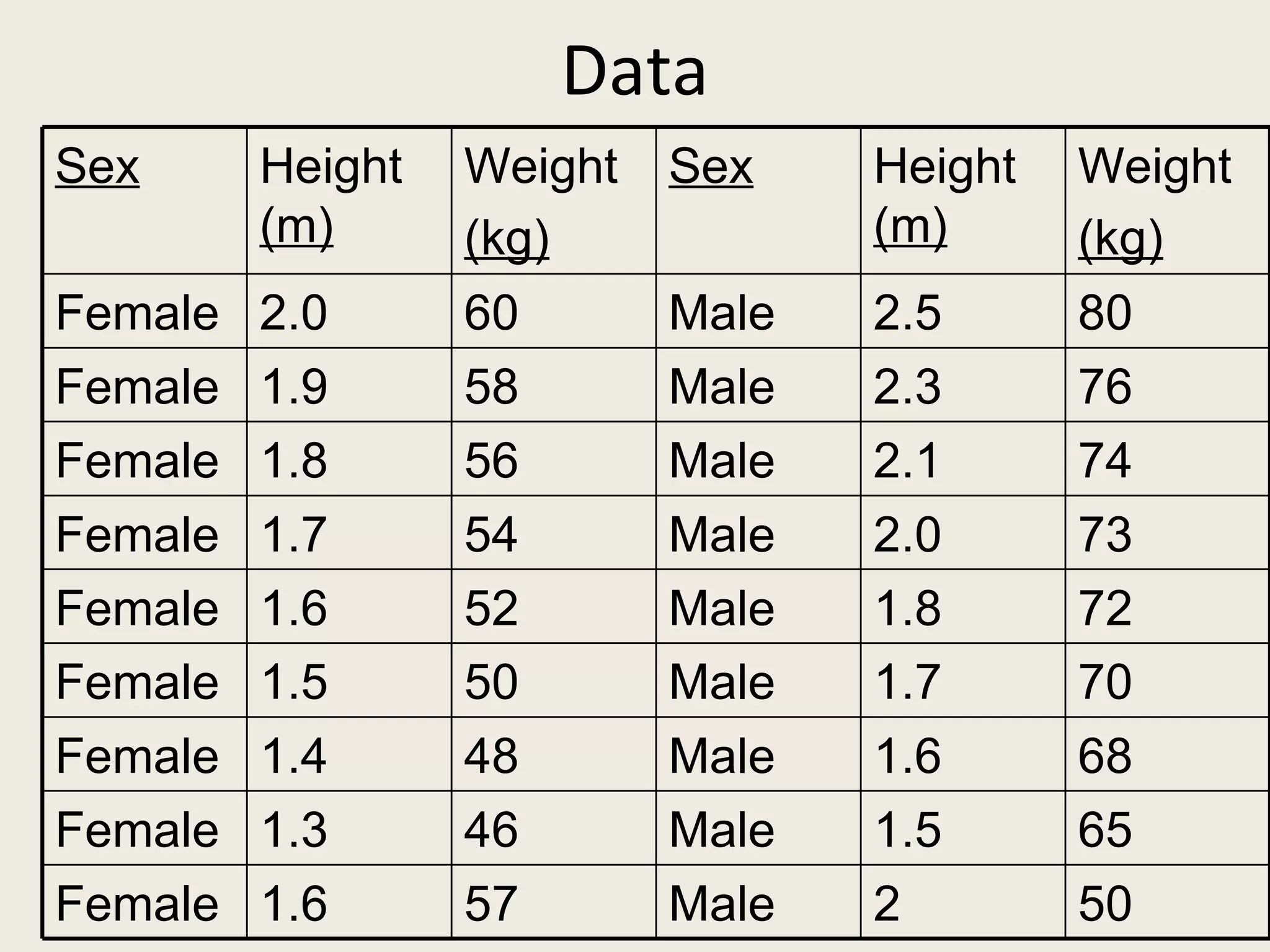
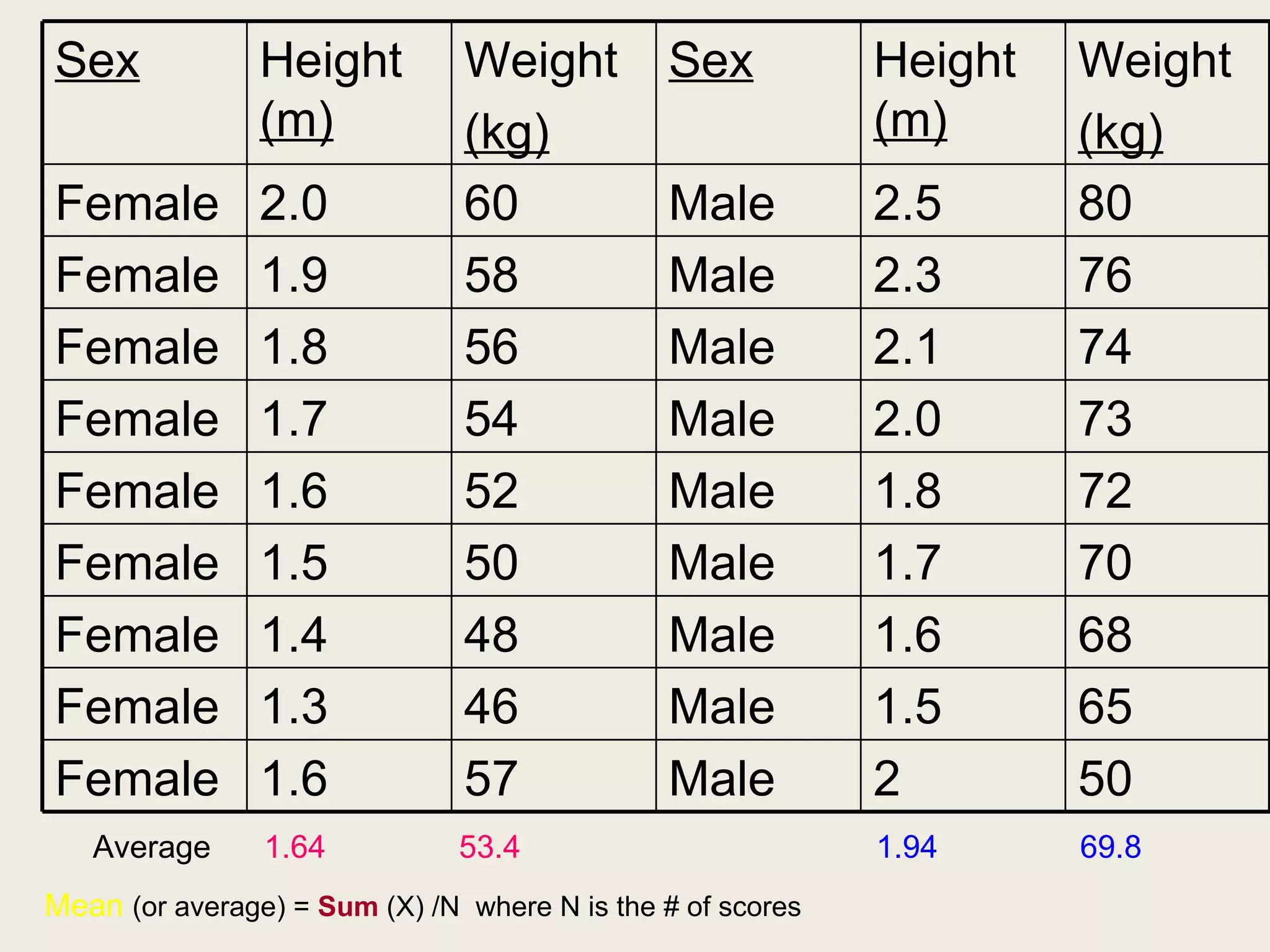
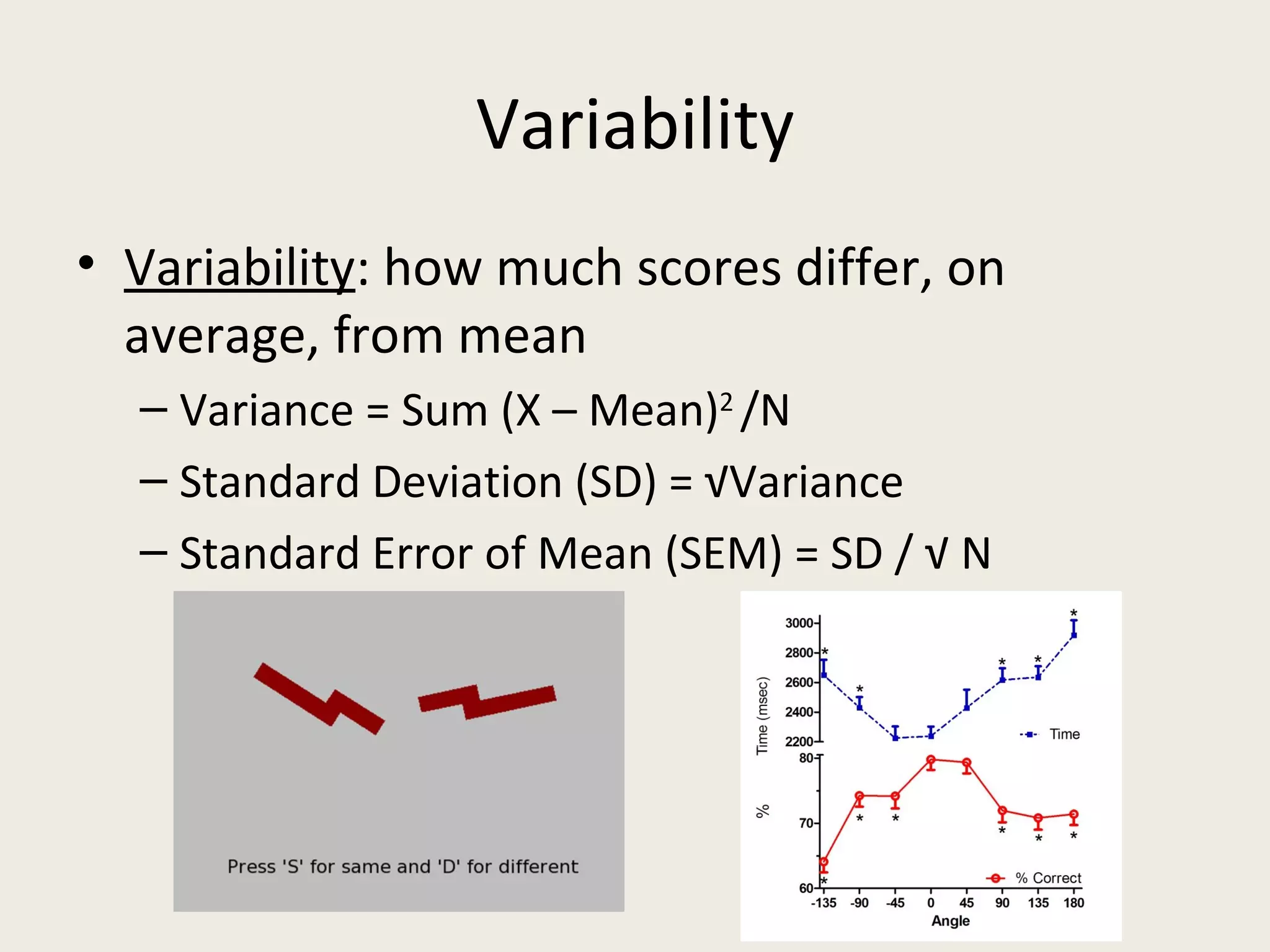
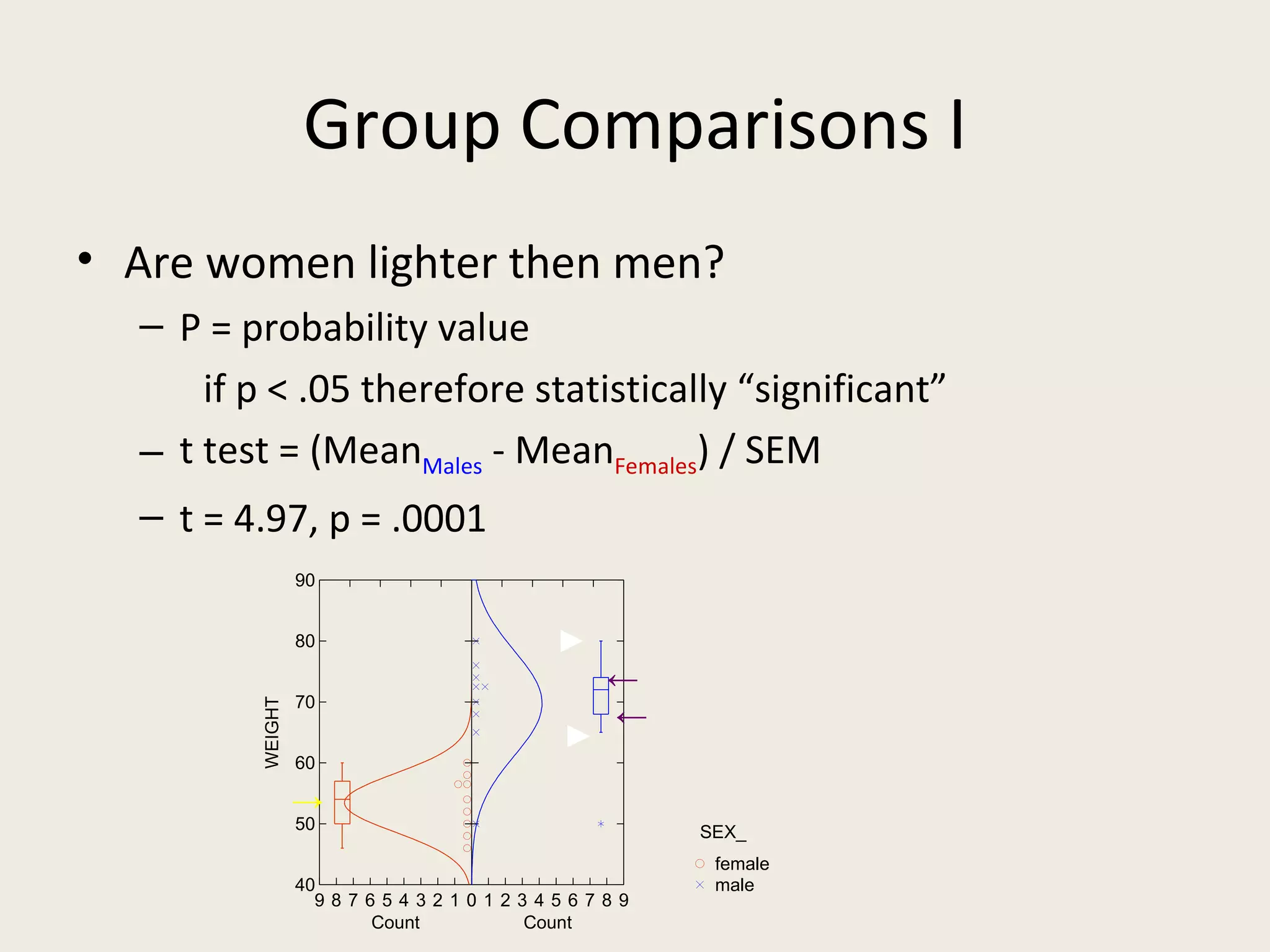
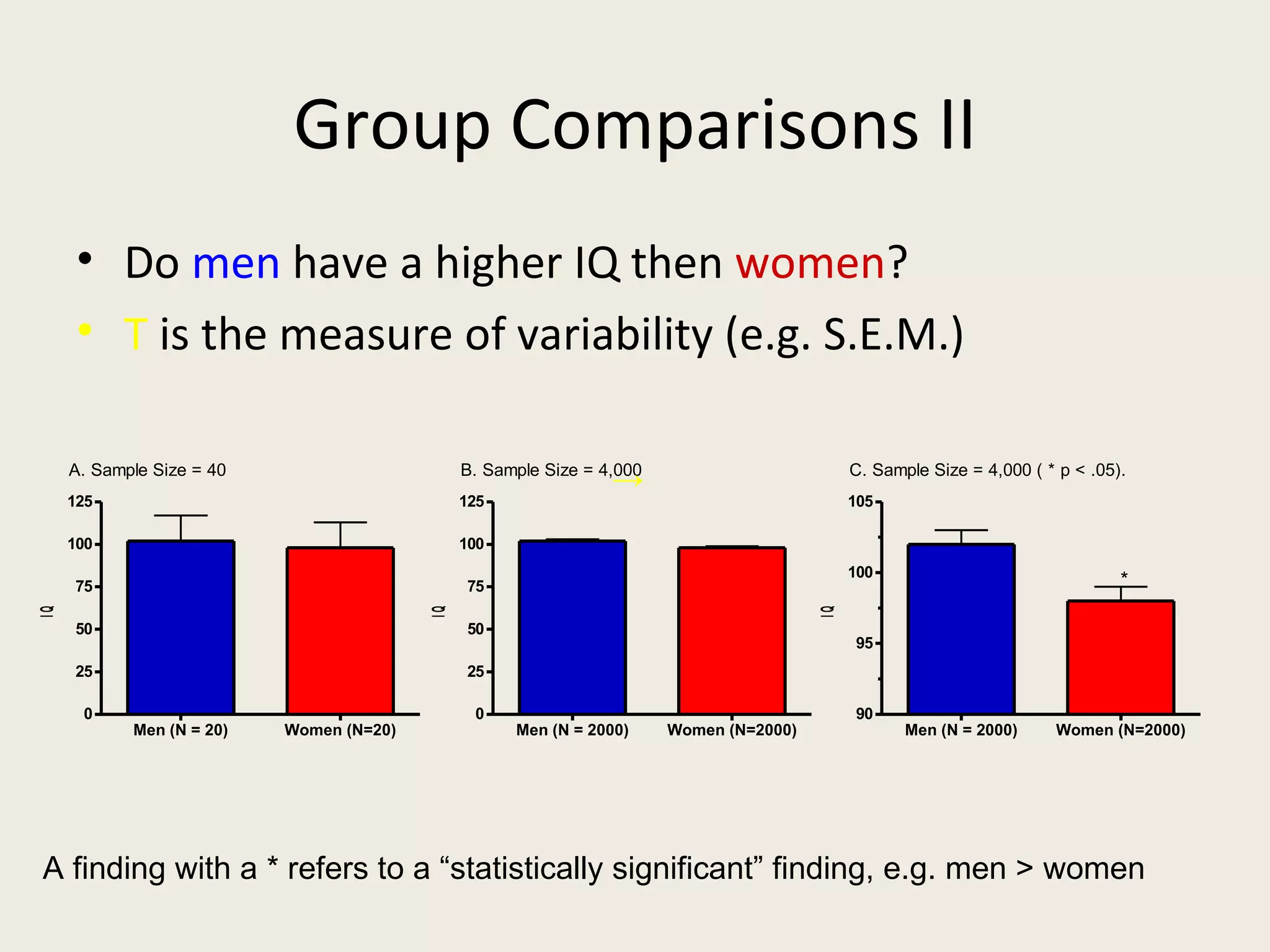
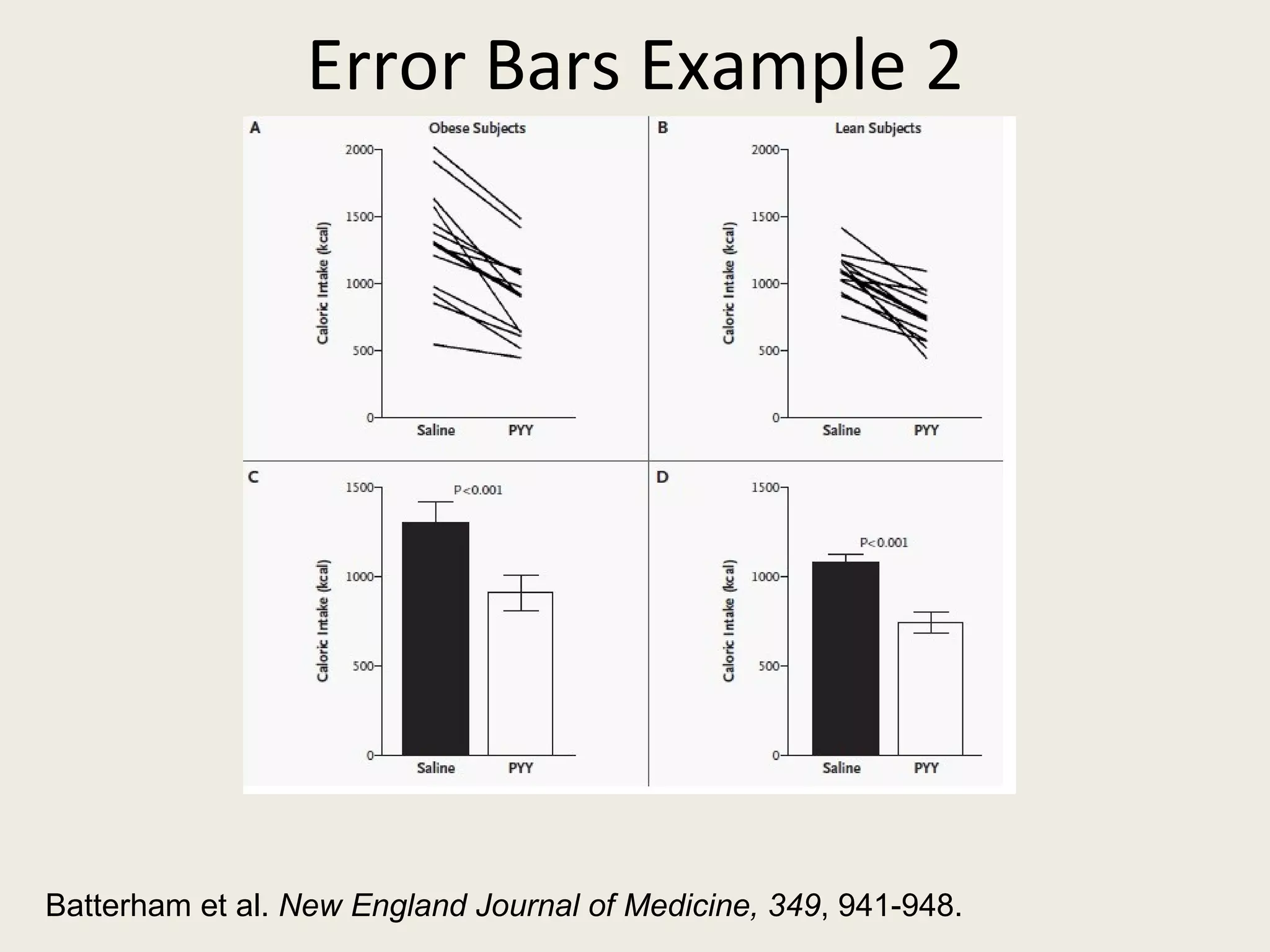
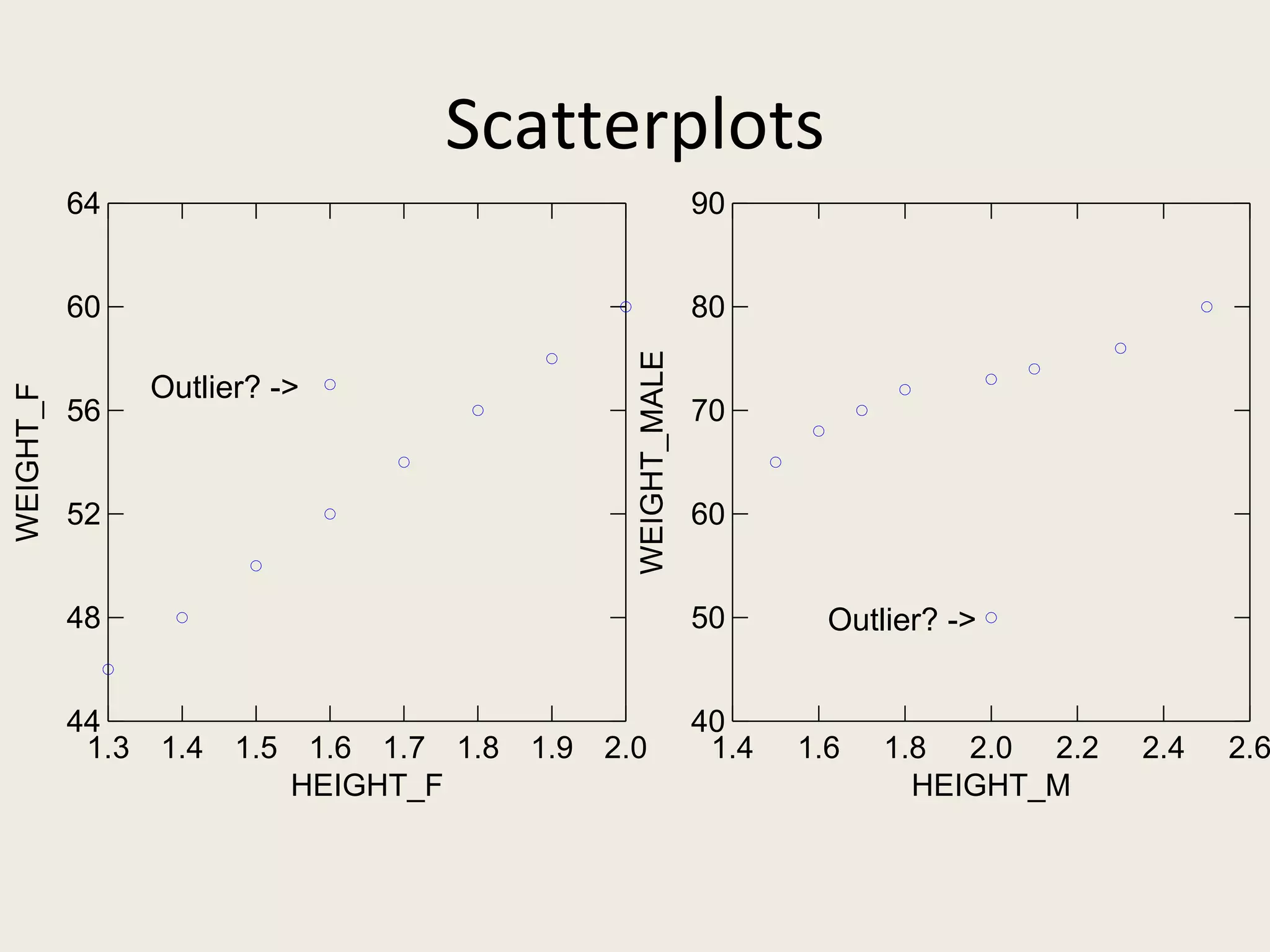
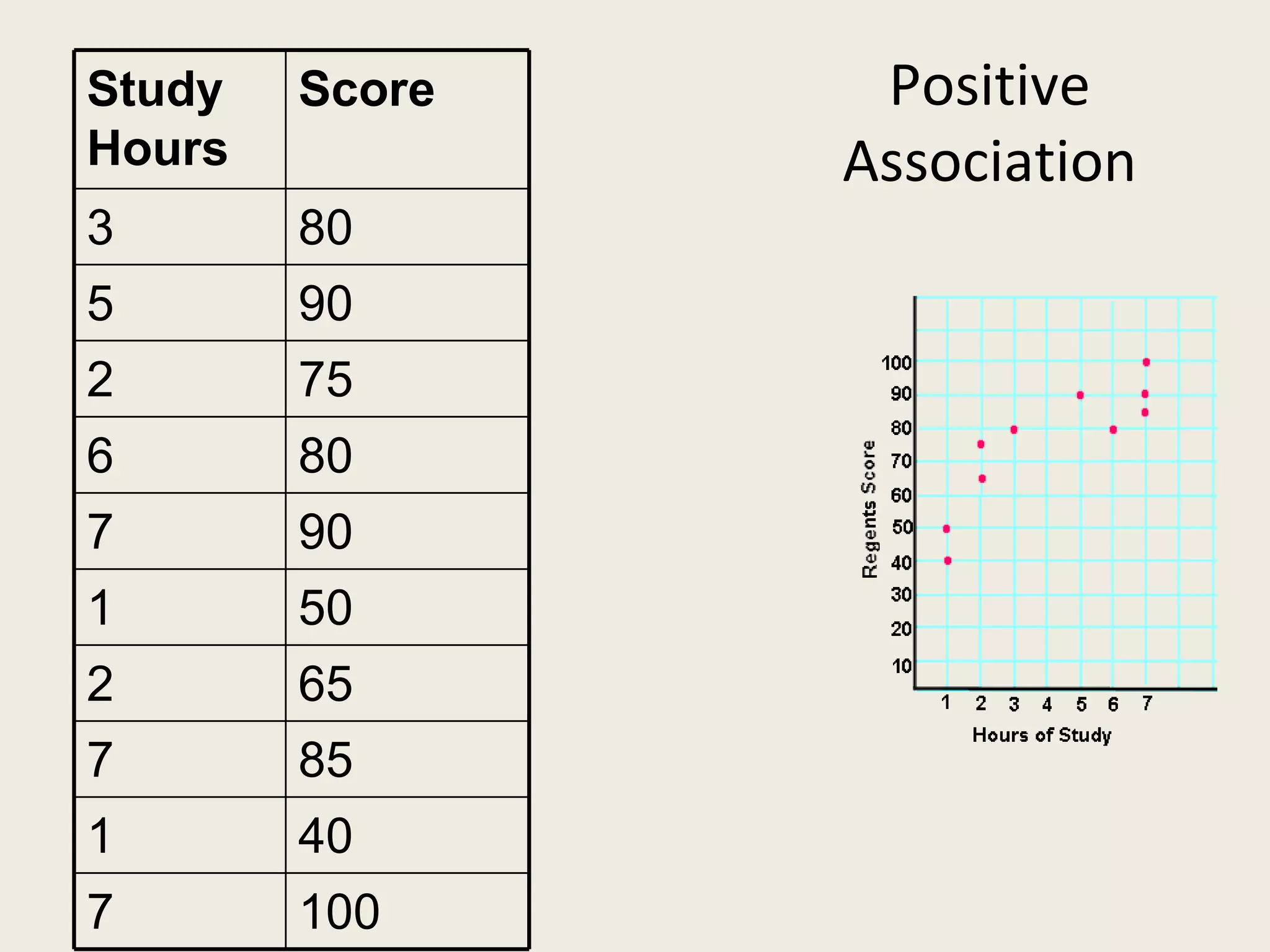
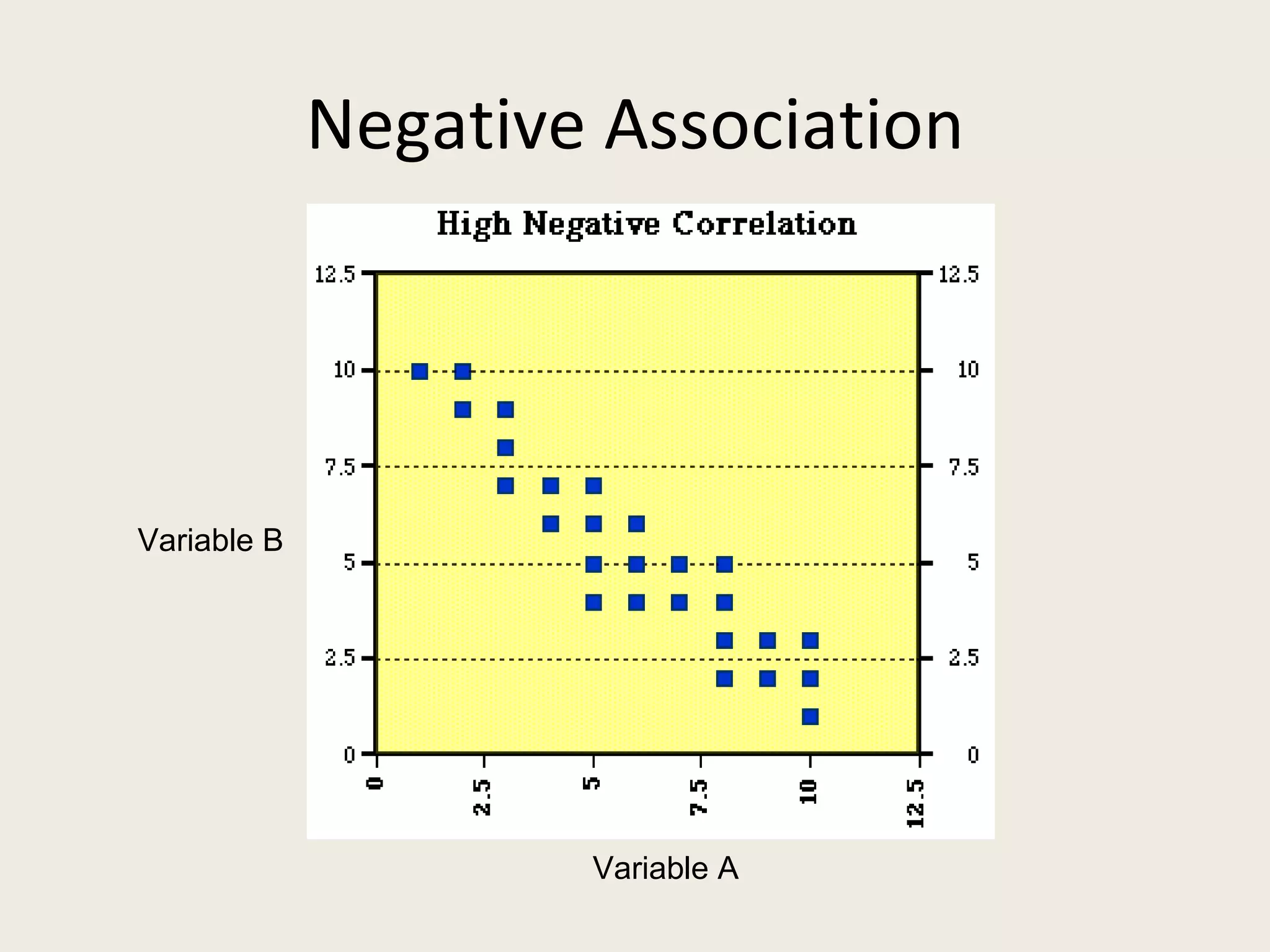
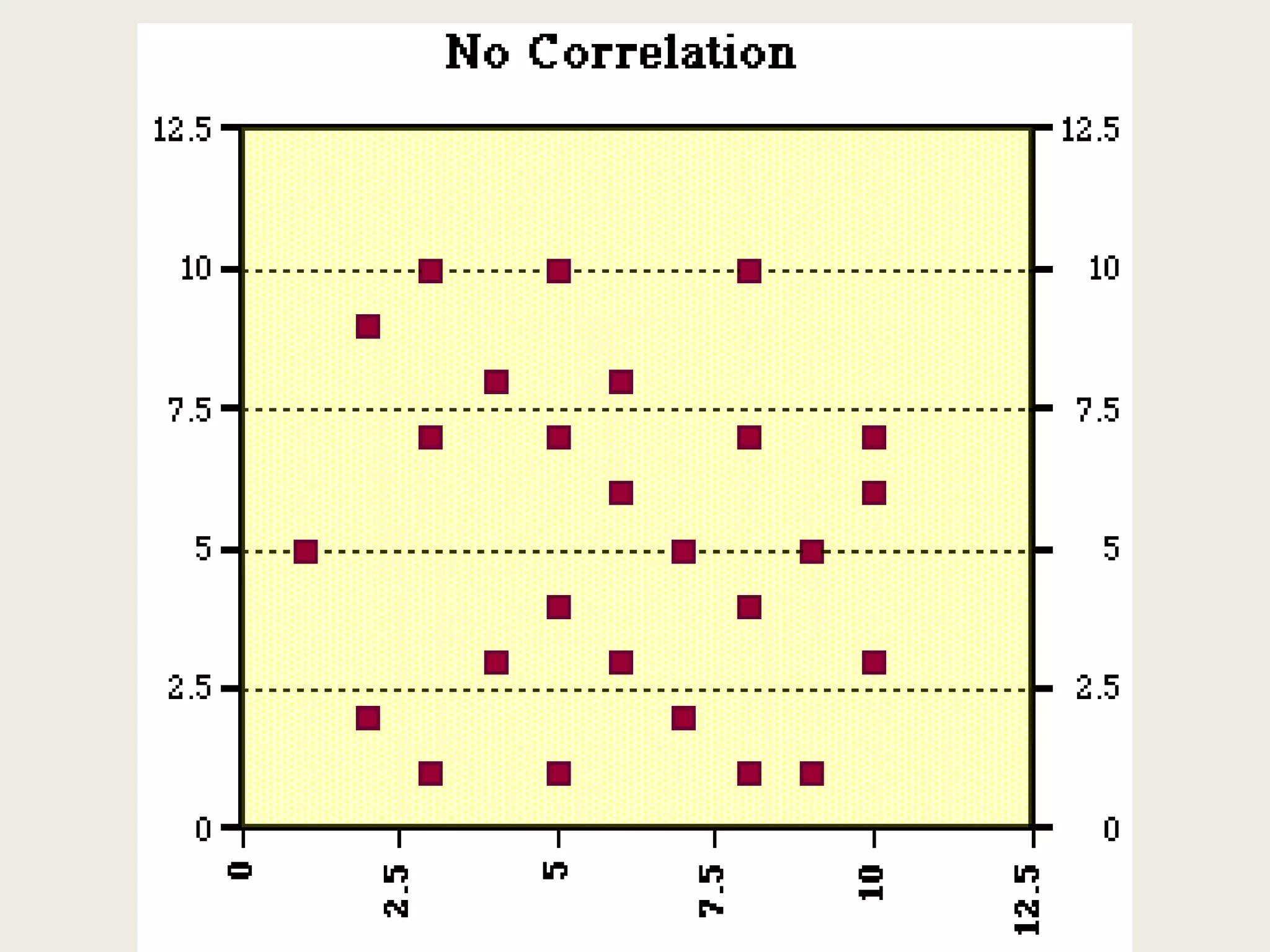
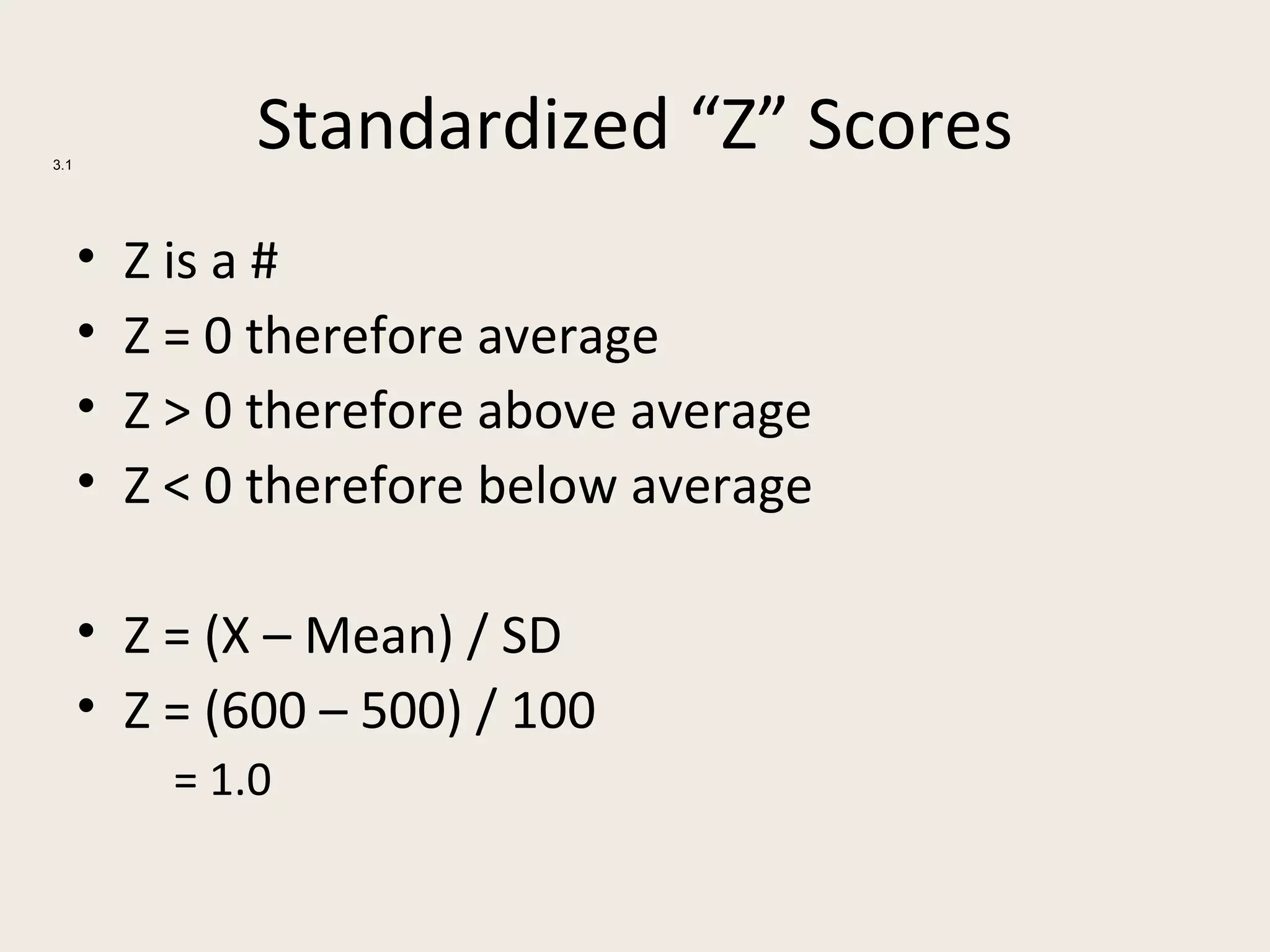
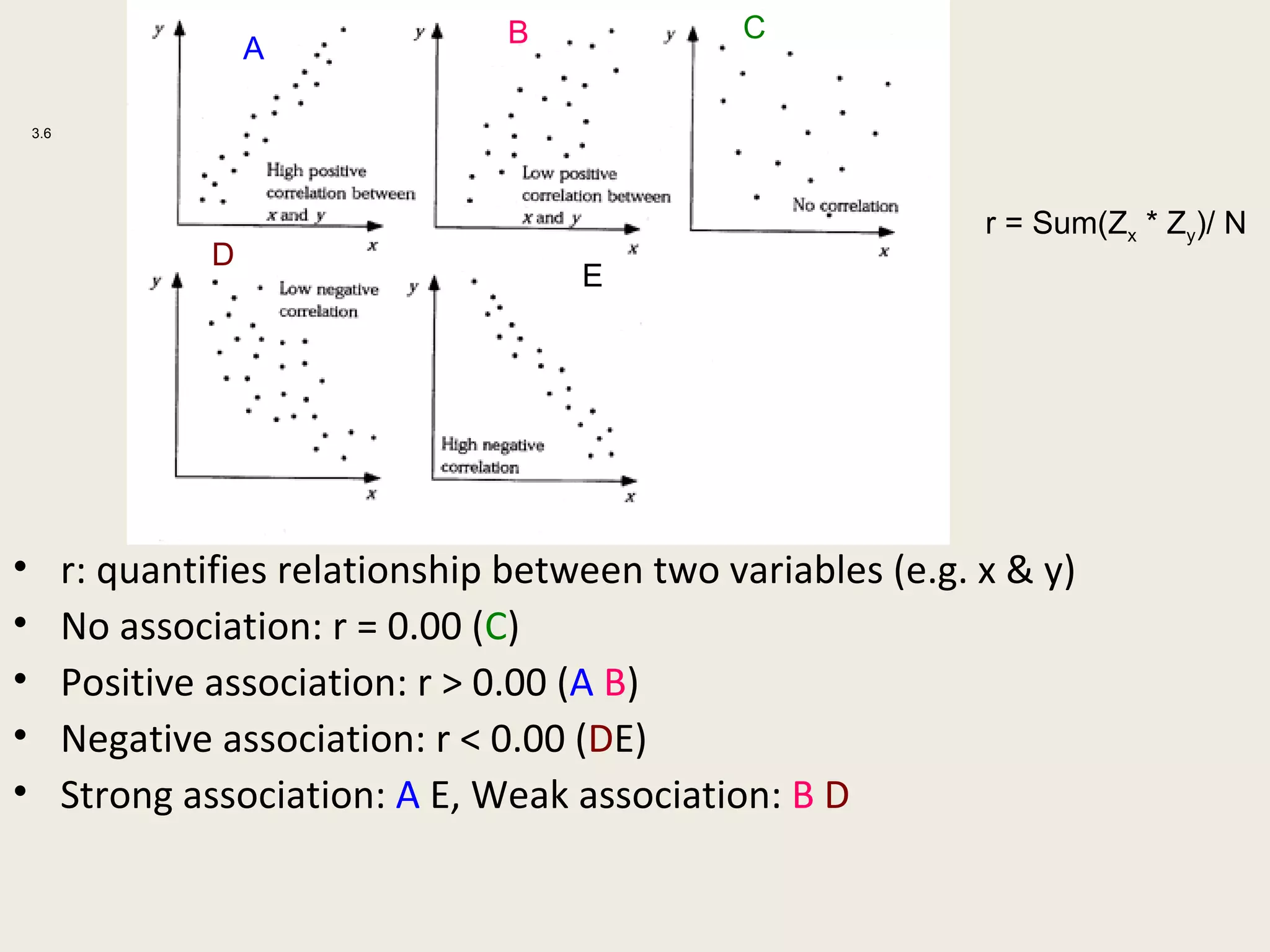
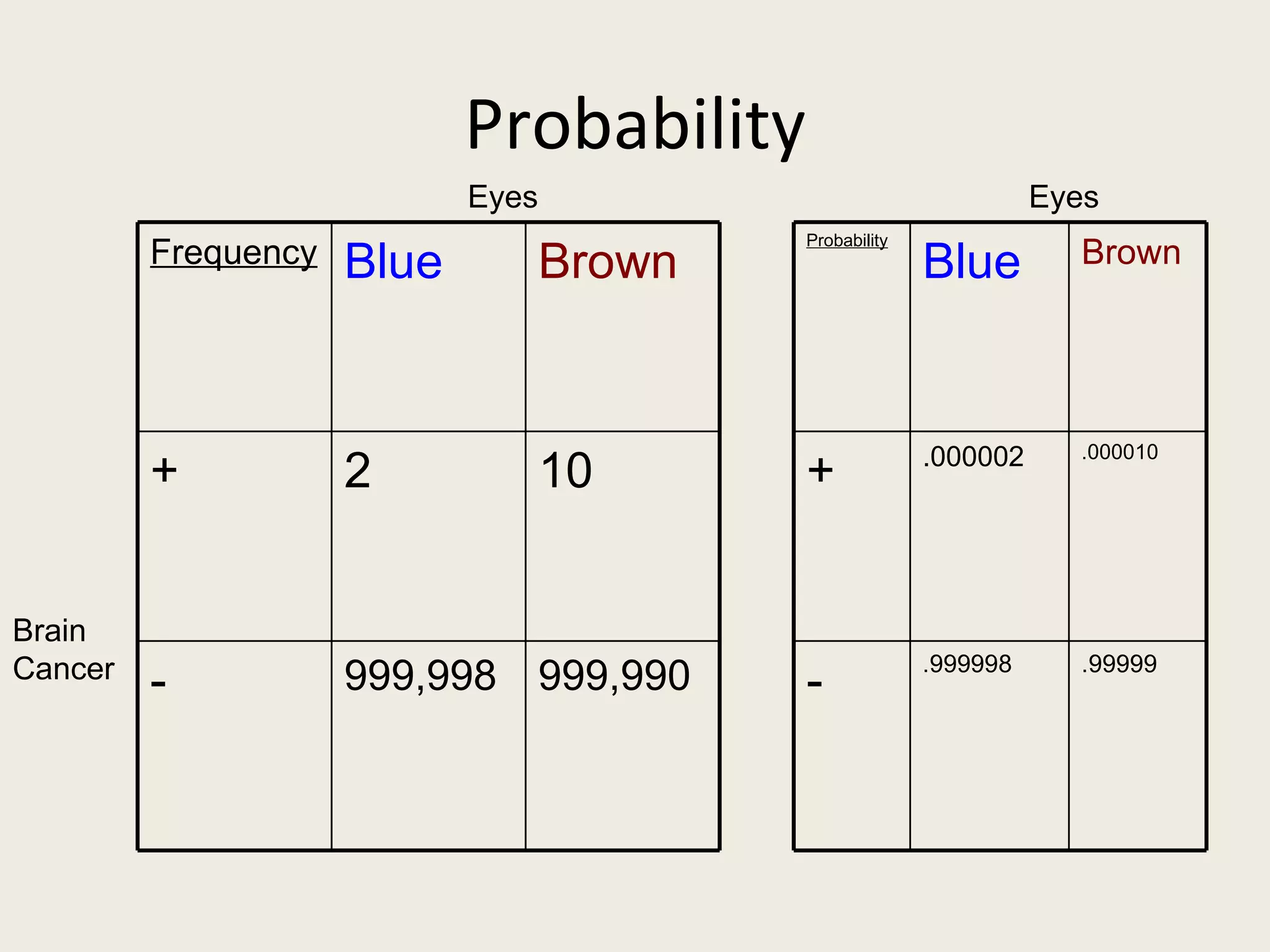
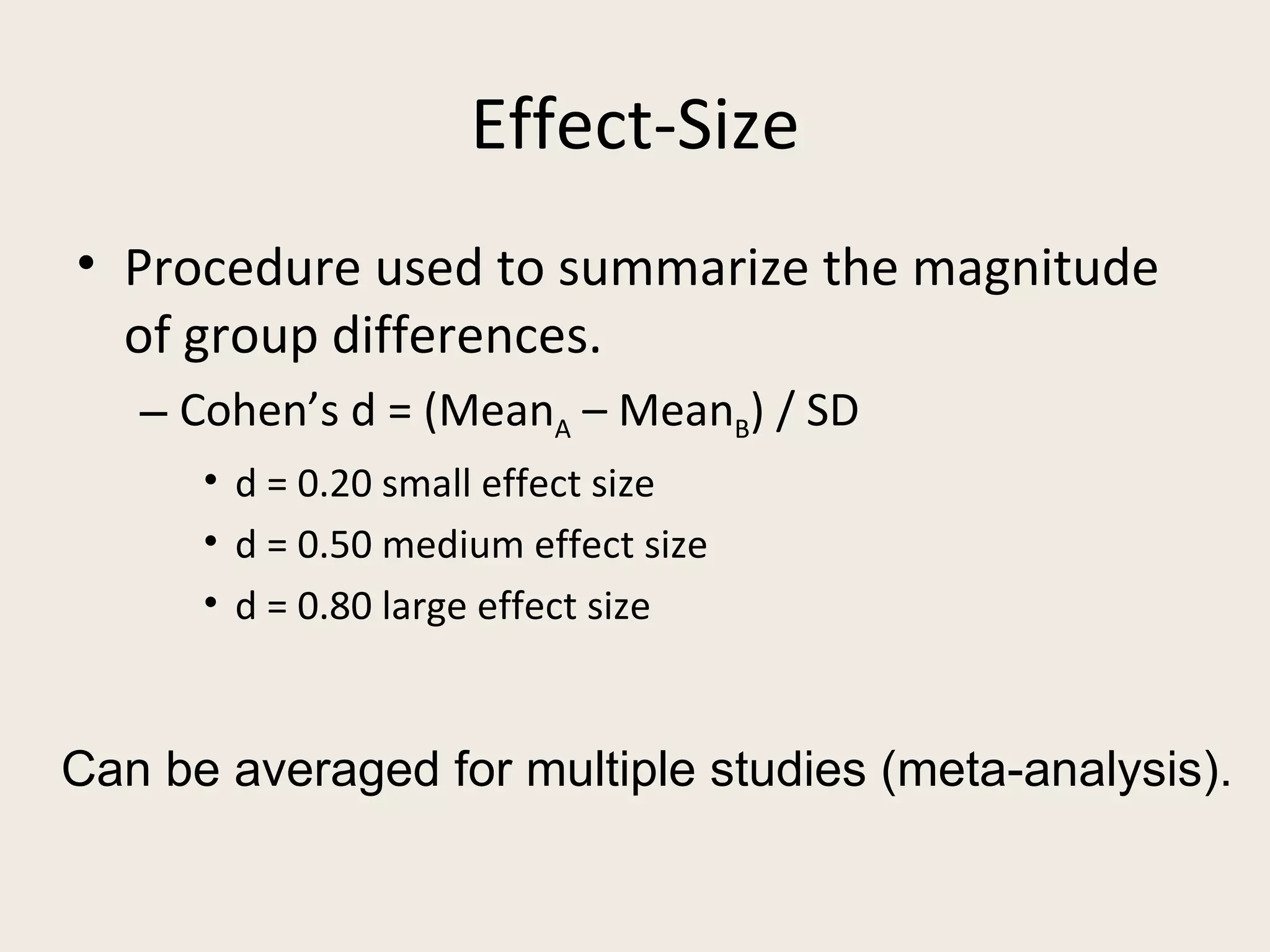
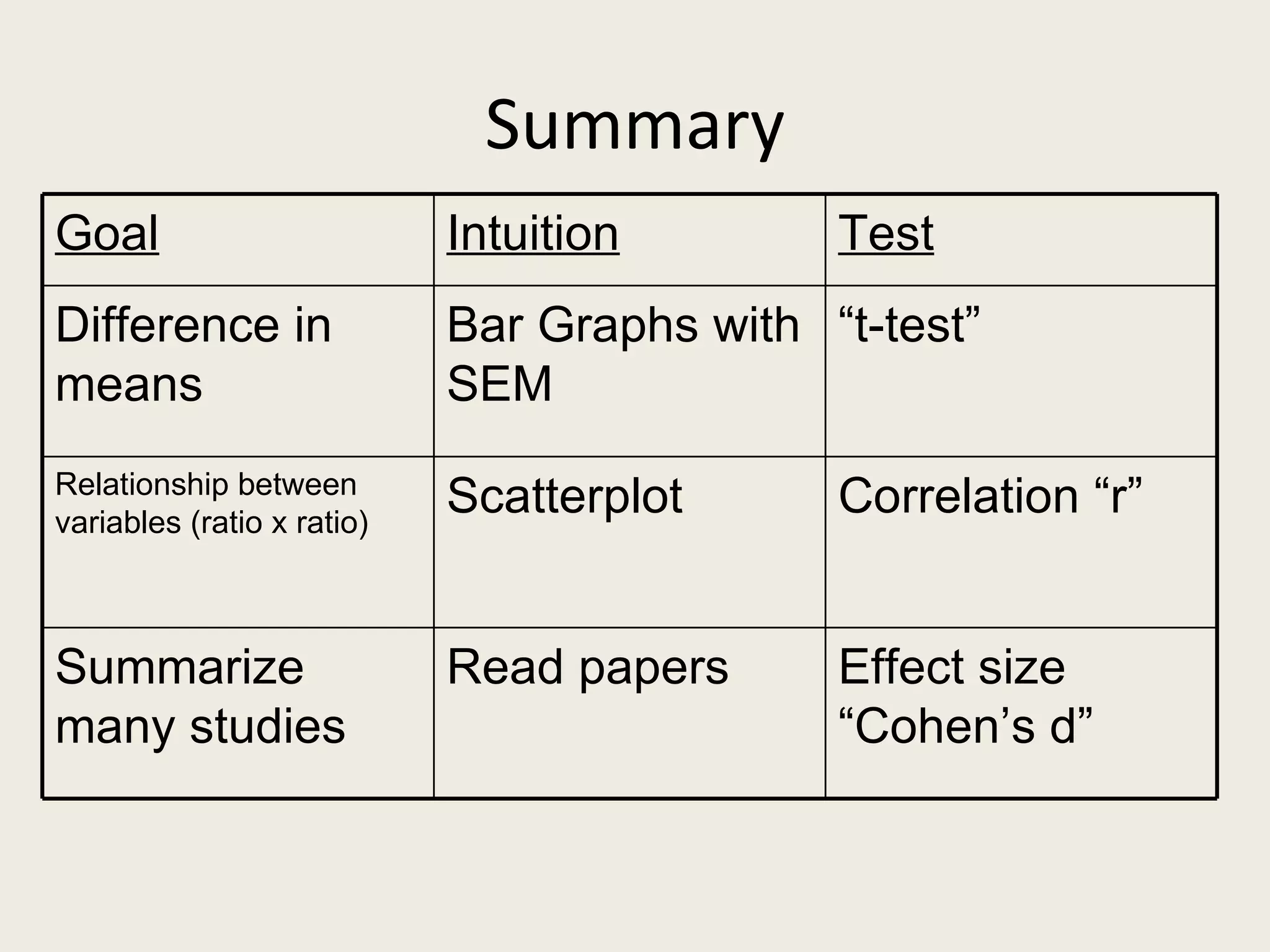
This document provides an overview of key statistical concepts including levels of measurement, group comparisons using t-tests, assessing associations with scatterplots and correlation coefficients, and calculating effect sizes. Examples are given of nominal, ratio and ordinal levels of measurement. Group comparisons are demonstrated using t-tests to compare means and determine statistical significance. Scatterplots and correlation coefficients r are discussed as ways to assess the association between two variables. Effect sizes such as Cohen's d are introduced as a method for summarizing differences between groups across multiple studies.