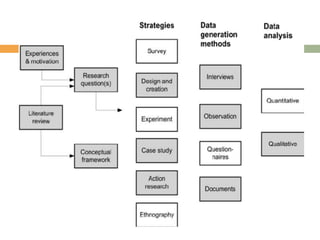
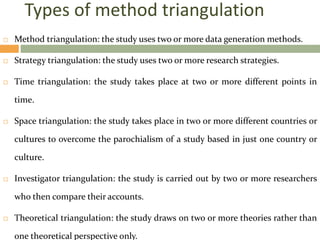
This document outlines the typical research process, including developing a research question based on personal experiences and a literature review, establishing a conceptual framework, choosing a research strategy and data generation methods, collecting and analyzing data, and evaluating the overall process. It describes common strategies like surveys, experiments, case studies, and ethnography. It also discusses using multiple data sources and analysis methods to validate findings through triangulation. The overall model presents research as a cyclical process of planning, implementation, analysis, and reflection.