Embed presentation
Downloaded 12 times




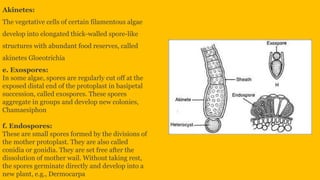

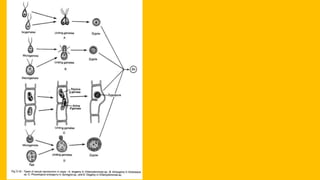

Vegetative reproduction in algae can occur through fragmentation, the formation of adventitious branches, bulbils, or hormogonia. Algae also reproduce asexually through spores like zoospores, aplanospores, tetraspores, akinetes, exospores, and endospores. Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of gametes, which can be isogamous (similar gametes), anisogamous (different sized gametes), or oogamous (egg and sperm). Zygotes form after gamete fusion and develop into new algae.






