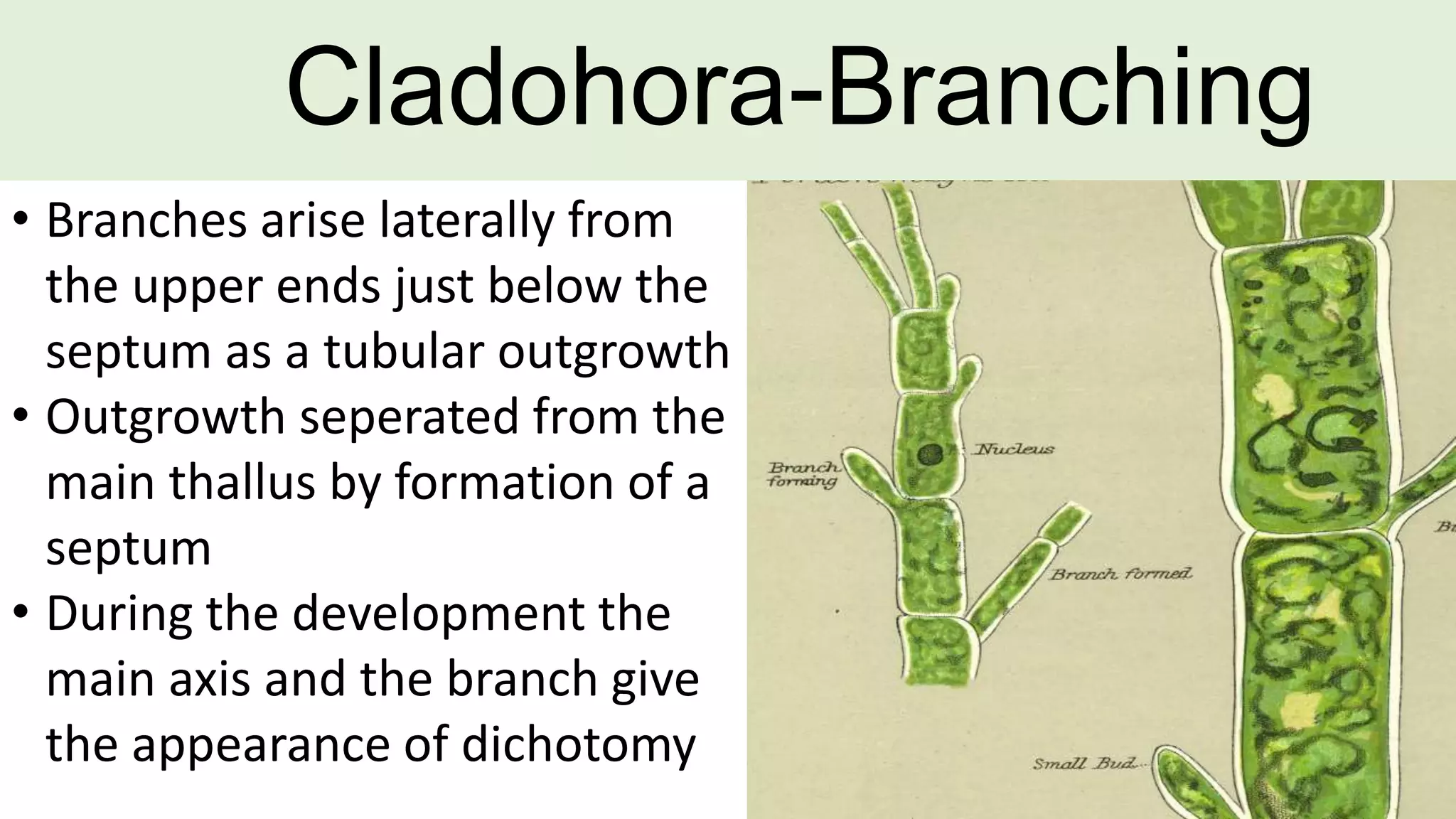
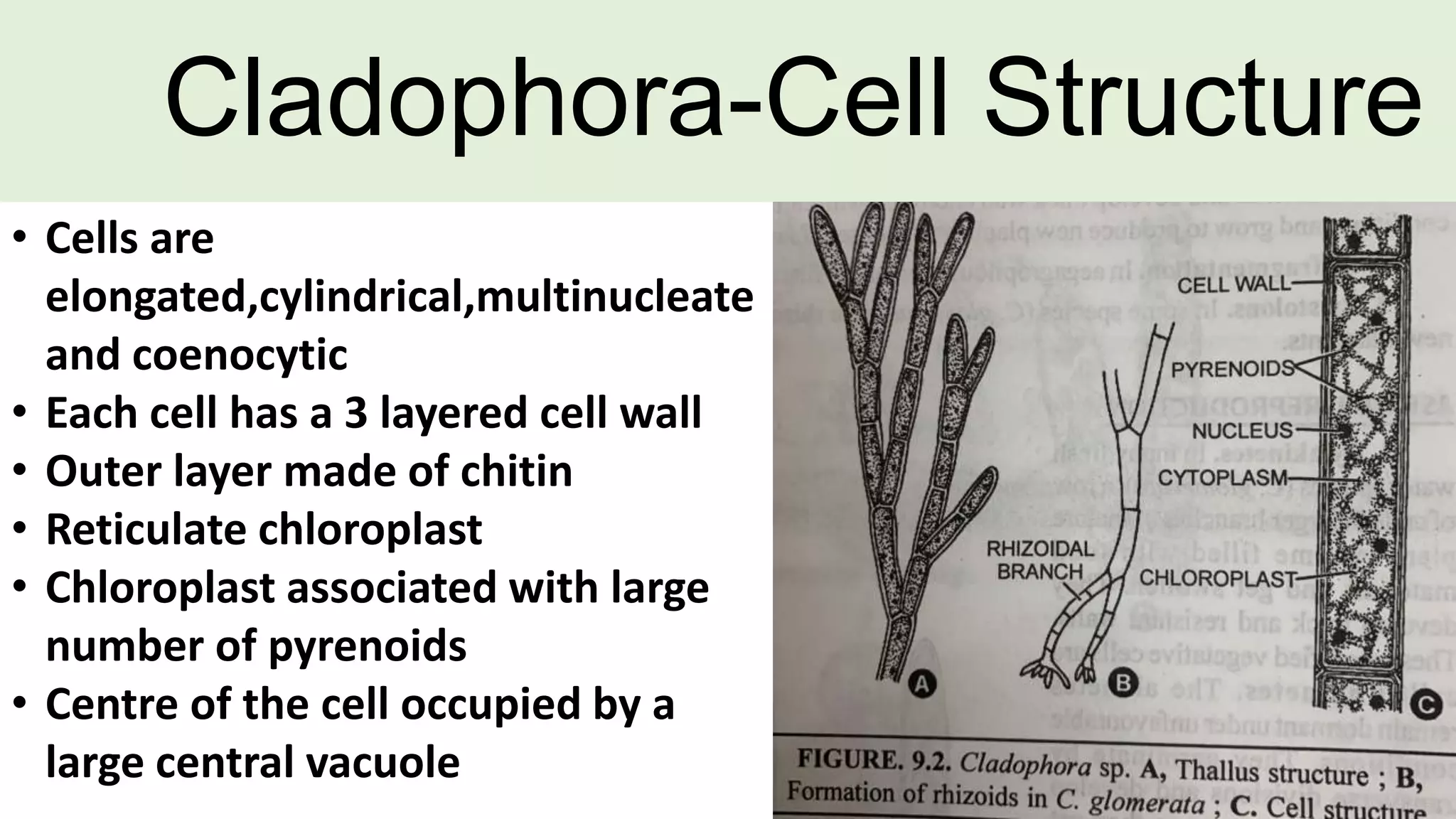
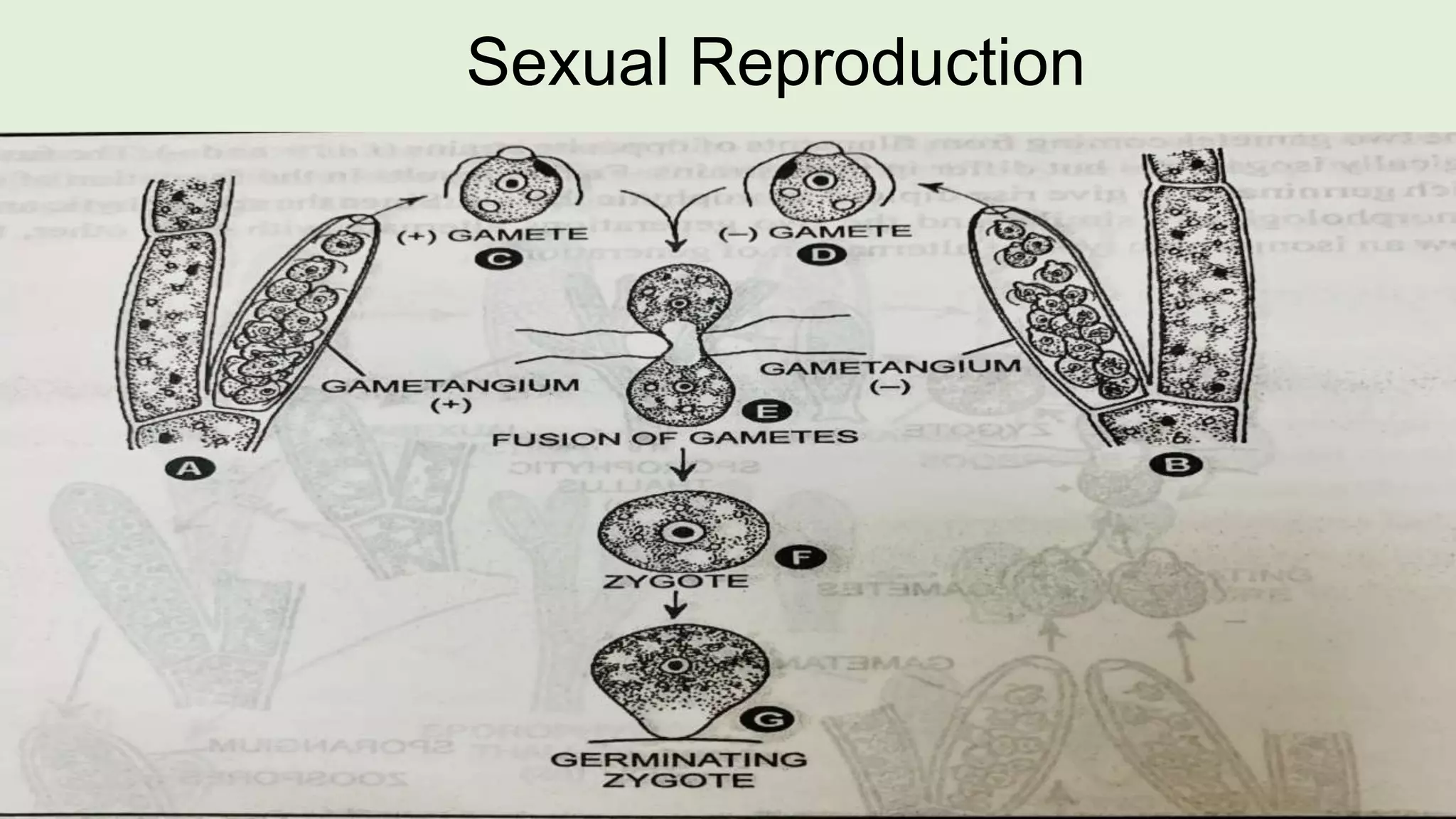
This document discusses the vegetative structure and reproduction of the green alga Cladophora. It describes Cladophora's classification, occurrence in freshwater and marine habitats, and multicellular filamentous plant body. Reproduction occurs through both asexual and sexual means. Asexual reproduction includes fragmentation, rhizoids, stolons, and akinetes. Sexual reproduction involves the production of haploid zoospores that develop into gametophytes upon which gametes are produced.