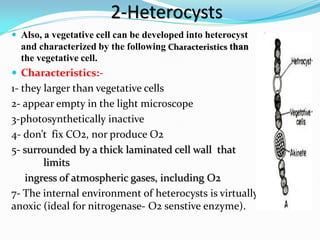
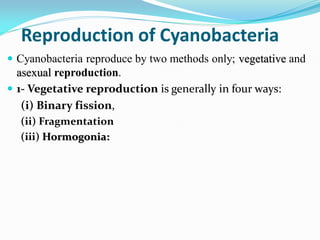
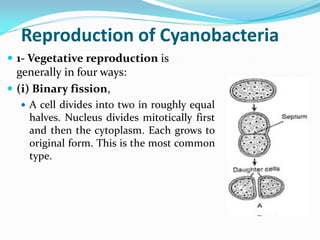
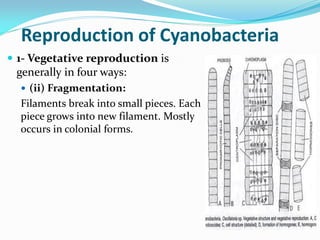
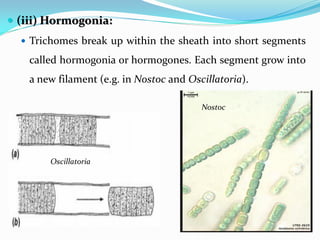
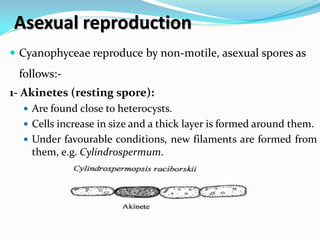
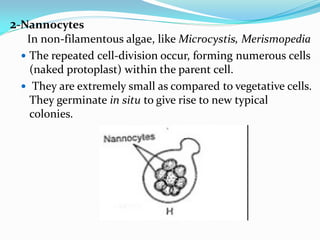
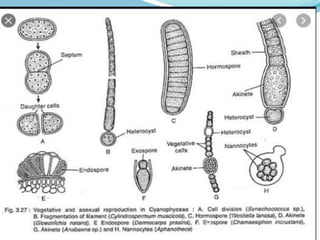
This document provides a comprehensive overview of cyanobacteria, detailing their classification within the kingdom Monera, characteristics, habitats, morphology, reproduction, and cell structure. It discusses the various forms of vegetative and asexual reproduction, including binary fission and akinetes, as well as their adaptations to diverse environments. Key features such as pigments, gas vacuoles, and specialized structures like heterocysts and akinetes are examined, highlighting their ecological significance and biological functions.





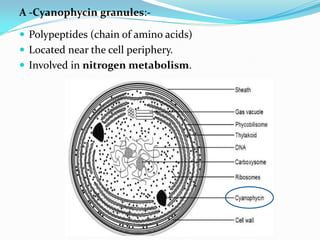
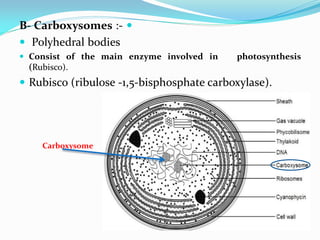
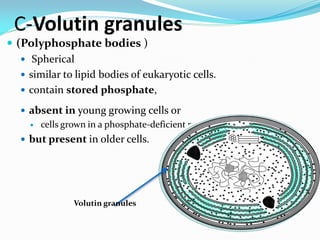

![E-Pigments
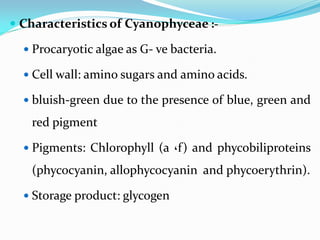
The major components:-
Chlorophyll a &f; Phycobilin)
Phycobilin [(phycoerythrin (red) + phycocyanin(blue)].
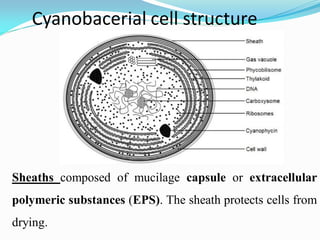
Cells have thylakoids (in the thylakoid membrane).
Phycobilisomes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cynophyceae-230115081850-4592bf40/85/cynophyceae-pdf-22-320.jpg)
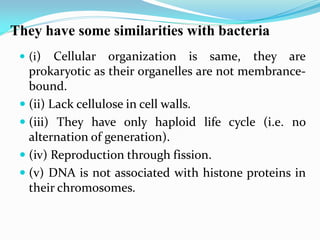
![ Phycobilin = [phycoerythrin + phycocyanin ].
Phycobiliproteins = (phycobilin+ protein)
Phycobilisomes = [Phycobiliproteins attached to
thylakoid memberane]
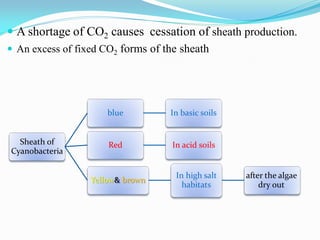
Pigment concentration changed in response to light quality and
growth conditions.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cynophyceae-230115081850-4592bf40/85/cynophyceae-pdf-23-320.jpg)