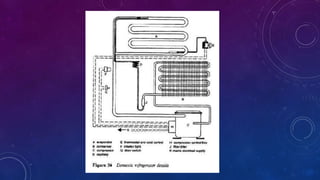
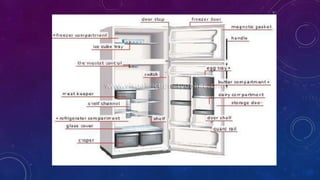
Refrigeration is a process that uses mechanical work to move heat from one location to another in a controlled manner, with applications including household refrigerators, freezers, air conditioning, and more. A refrigerator contains internal parts like refrigerant, a compressor, condenser, evaporator, and thermostat that circulate refrigerant to absorb heat from the refrigerator compartment and expel it outside. External parts include the freezer and refrigerator compartments, temperature controls, crisper, door shelves, and an interior light controlled by a switch. Refrigeration has had significant impacts on industry, lifestyle, agriculture, and development.