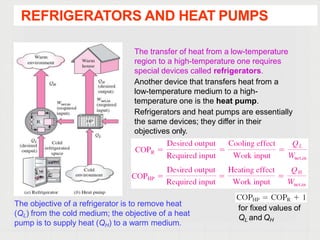
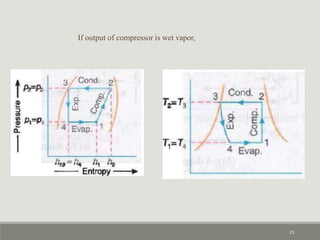
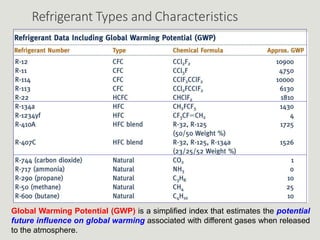
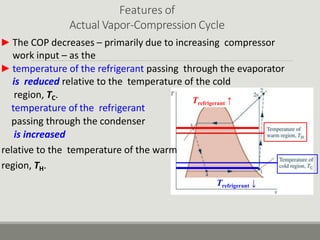
Refrigerators and heat pumps transfer heat from a low-temperature medium to a high-temperature medium. They differ only in their objectives - refrigerators remove heat (cooling), while heat pumps supply heat.
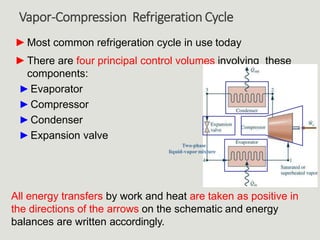
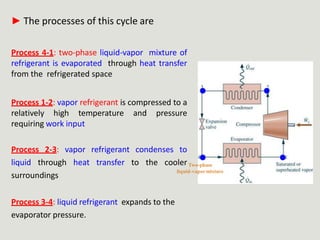
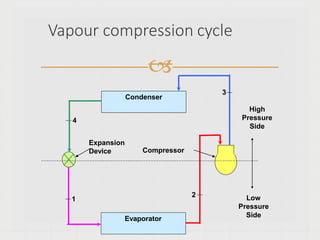
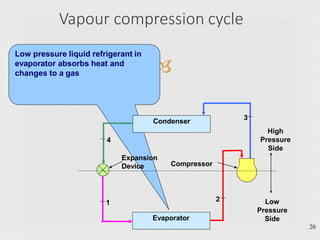
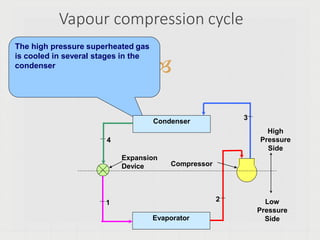
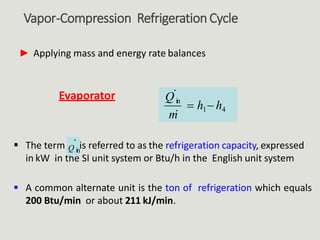
The vapor-compression cycle is the most common refrigeration cycle. It involves four main components: evaporator, compressor, condenser, and expansion valve. Heat is absorbed in the evaporator and rejected in the condenser. The compressor raises the refrigerant pressure and temperature between these components.
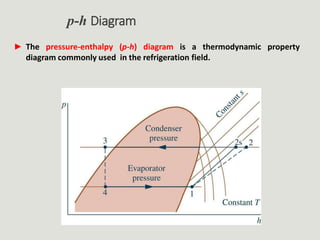
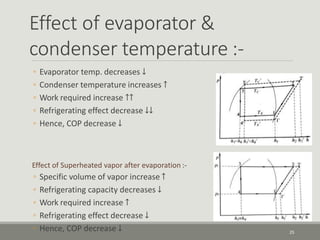
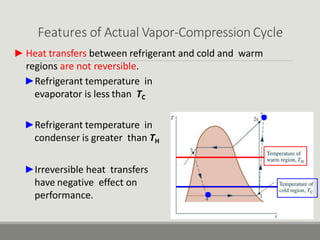
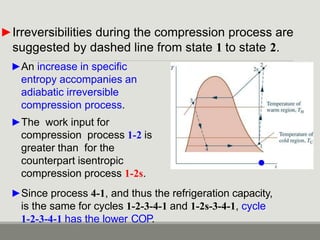
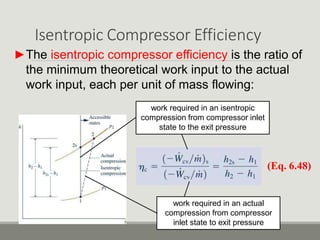
The performance of vapor-compression refrigeration systems depends on factors like evaporator/condenser temperatures and pressures. Actual cycles are less efficient than ideal cycles due to irreversibilities like heat transfer across a temperature