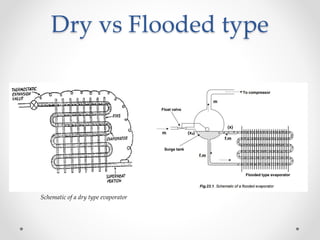
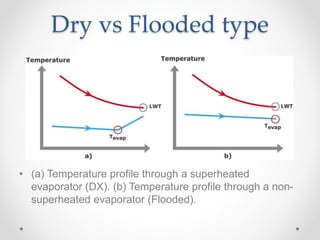
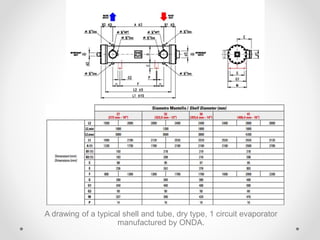
Dry expansion evaporators use an expansion valve to control the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator as a liquid. By the end of the evaporator coil, the refrigerant has vaporized by absorbing heat from the substance being refrigerated. They have advantages like good control and low cost, but disadvantages like lower efficiency compared to flooded evaporators. Common materials include carbon steel, copper, and plastic. Typical applications include water chilling, liquid cooling, and household refrigerators.