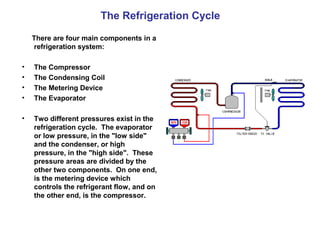
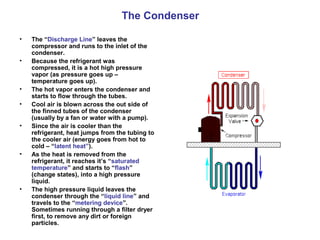
Refrigeration works by removing heat from a space using a refrigerant in a closed loop system. As the refrigerant absorbs heat, it changes state from a liquid to a gas. It is then condensed back to a liquid, releasing the heat. The four main components are the compressor, condenser, metering device, and evaporator. Refrigerants have saturation temperatures where they change state based on pressure. Proper refrigerant charging can be done using pressure/temperature charts and measuring subcooling or superheat.