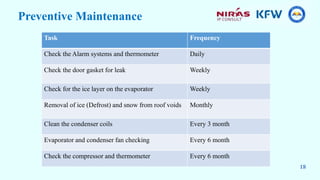
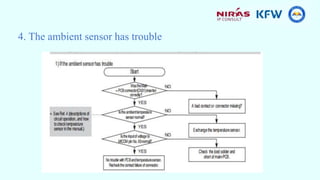
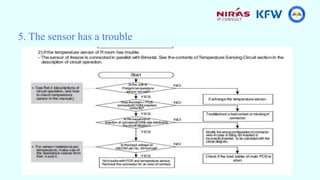
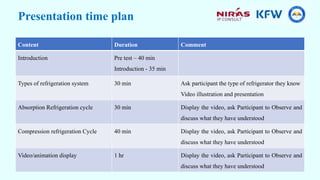
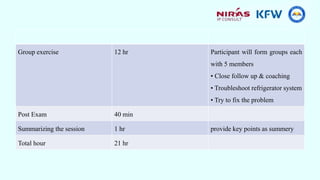
This document provides information about a training course on refrigerators. The course will cover the functional principles, parts, installation, safety considerations, preventative maintenance, and troubleshooting of the Samsung RS26 refrigerator. It will include presentations on absorption and compression refrigeration cycles, the principal parts of refrigerators like the condenser and electrical components, and a group exercise for troubleshooting refrigerator systems.