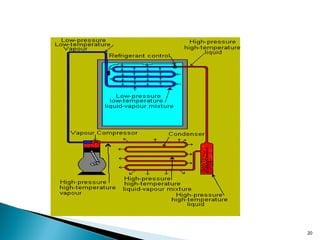
The document discusses refrigeration systems, which operate by transferring heat from a low-temperature environment to a higher one. It outlines various refrigerants, including ammonia, carbon dioxide, and different chlorofluorocarbons, as well as their properties and applications in various refrigeration setups. Additionally, it explains the operation of vapor compression and absorption refrigeration systems and their applications in domestic and industrial contexts.