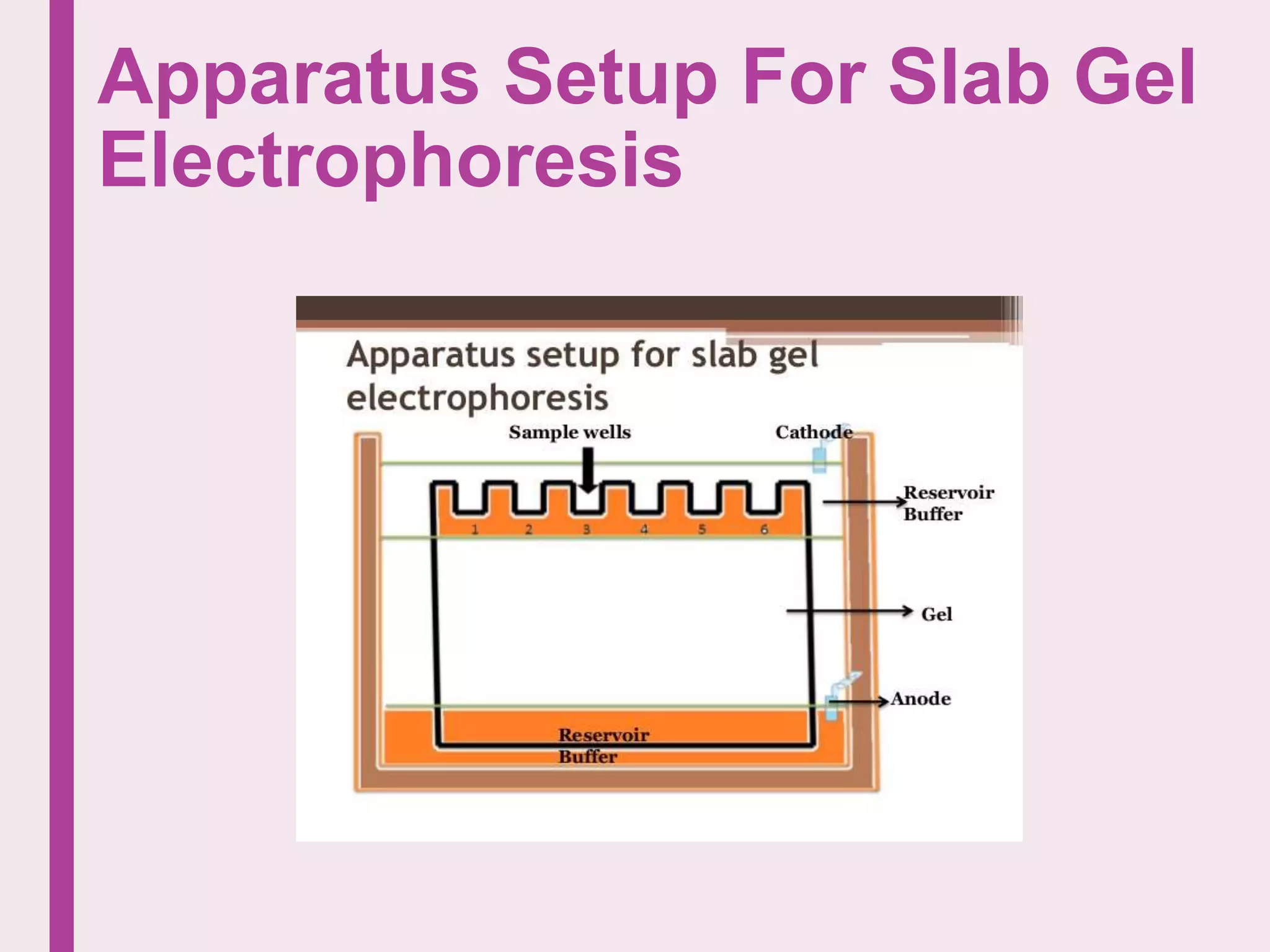
Electrophoresis is a technique used to separate charged particles in a fluid under an electric field, first observed in 1807. It is utilized in laboratories for analyzing macromolecules like DNA and proteins, with variations such as slab and capillary electrophoresis tailored for different applications. The method relies on the size, charge, and shape of molecules, with factors such as pH and viscosity influencing their mobility in the electric field.