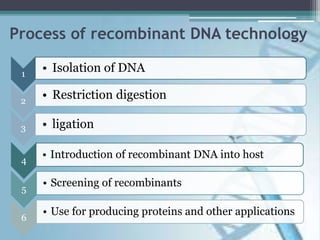
Recombinant DNA technology involves joining DNA molecules from different sources and inserting them into a host organism to produce multiple copies. It was first done in 1973 by Boyer and Cohen. The process involves isolating DNA, cutting it with restriction enzymes, ligating the DNA pieces together, introducing the recombinant DNA into a host, and screening for the recombinant organisms. This technology is used to produce important proteins like human insulin in bacteria and create transgenic plants with useful traits such as pest resistance.