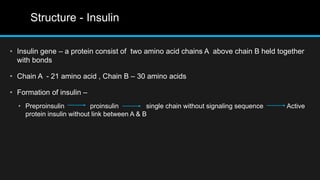
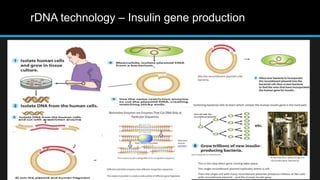
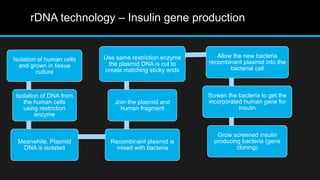
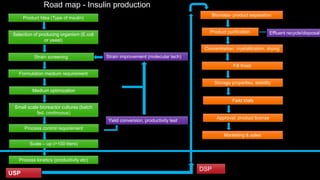
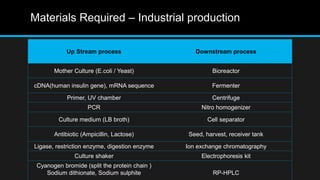
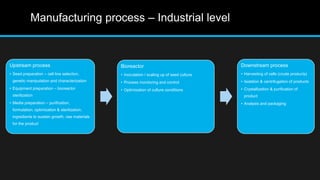
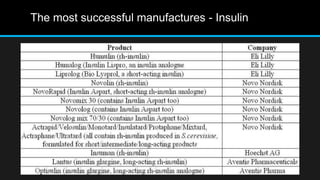
Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood glucose levels. It is normally produced by the pancreas but can also be produced synthetically using recombinant DNA technology. There are three main types of synthetic insulin production. Type 1 involves growing the insulin A and B chains separately in E. coli and linking them. Type 2 uses proinsulin processing in E. coli. Type 3 produces analog insulins with modified amino acid sequences. The industrial production process involves an upstream process of cell line preparation in microbes and gene insertion, and a downstream process of fermentation, purification, and packaging. Careful selection of production organism, conditions, equipment and purification methods is needed to successfully manufacture synthetic insulin at scale.