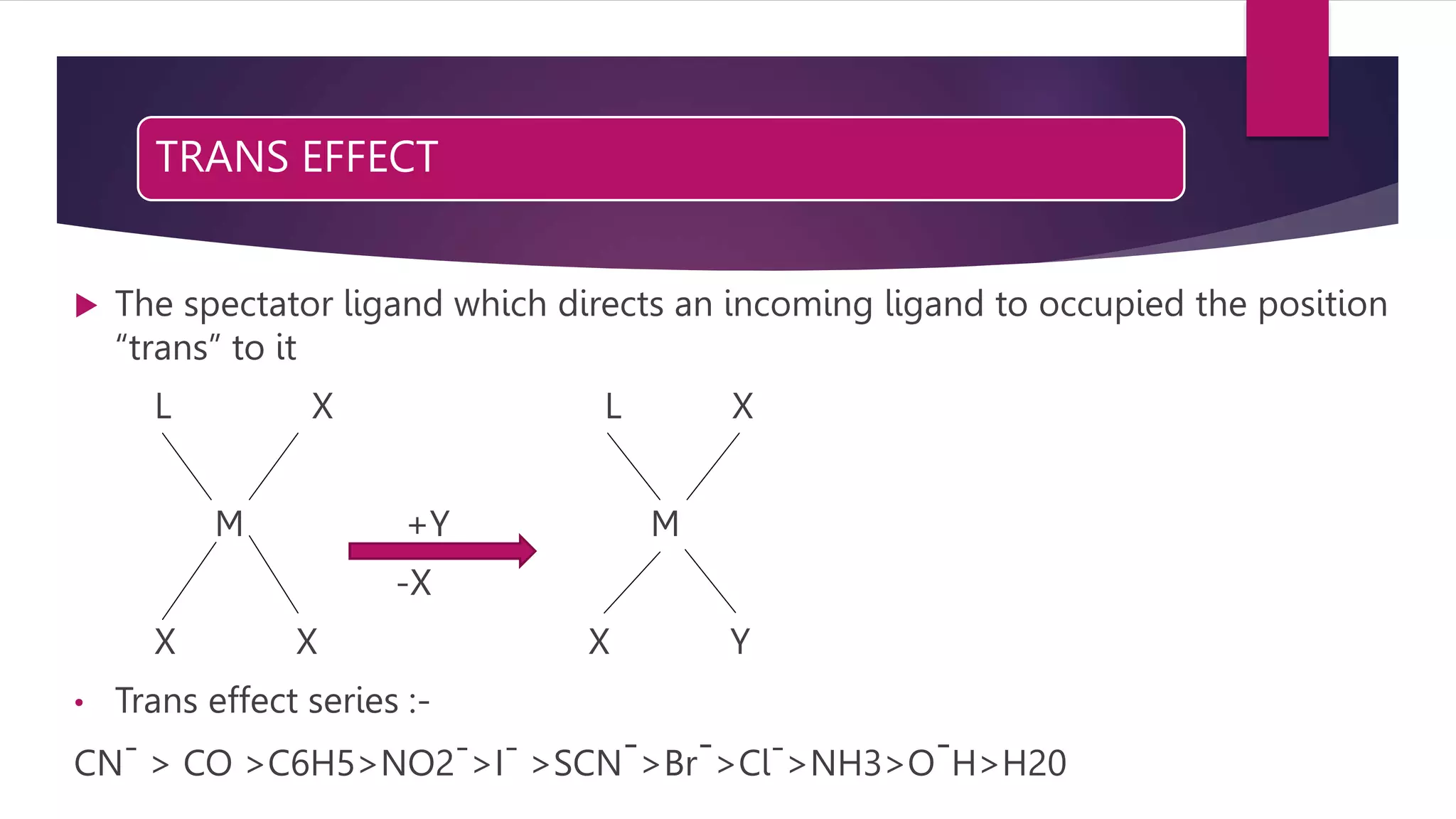
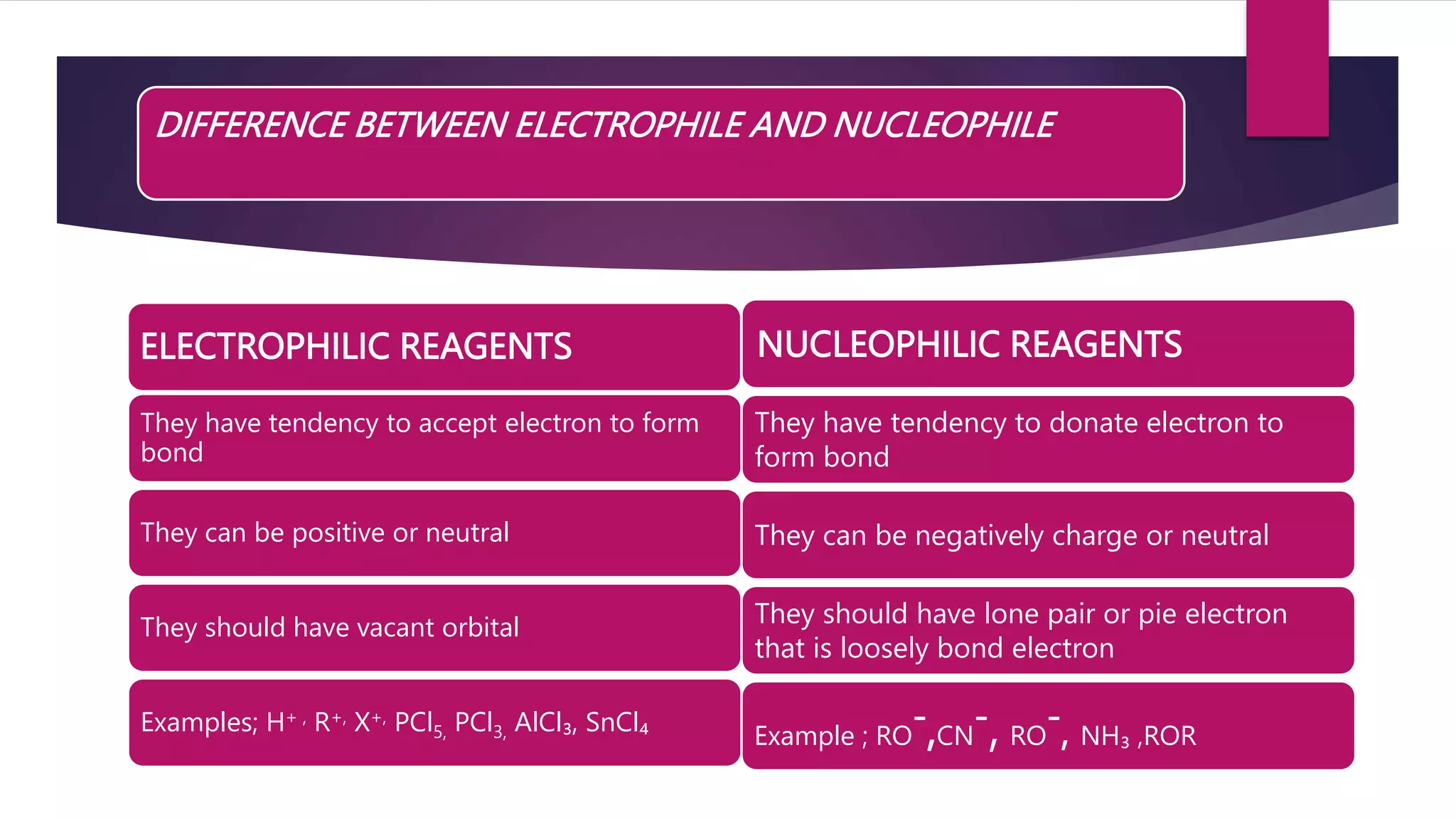
The document discusses reaction mechanisms in complex compounds. It begins by defining reaction mechanisms and factors studied like stereochemistry and equilibrium. It then differentiates between electrophilic and nucleophilic reagents. It describes substitution reactions of metal complexes, including ligand substitution reactions that can occur through dissociative or associative mechanisms. Specific ligand substitution reactions like ligand exchange, solvent exchange, and acid/base hydrolysis are mentioned. Trans effect and substitution reactions of square planar complexes are also summarized.

![SUBSTITUTION REACTION OF METAL COMPLEX
ELECTROPHILIC SUBSTITUTION REACTION
In reaction of metal complex metal ions is replaced by
another metal ion .
Also known as metal substitution reaction
[MLn] +M` [M`Ln] +M
In a chemical reaction
in which an atom ,ions,
molecule is replaced
by another atom ,ions
or molecule is known
as substitution
reaction
NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTION REACTION
In reaction of metal complex .ligand is replaced by another
ligand
Also known as ligand substitution reaction
[MLn] + L’ [MLn-1L’] +L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biszbtcptss8p2hh53zt-amit-ppt-sem-1-230201074543-1f89e90b/75/Reaction-mechanism-in-complex-compounds-5-2048.jpg)
![LIGAND SUBSTITUTION REACTION OR SN REACTION
DISSOCIATIVE MECHANISM OR SN1
[MA5L] +E [MA5E]+L
-
STEP 1 -break down of metal ligand bond into (MA5 + L-) MA5 which is 5 coordination no.
compound and It is slow step and rate determining step .
MA5 intermediate form which is electron deficient compound .
STEP 2- attack of E
- ligand on the 5 coordinate compound [MA5] which is a fast step
As a resultant product MA5E is formed
RATE = k [COMPLEX].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biszbtcptss8p2hh53zt-amit-ppt-sem-1-230201074543-1f89e90b/75/Reaction-mechanism-in-complex-compounds-6-2048.jpg)
![ASSOCIATIVE MECHANISM OR SN2
[ML5Y] +Z slow [ML5YZ] fast [ML5Z]
STEP 1 – It is a slow step and rate determining step , in this step incoming
ligand attach with metal complex and 7 coordination compound is formed
which is a transition state.
In this step metal complex and incoming ligand both take part in reaction
so this reaction is bimolecular reaction.
Step 2 –In this step Y Ligand is a leave and resultant product is form that is
[ML5Z]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biszbtcptss8p2hh53zt-amit-ppt-sem-1-230201074543-1f89e90b/75/Reaction-mechanism-in-complex-compounds-7-2048.jpg)
![DIFFERENT TYPE OF LIGAND SUBSTITUTION REACTION
LIGAND EXCHANGE
[PtCl2 (Py)2] +2Cl* [PtCl2*(Py)2]
SOLVENT EXCHANGE
[M(H2O)6]n+ + H2
18O [M (H2O)5 (H2
18O )] n+ + H2O
• This reaction is also called water exchange reaction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biszbtcptss8p2hh53zt-amit-ppt-sem-1-230201074543-1f89e90b/75/Reaction-mechanism-in-complex-compounds-9-2048.jpg)
![ ACID HYDROLYSIS :-
[Co(NH3)5X]+2 + H2O [Co(NH3)5(H2O)]+3
BASE HYDROLYSIS:-
[Co(NH3)5X]+2 +OH [Co(NH3)5(OH)]+2
SOLVOLYSIS:-
M-L +S M-S + L (here S is the solvent
[Cr(CO)6] THF [CrS(CO)5] &L is the ligand.)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biszbtcptss8p2hh53zt-amit-ppt-sem-1-230201074543-1f89e90b/75/Reaction-mechanism-in-complex-compounds-10-2048.jpg)
![“
”
ANATION REACTION
MECHANISM: STEP 1: [CO(NH3)5(H2O)] [CO(NH3)5] +H2O
C.N =6 C.N =5
STEP2 : [CO(NH3)5] +Z
- [CO(NH3)5Z]
C.N =5 C.N=6
In this reaction , the anionic molecule replaces the aqua
(water) molecule present in the complex.
[Co(NH3)5(H2O)]+3 +Z [Co(NH3)5Z]+2 +H20
Rate =k[Co(NH3)5(H2O)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biszbtcptss8p2hh53zt-amit-ppt-sem-1-230201074543-1f89e90b/75/Reaction-mechanism-in-complex-compounds-11-2048.jpg)
![SUBSTITUTION REACTION WITHOUT M-L BOND CLEAVAGE
Generally in substitution reaction takes place by cleavage of
metal ligand bond and a new bond is formed.
Here are some substitution reaction in which M-L bond is not
broken
Example :
conversion of[Co(NH3)5CO3]+1 to [Co(NH3)5H2O]+3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biszbtcptss8p2hh53zt-amit-ppt-sem-1-230201074543-1f89e90b/75/Reaction-mechanism-in-complex-compounds-12-2048.jpg)
![MECHANISM :
[(NH3)5 Co-O-CO2]+ +2H+ [(NH3)5Co-OH2] +CO2
STEP1 O + OH 2+ H O 2+
(NH3)5-Co-O-C + H+ (NH3)5-Co-O-C (NH3)5-Co-O-C
O O + O
DECARBOXYLATION OF ABOVE FORMED BICARBONATE COMPLEX
H O 2+ 2+ 3+
(NH3)5Co-O-C Slow (NH3)5-Co-OH + CO2 Fast /H+ (NH3)5Co –O+H2
+ O](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biszbtcptss8p2hh53zt-amit-ppt-sem-1-230201074543-1f89e90b/75/Reaction-mechanism-in-complex-compounds-13-2048.jpg)
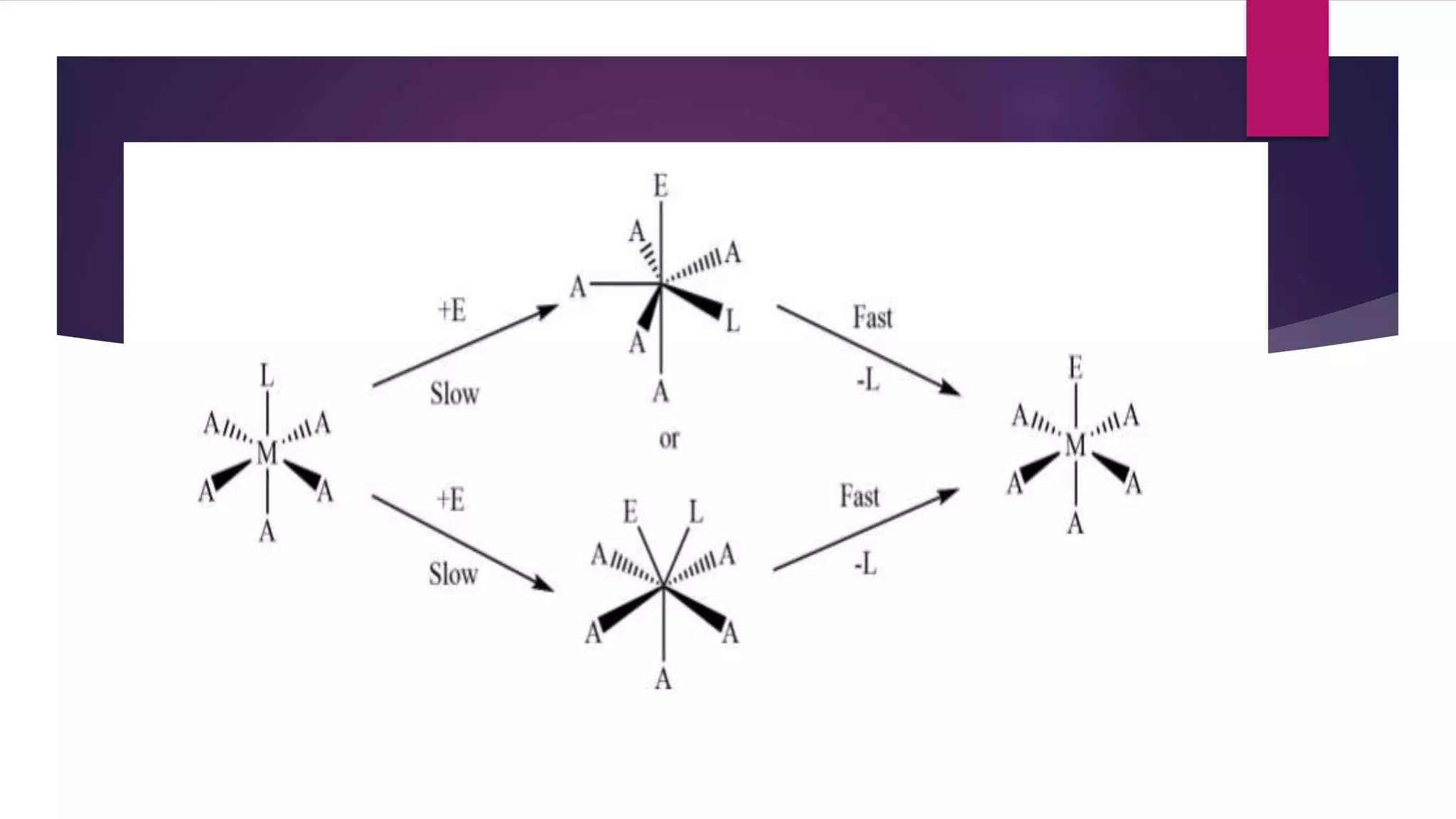
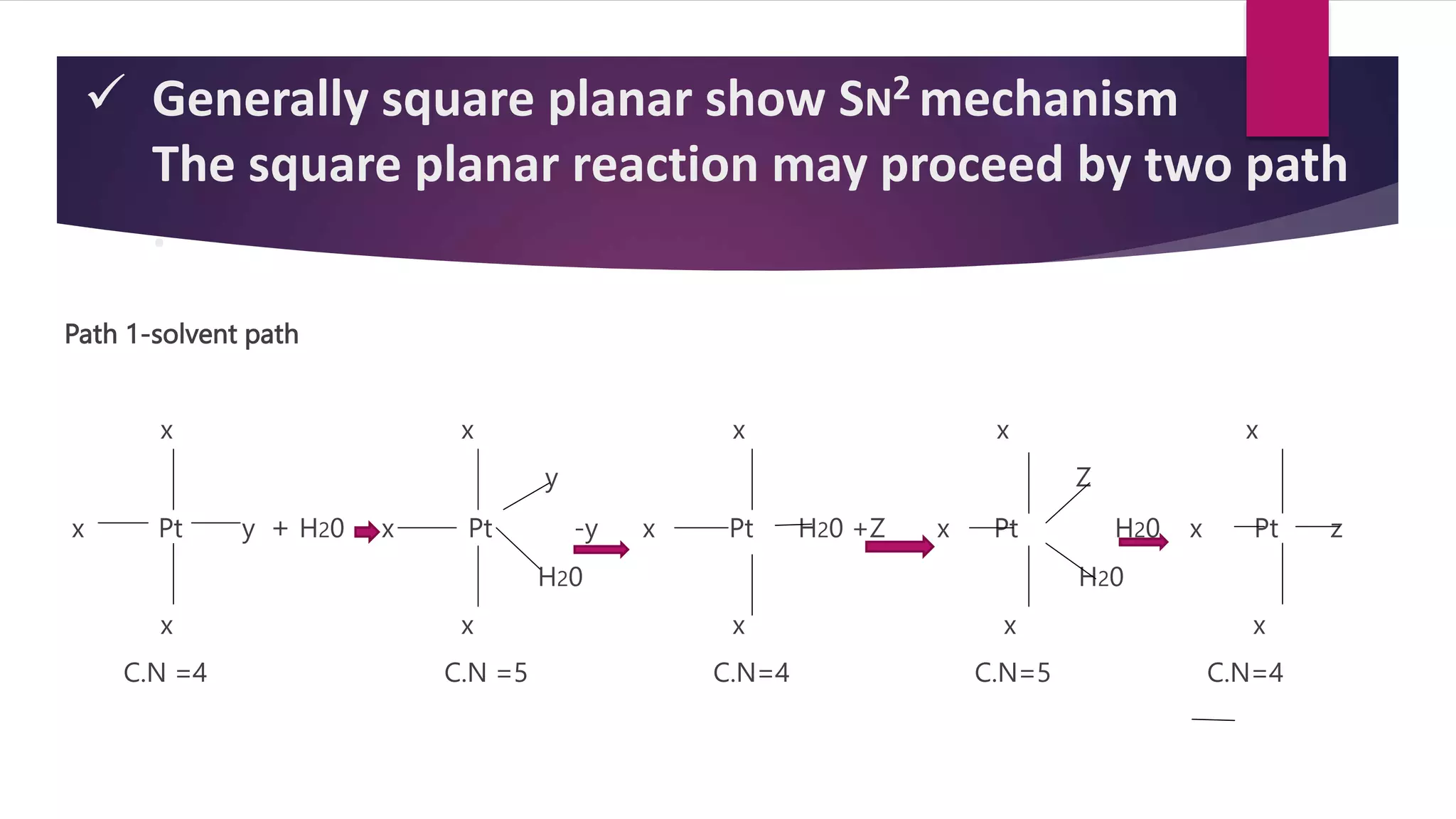
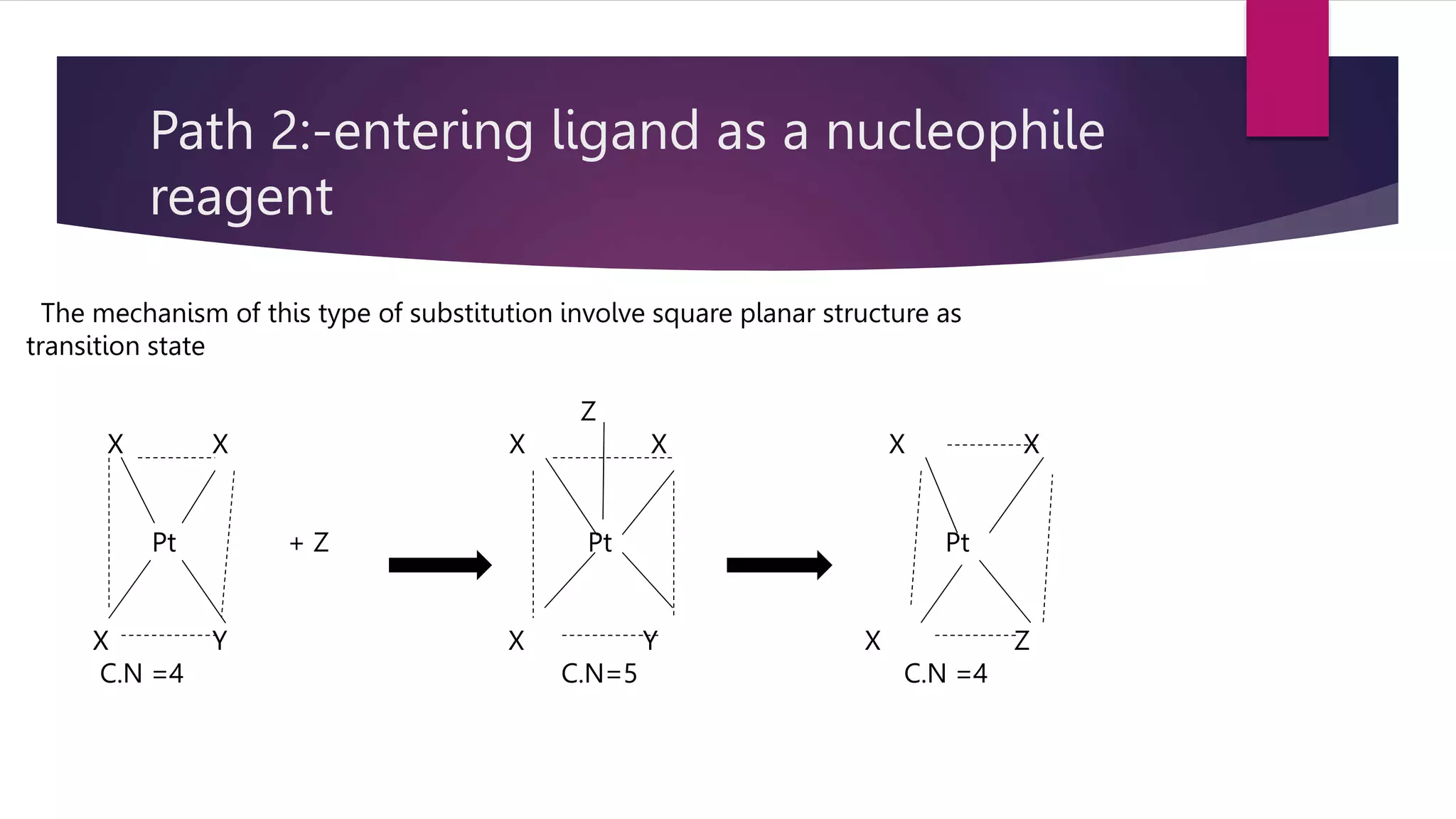
![SUBSTITUTION REACTION IN SQUARE PLANAR COMPLEX
The kinetics of reaction
such as
[PtA2LX] + Y [PtA2LY] +X-
A L
Pt
A X
Complexes with d8 electronic configuration
usually are 4-coordination no. and have square
planar geometry.
These configurations include complex of Pt(II) ,Pd
(II) ,NI (II).
Complex of Pt (II) have been attractive for the
rate studies because they are stable ,relatively
easy to synthesized and undergo substitution
reaction.
It is easy to monitor Pt (II) reaction.
Rate =k1 [complex] + k2 [complex] [y]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biszbtcptss8p2hh53zt-amit-ppt-sem-1-230201074543-1f89e90b/75/Reaction-mechanism-in-complex-compounds-14-2048.jpg)
![Substitution reaction of cis and trans of Pt (||)
complex
Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl NH3
Pt +NH3 Pt +NH3 Pt
-Cl -Cl
Cl Cl Cl NH3 Cl NH3
cis [PtCl2(NH3)2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biszbtcptss8p2hh53zt-amit-ppt-sem-1-230201074543-1f89e90b/75/Reaction-mechanism-in-complex-compounds-17-2048.jpg)
![NH3 NH3 NH3
NH3 Pt NH3 +Cl NH3 Pt Cl +Cl Cl Pt Cl
-NH3 -NH3
NH3 NH3 NH3
Trans [Pt Cl2(NH3)]
• Trans effect Cl > NH3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biszbtcptss8p2hh53zt-amit-ppt-sem-1-230201074543-1f89e90b/75/Reaction-mechanism-in-complex-compounds-18-2048.jpg)