The document discusses metal alkene complexes, including their preparation and properties through various synthesis methods such as substitution reactions, reduction, and from alkyls. It also covers the structural aspects and bonding characteristics of metal olefinic compounds, highlighting factors that affect the C=C bond length in these complexes. Transition metals play a critical role in the stability and formation of these compounds, with observations on their oxidation states and bonding capabilities.

![Metal Alkene Compounds: Synthesis
1. Substitution reaction (low valent metals)
K2[PtCl4] + C2H4 → K[PtCl3(C2H4)].H2O + KCl](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1metalalkenecomplexes-220501162736/85/Metal-alkene-complexes-ppt-2-320.jpg)
![Metal Alkene Compounds: Synthesis
1. Substitution reaction (low valent metals)
[CpFe(CO)2I] + AgBF4 + C2H4 → [CpFe(CO)2(C2H4)]BF4 + AgI
Fe(CO)5 +
PdCl2(PhCN)2 + C8H12 →](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1metalalkenecomplexes-220501162736/85/Metal-alkene-complexes-ppt-3-320.jpg)
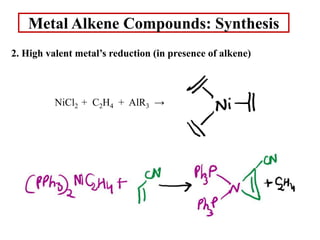
![Metal Alkene Compounds: Synthesis
2. High valent metal’s reduction (in presence of alkene)
RhCl3 + CH3CH2OH + nbd → [(nbd)Rh(μ-Cl)]2 + CH3CHO + HCl](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1metalalkenecomplexes-220501162736/85/Metal-alkene-complexes-ppt-5-320.jpg)











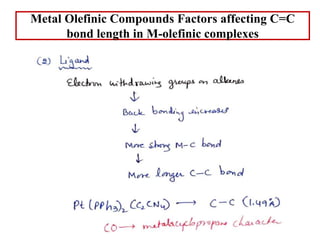
![Metal Olefinic Compounds Factors affecting C=C
bond length in M-olefinic complexes
Binding of metal lengthens the C=C bond length in M-
olefinic complexes
They are formed only by transition metal atoms, and
especially with those in which there are one or more filled
d orbitals available for donation to the p orbitals of the
carbon atom.
Become more stable as one descends a vertical transition
metal triad, e.g. Pt(II)> Pd(II)> Ni(II). however, Ag(I)
appears to be a better olefin acceptor than Cu(I) or Au(I)].
The oxidation state of a metal atom increases, ease of
complex formation with olefin decreases; thus Pt(II)
forms many olefin complexes whereas none of Pt(IV) are
known.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1metalalkenecomplexes-220501162736/85/Metal-alkene-complexes-ppt-19-320.jpg)