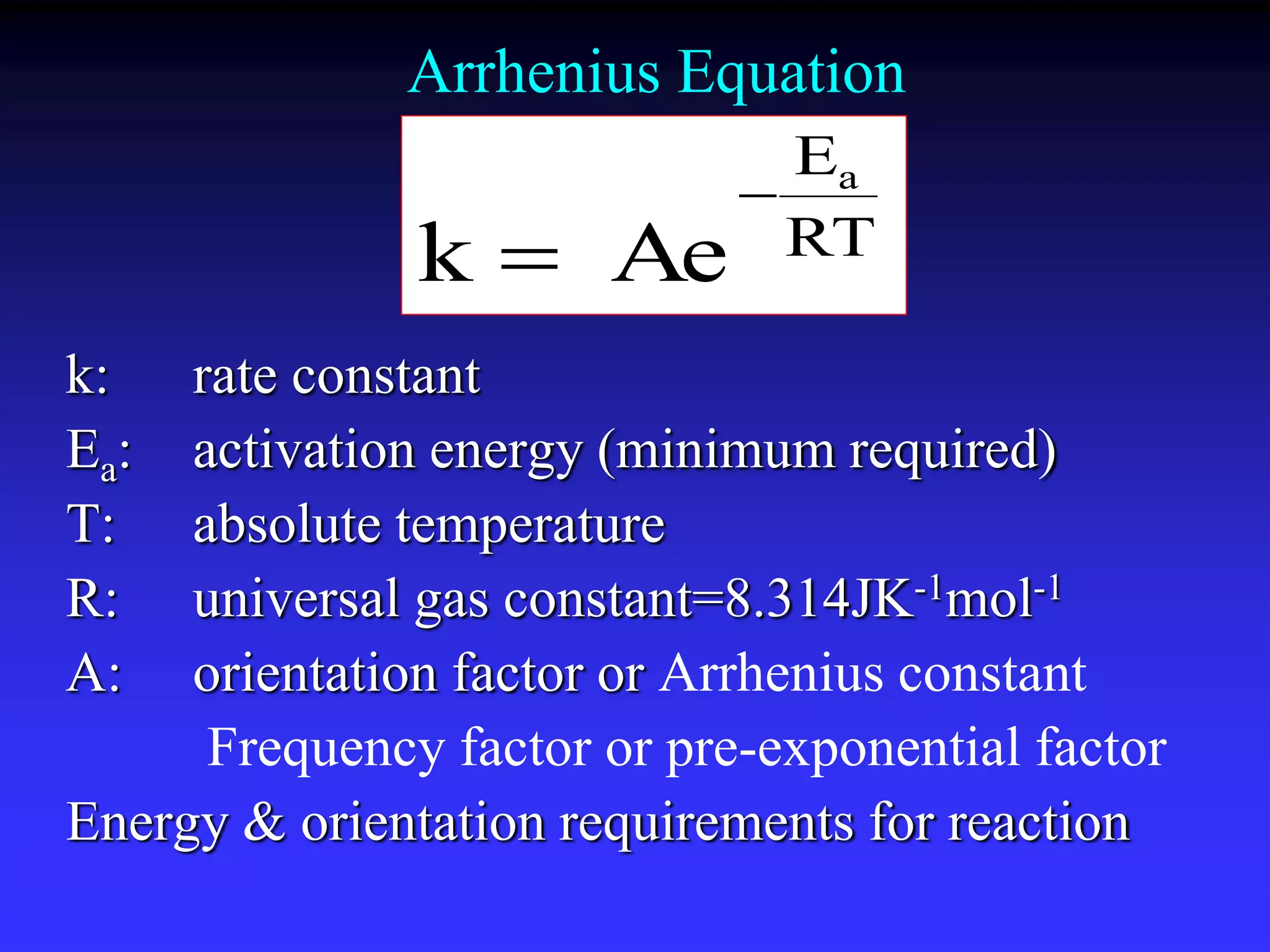
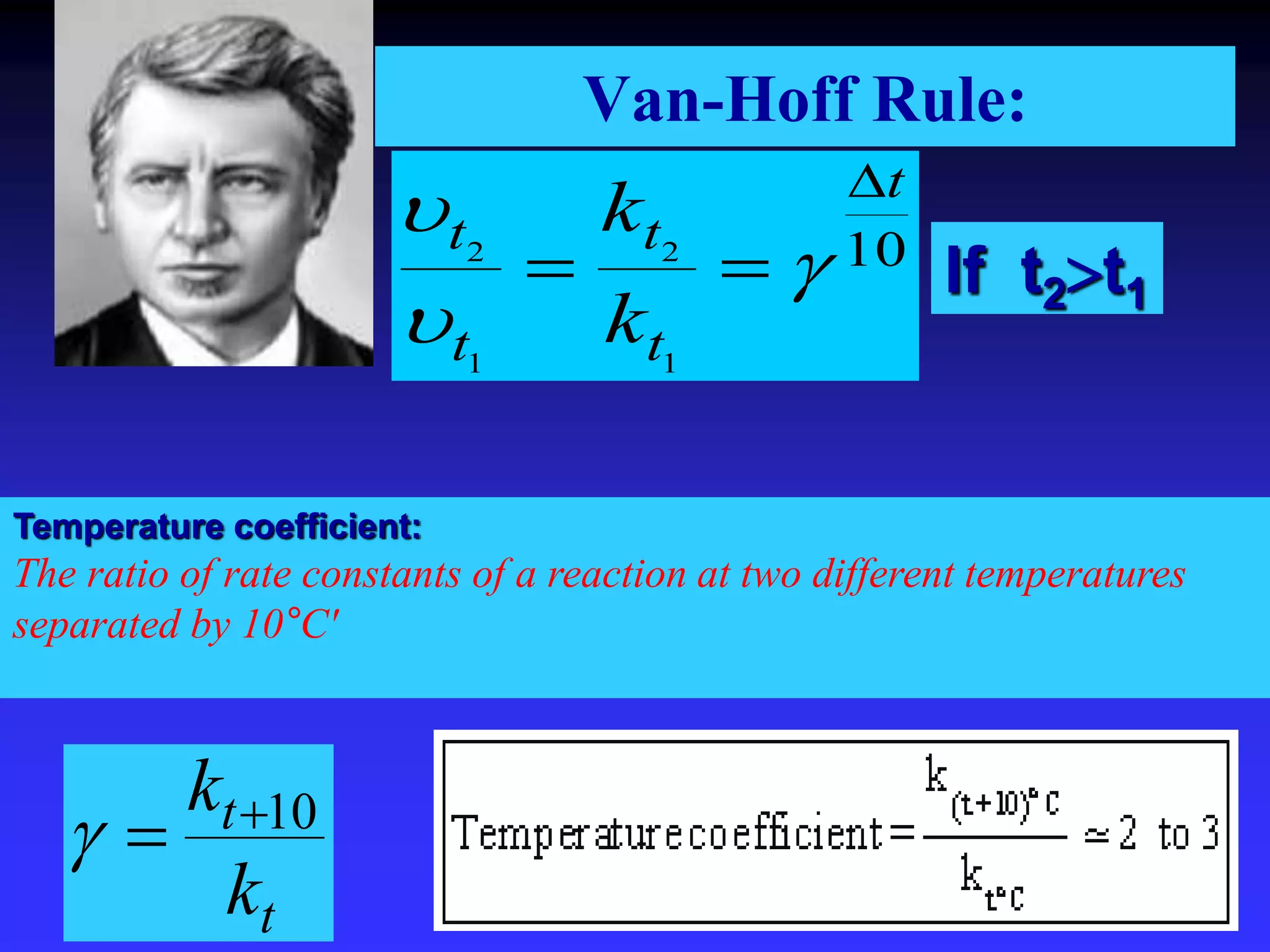
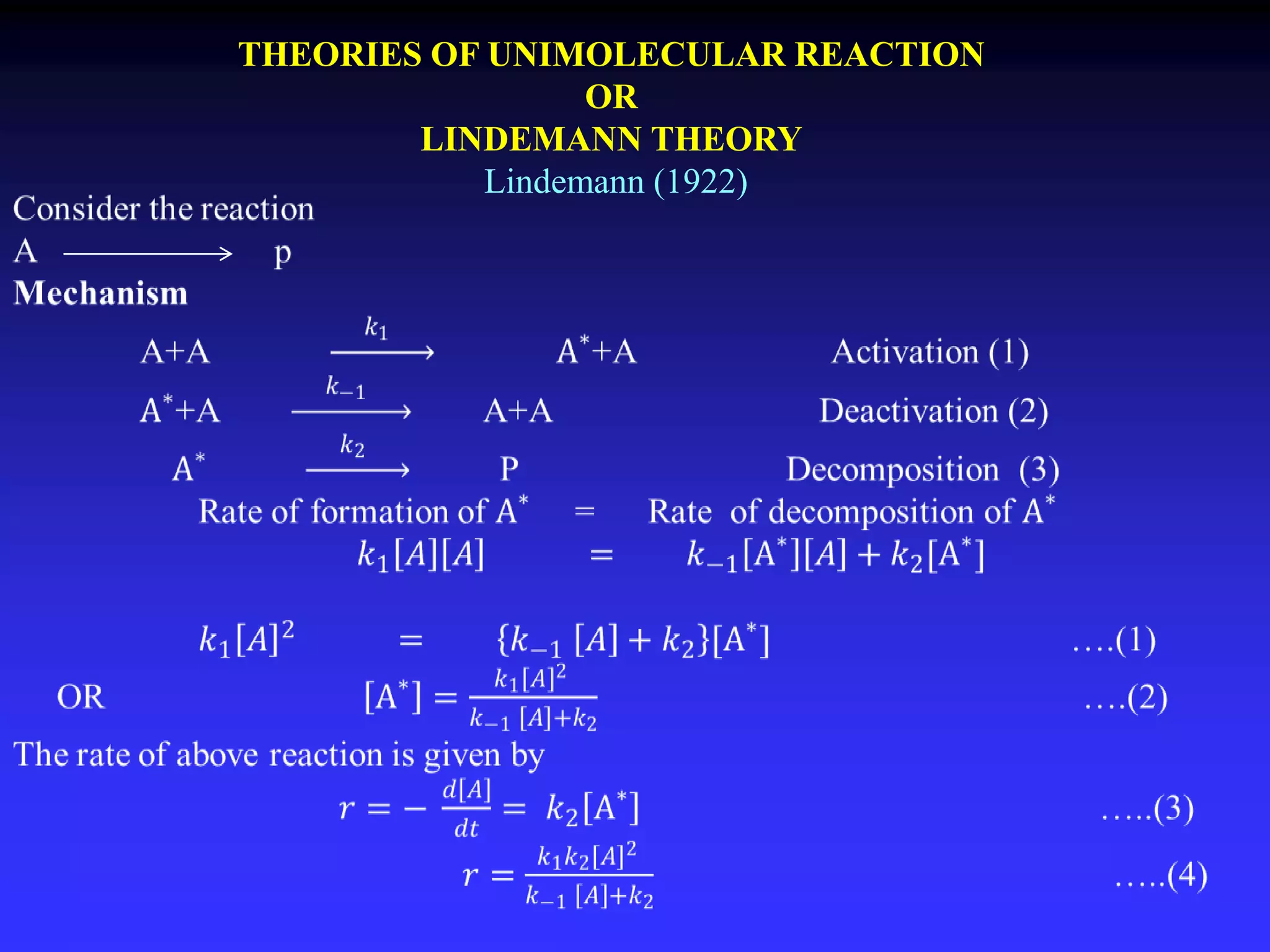
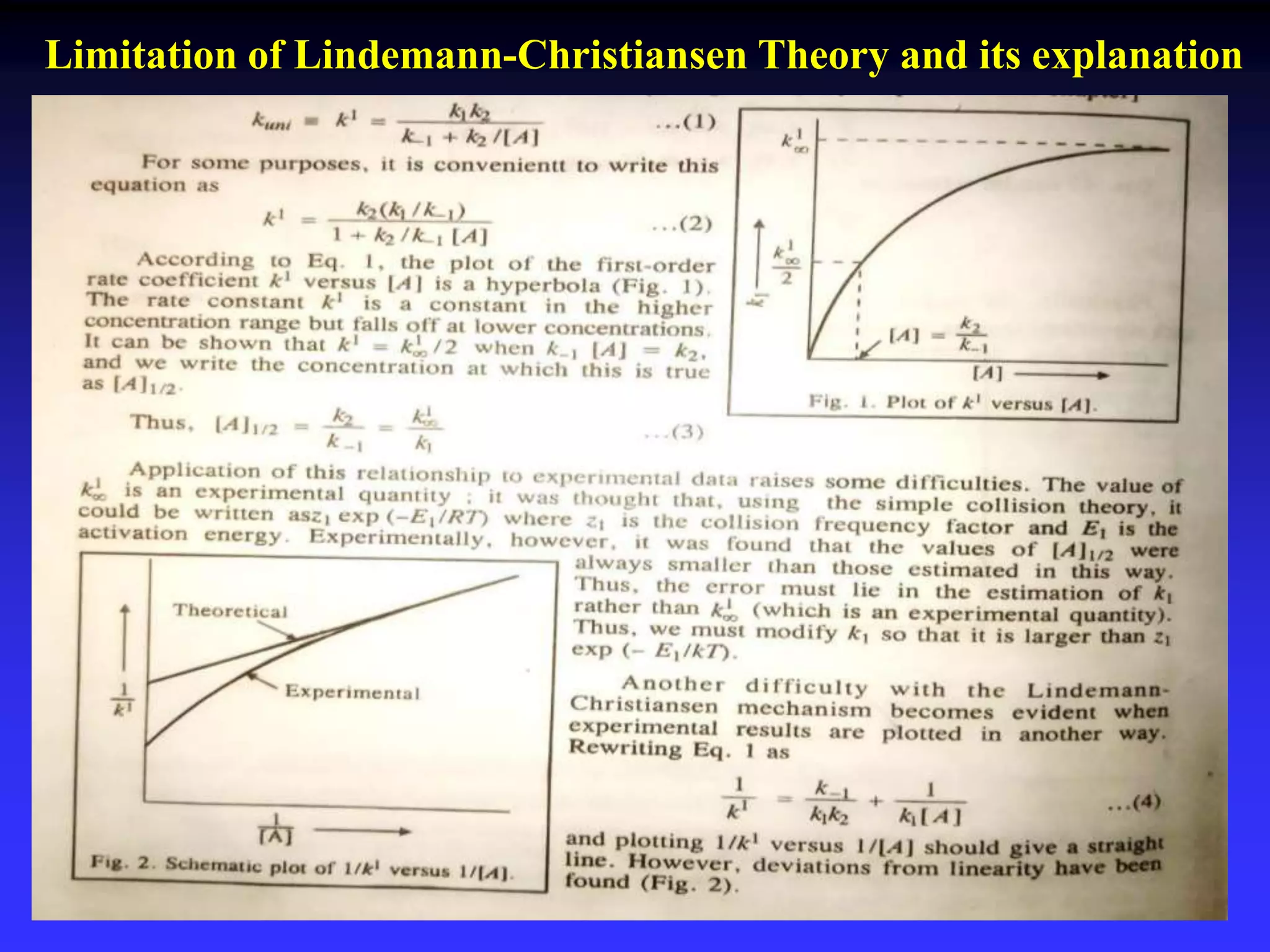
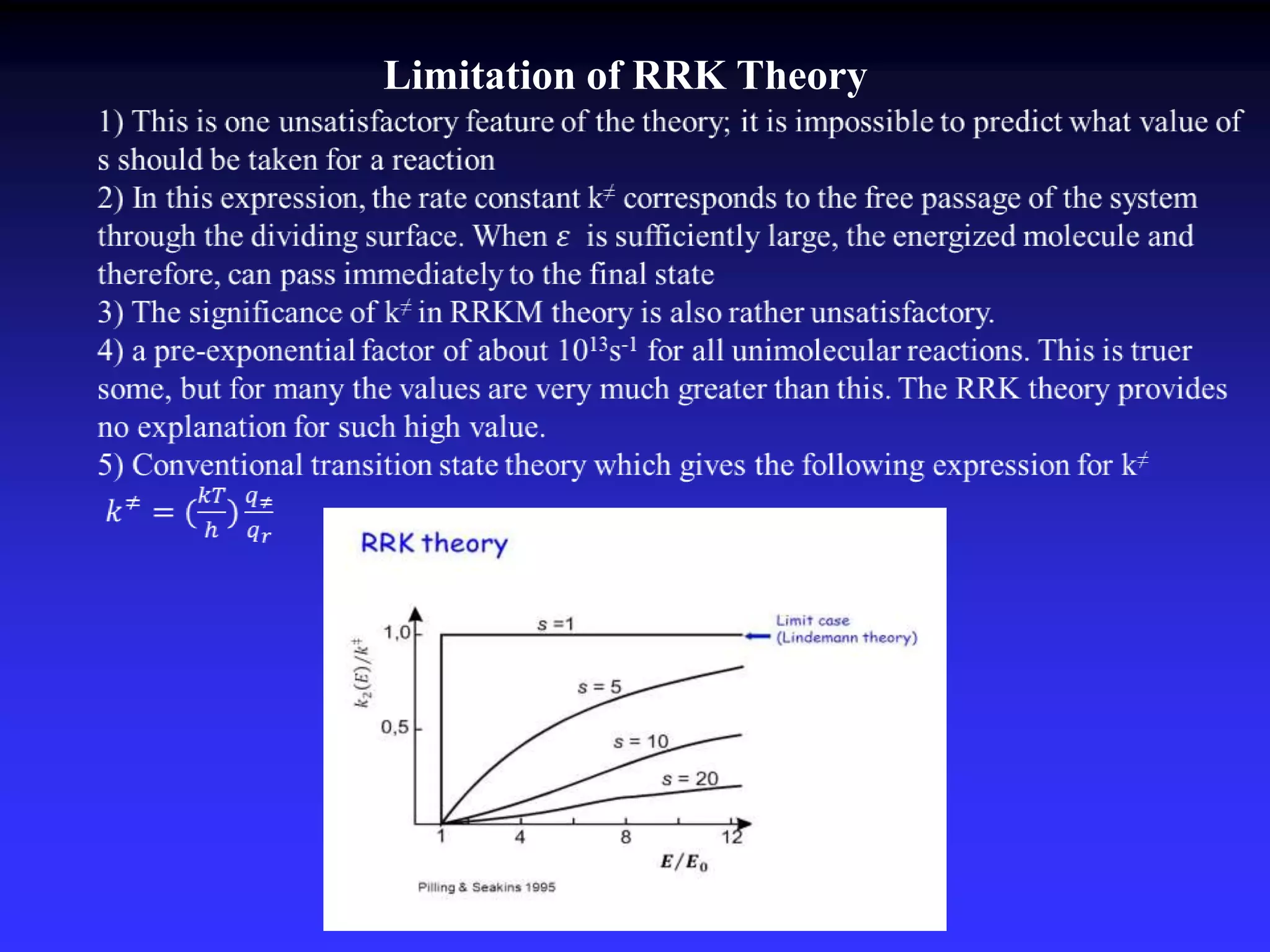
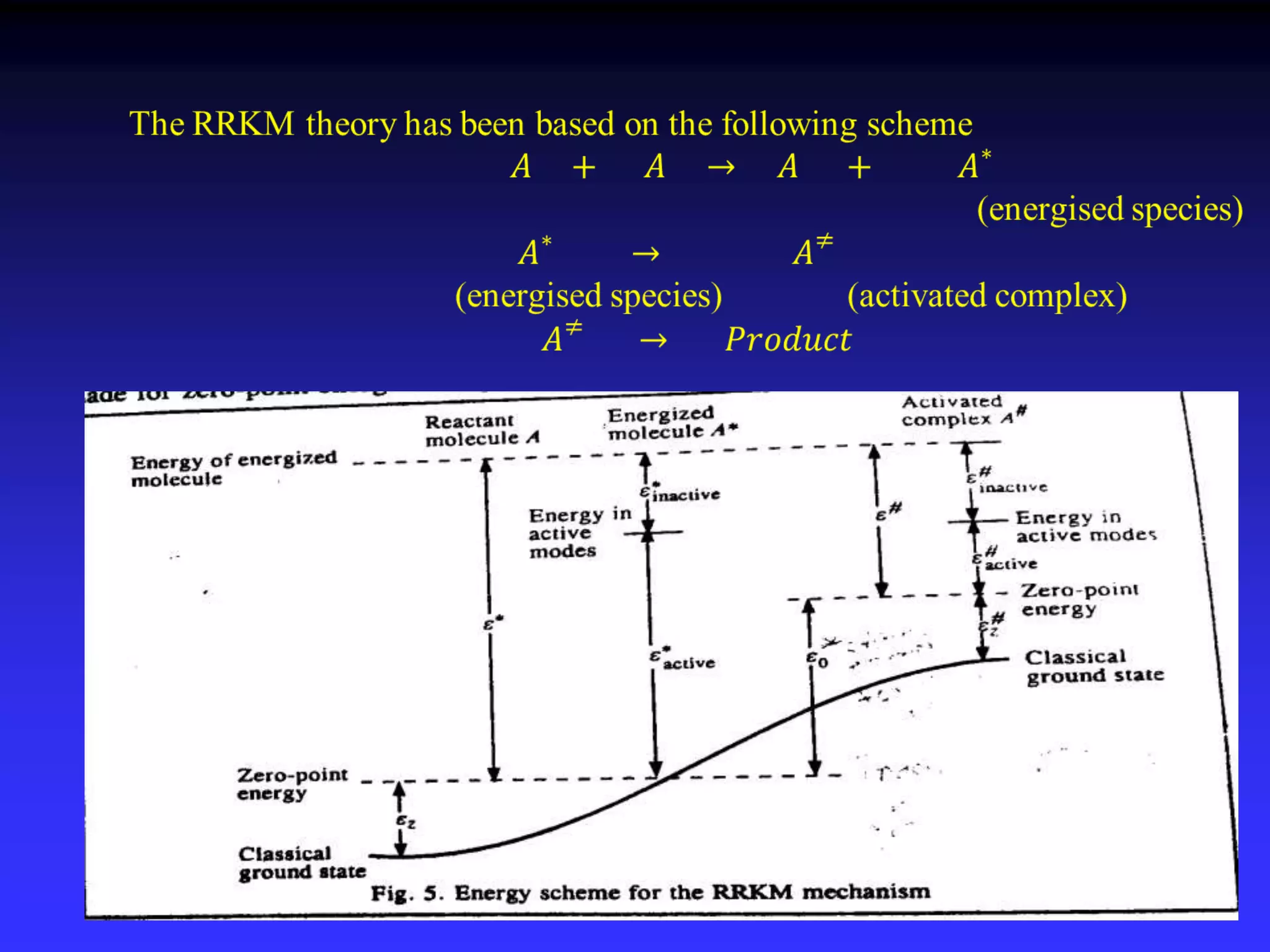
This document discusses theories of unimolecular reaction kinetics, including the Lindemann-Christiansen theory, Hinshelwood theory, RRK theory, and RRKM theory. It notes limitations of earlier theories in explaining experimental data. The RRKM theory, developed by Marcus in 1951-1952, redefined the RRK treatment and addressed prior limitations. RRKM theory is now widely used to interpret thermal and photochemical reactions and allows calculating reaction rates from known vibrational frequencies of molecules.