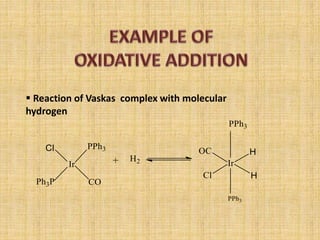
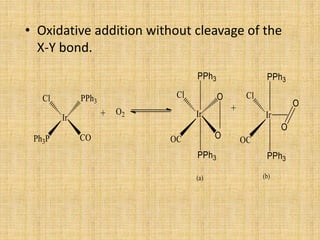
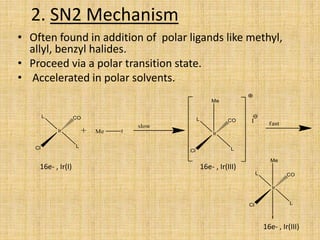
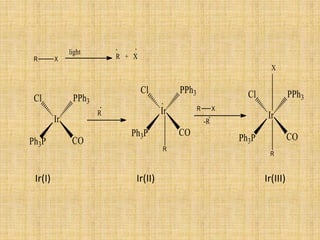
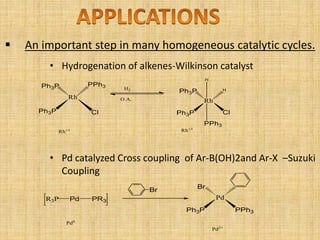
Oxidative addition is a process where a metal complex increases its oxidation state and coordination number by addition of two ligands. It is the reverse of reductive elimination. It requires the metal to have available orbitals and be in a lower oxidation state. There are four mechanisms for oxidative addition: concerted, SN2, radical, and ionic. Oxidative addition and reductive elimination are important steps in many catalytic cycles in organometallic chemistry and homogeneous catalysis.