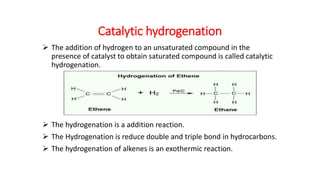
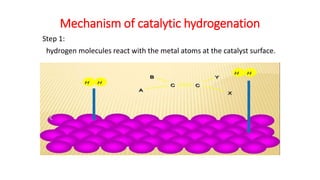
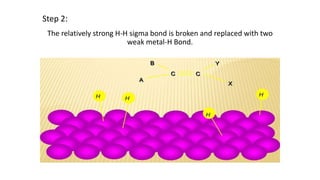
This document discusses catalytic hydrogenation, which is the addition of hydrogen to unsaturated compounds in the presence of a catalyst. It defines catalytic hydrogenation and mentions some common catalysts used like palladium, platinum dioxide, and raney nickel. The mechanism of catalytic hydrogenation is described as hydrogen molecules reacting with the metal catalyst surface before transferring hydrogen atoms to the unsaturated compound. Factors that affect the reaction rate like catalyst surface area, temperature, and pressure are also outlined. Some advantages of catalytic hydrogenation are its ability to proceed at lower temperatures and with higher specificity and activity compared to non-catalytic hydrogenation. Applications mentioned include producing alkanes from alkenes and making vegetable ghee and margarine