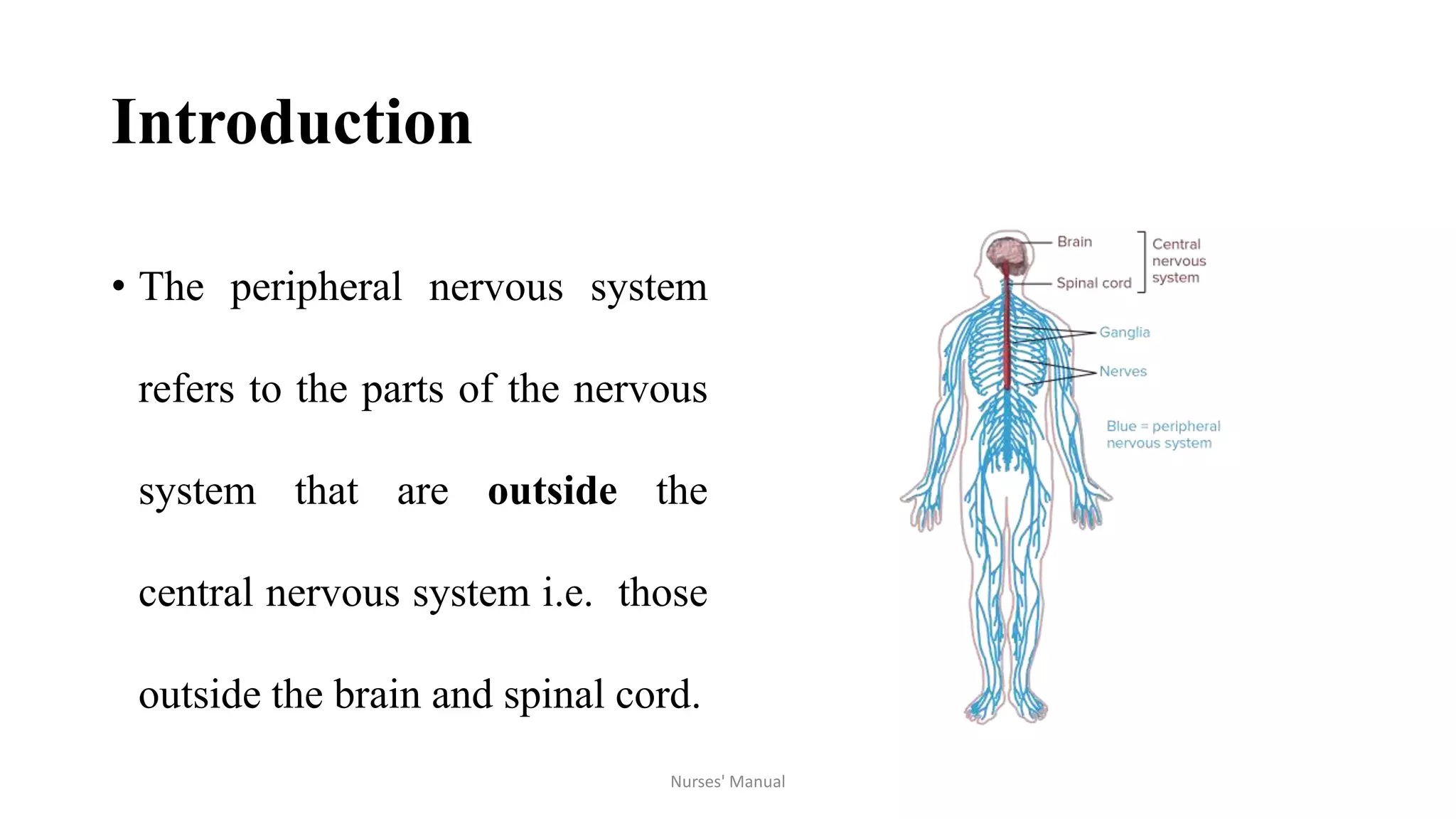
Peripheral neuropathy is a disorder affecting motor, sensory or autonomic nerves outside of the central nervous system. There are two main types: mononeuropathy, which damages a single nerve, and polyneuropathy, which affects multiple nerves. Causes include diabetes, alcoholism, toxins, medications and genetic factors. Symptoms depend on the affected nerves and may include numbness, tingling, pain, muscle weakness and autonomic issues. Diagnosis involves examinations, tests and imaging. Treatment focuses on managing the underlying cause, pain relief medications, nerve stimulation, splinting and self-care techniques. Nursing care includes education, medication management, safety measures and physical therapy.