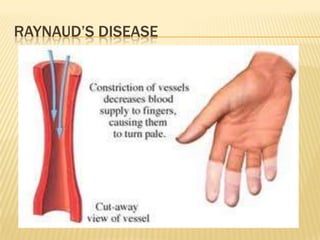
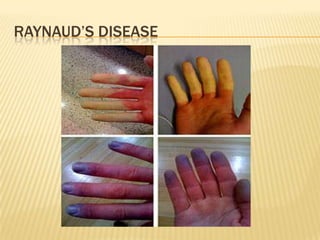
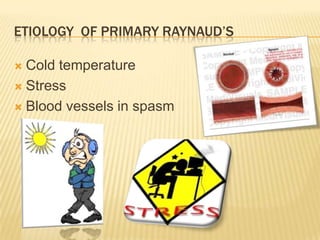
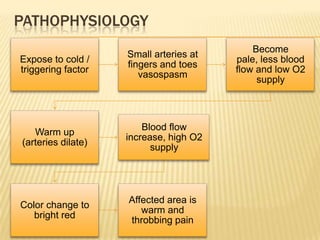
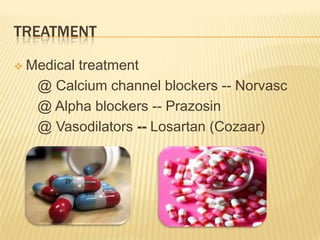
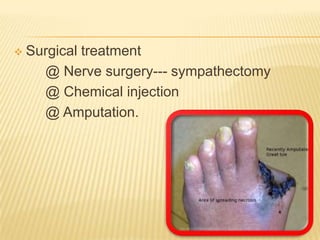
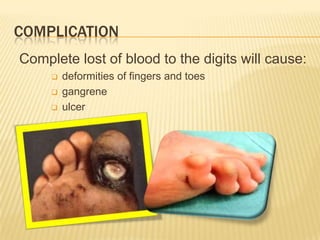
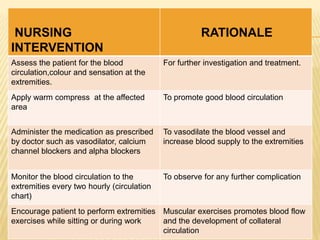
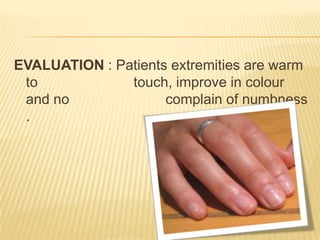
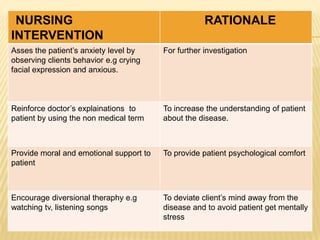
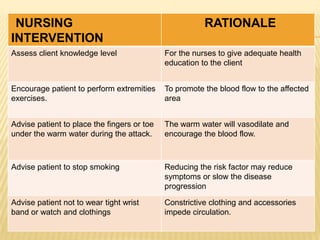
Raynaud's disease is a rare disorder characterized by vasospasm of the arteries, causing reduced blood flow to the fingers and toes. It can be classified as either primary Raynaud's, whose cause is unknown, or secondary Raynaud's, which has an underlying cause such as scleroderma or rheumatoid arthritis. Symptoms include pale, cold, painful fingers and toes during attacks triggered by cold temperatures or stress. Treatment focuses on vasodilators and lifestyle changes to promote blood circulation. Nursing care involves assessing circulation, providing warm compresses, administering medications, educating on self-care activities, and reducing anxiety.