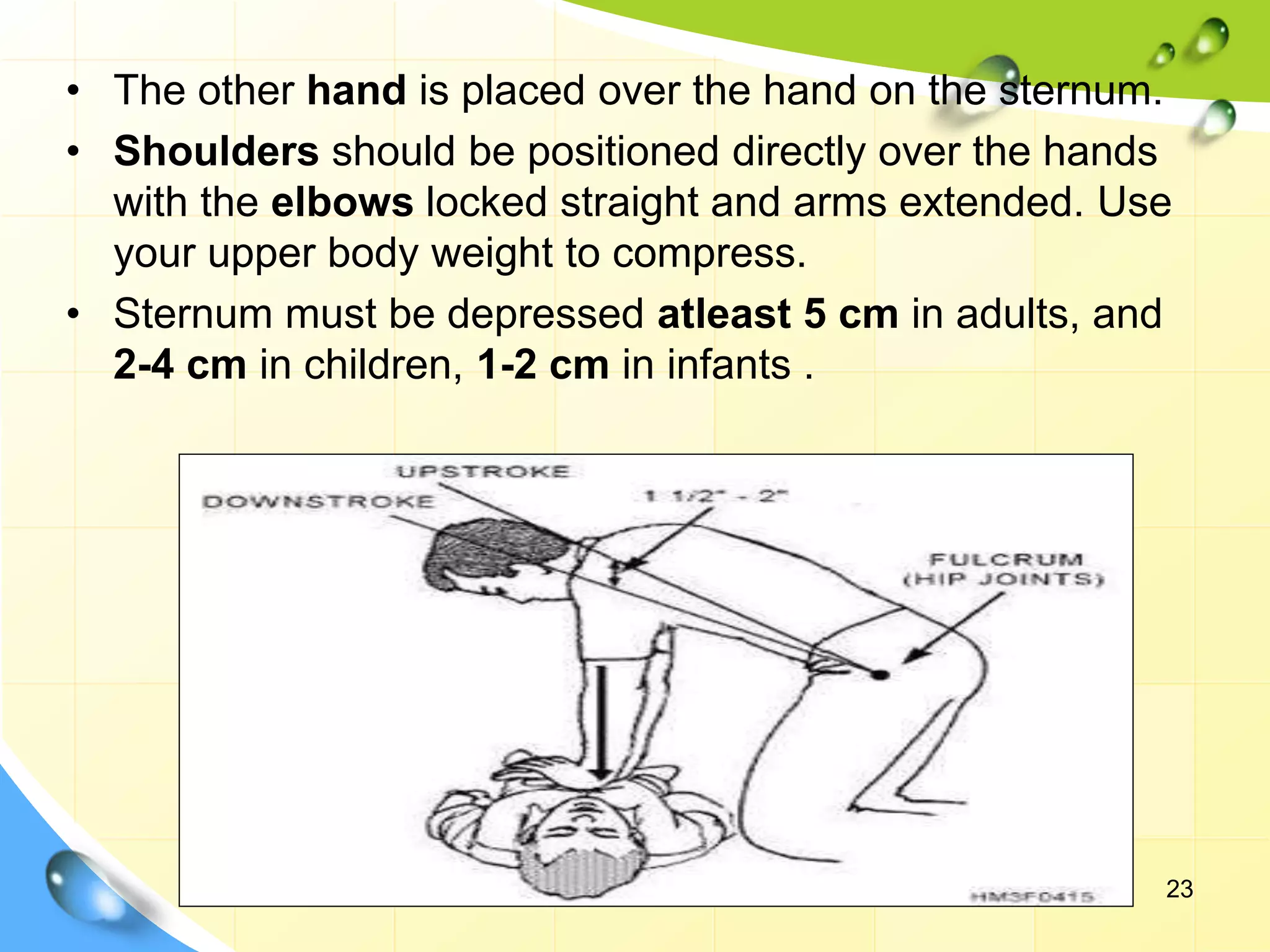
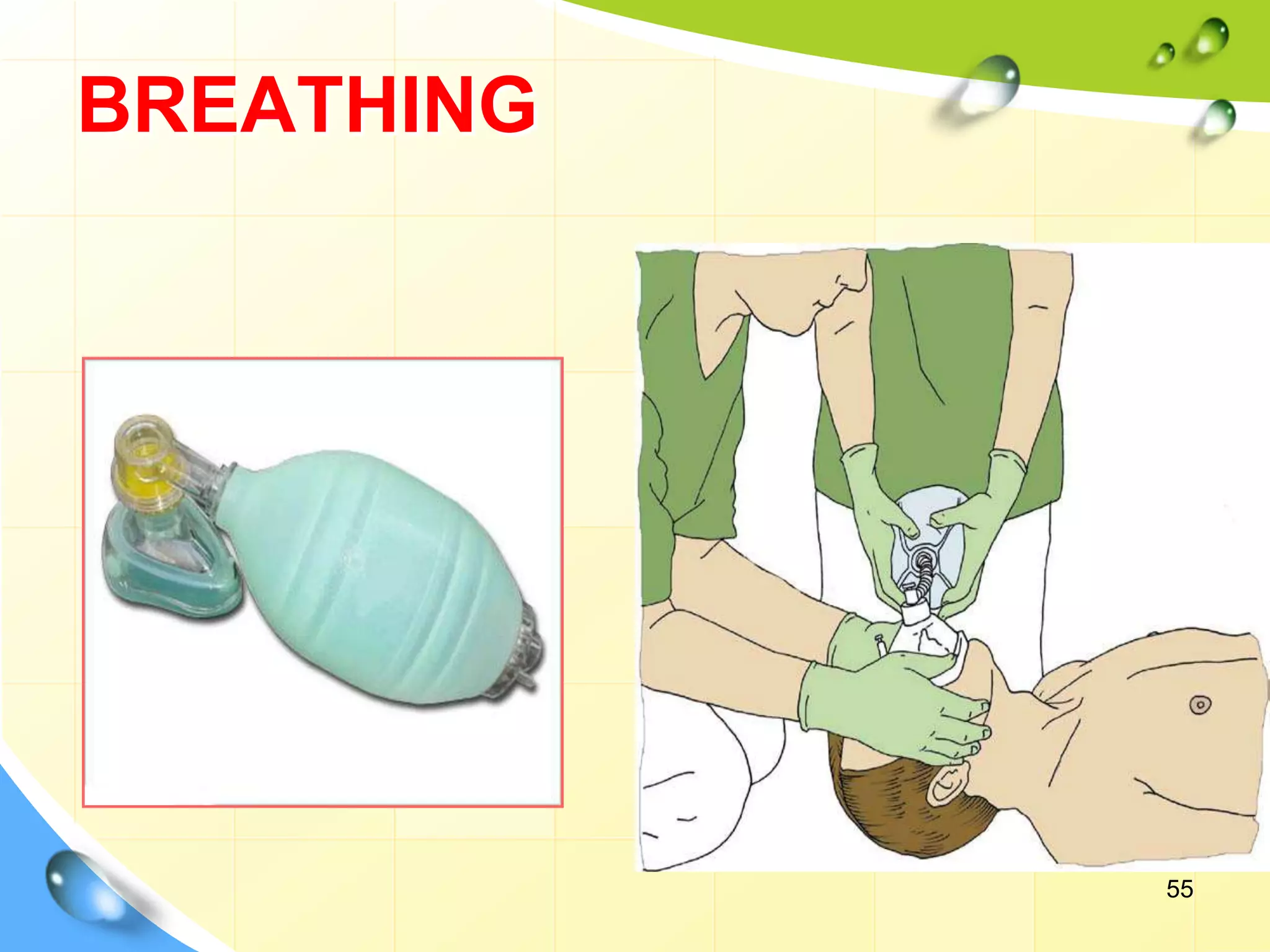
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a technique used to manually maintain heart function and breathing in a person whose heart and breathing have stopped. It involves chest compressions to pump the heart and artificial ventilation to oxygenate the lungs until emergency medical treatment can restore normal heart function and breathing. The key steps of CPR include opening the airway, providing rescue breaths, and performing chest compressions at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute. Advanced CPR techniques involve use of equipment like defibrillators, endotracheal tubes, and medications to further support circulation and breathing. The goal of CPR is to prevent irreversible brain damage by maintaining oxygenated blood flow until normal heart function can