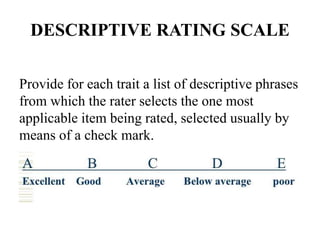
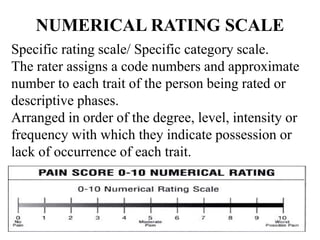
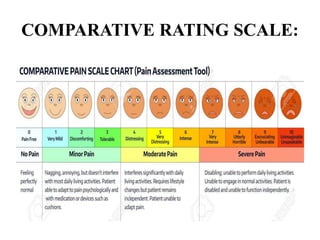
This document discusses different types of rating scales used to evaluate attributes of people or objects. It describes descriptive rating scales, numerical rating scales, graphic rating scales, and comparative rating scales. Descriptive rating scales provide phrases to describe traits, numerical scales assign code numbers, graphic scales use a line to indicate degrees of traits, and comparative scales define positions in terms of a population. The document also outlines principles for developing rating scales and notes they can be used to evaluate skills, products, activities, interests, attitudes, and personnel characteristics, but may decrease objectivity if misused.