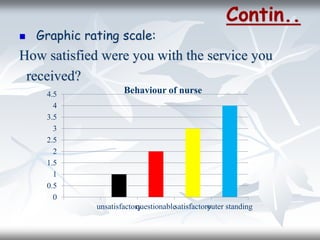
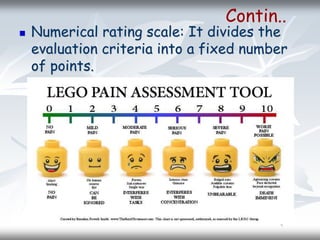
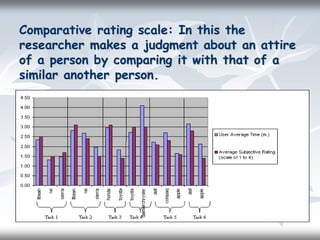
This document discusses rating scales, which are tools used to measure attributes or performance on a continuum. It defines rating scales as scales with sets of opinions that describe varying degrees of dimensions of an attitude. Common types of rating scales include 3-point, 5-point, and 7-point scales. The document also describes four specific types of rating scales: graphic, descriptive, numerical, and comparative. It outlines principles for developing rating scales and discusses their uses and disadvantages, such as potential decreases in objectivity and chances of subjective evaluation.