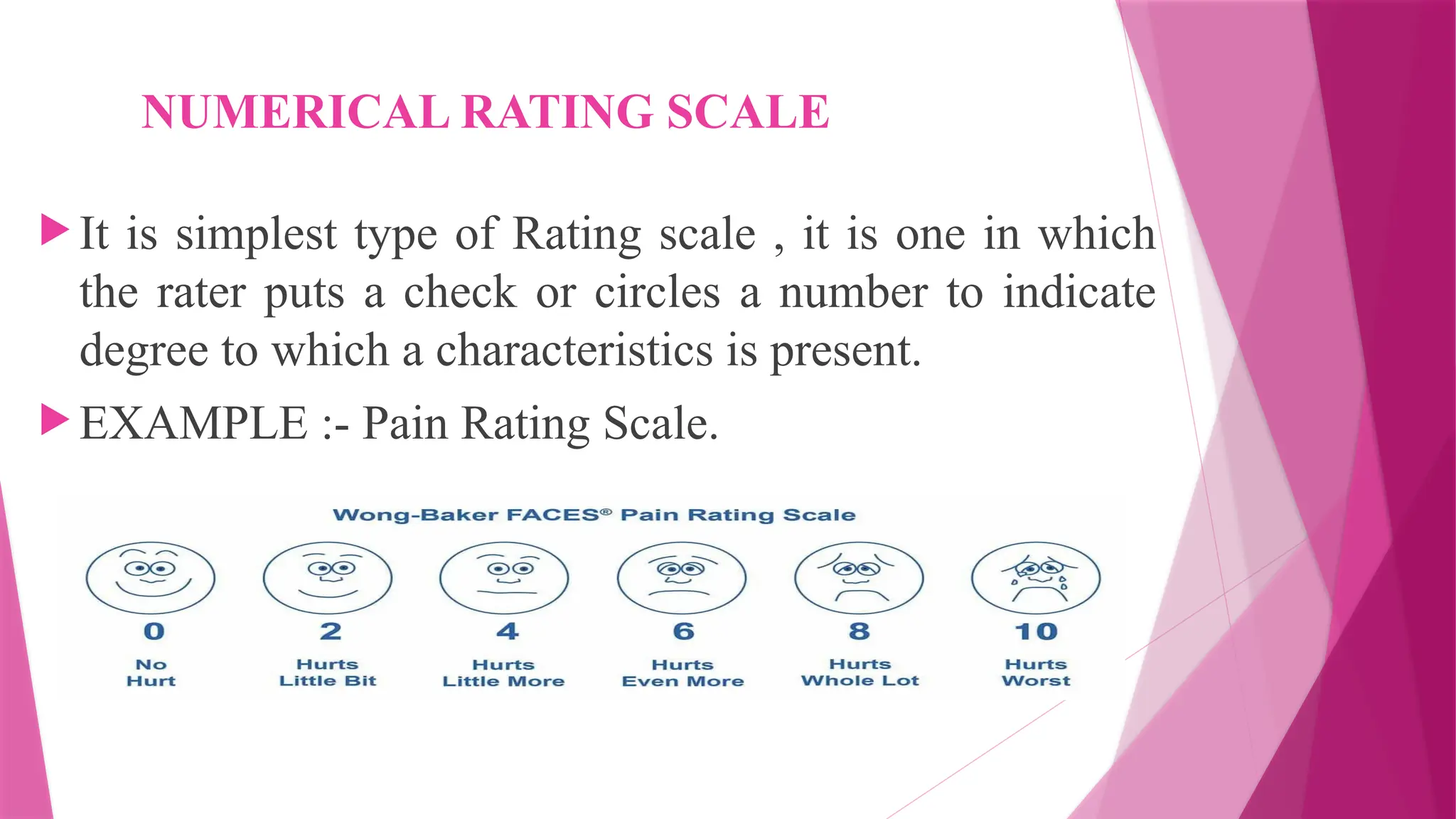
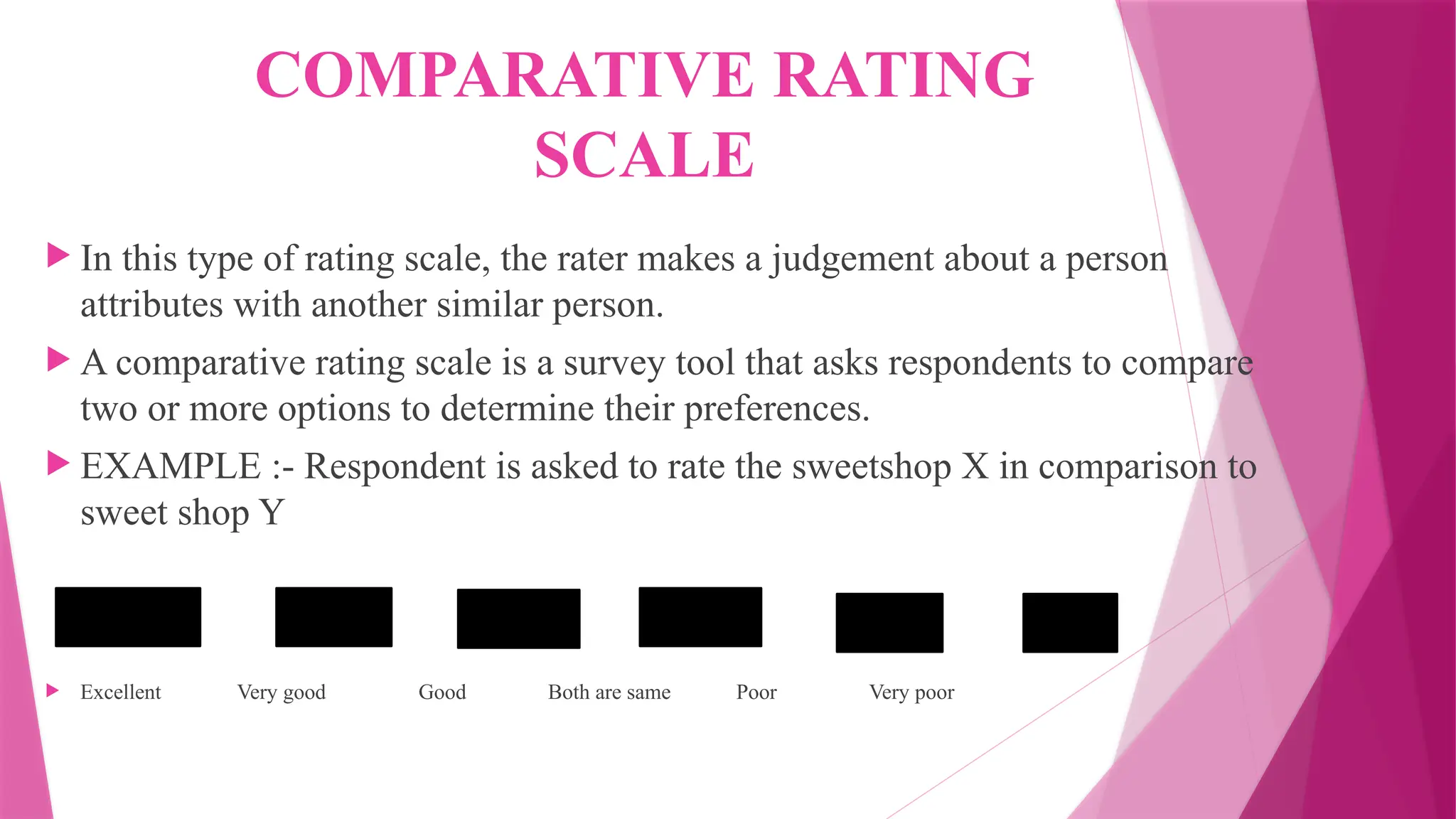
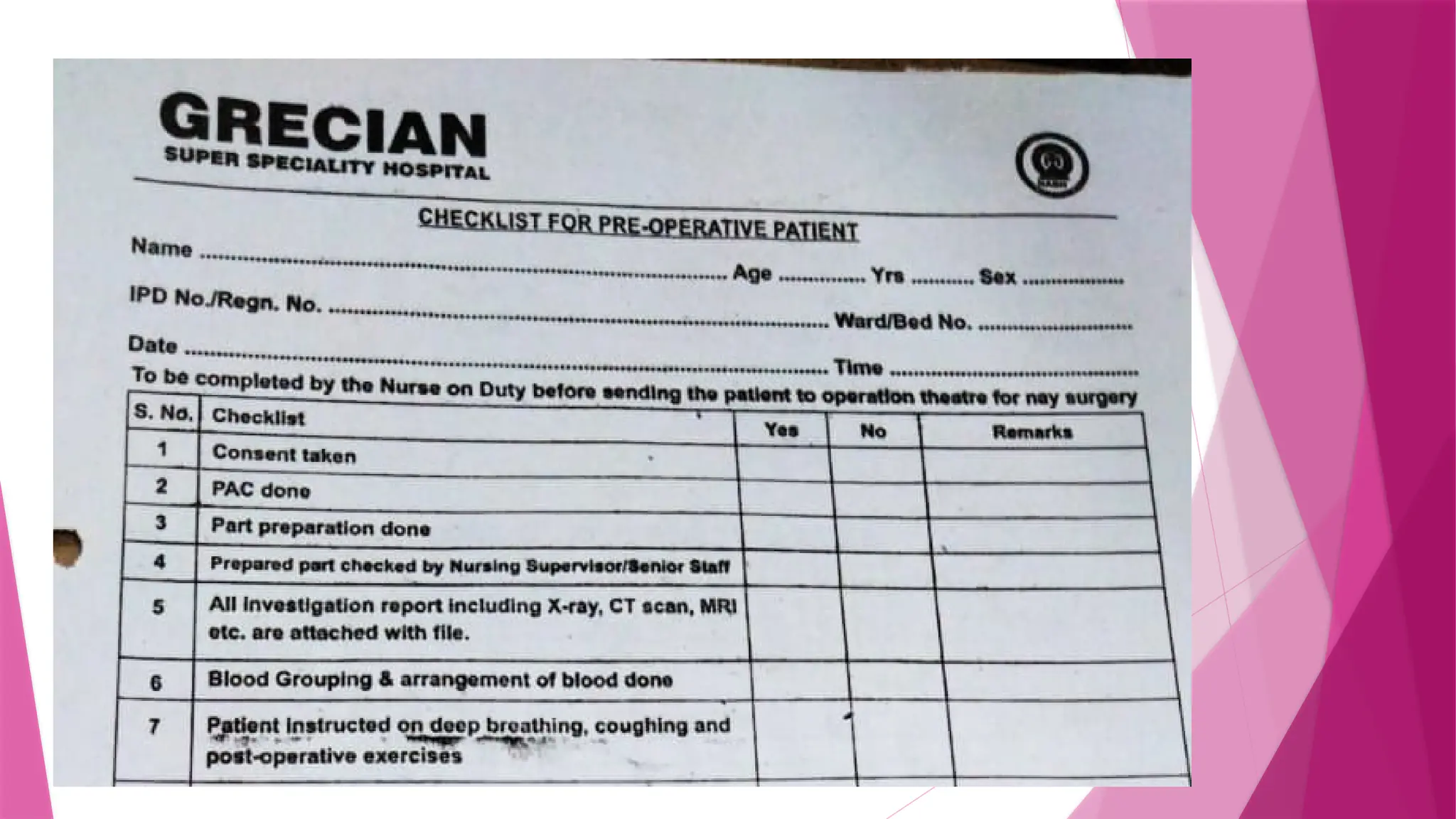
The document provides a comprehensive overview of rating scales and checklists used for performance evaluation. It discusses various types of rating scales, their characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and limitations, as well as the purposes and features of checklists. The conclusion emphasizes the utility of these tools in assessing skills and behaviors, particularly in educational settings.