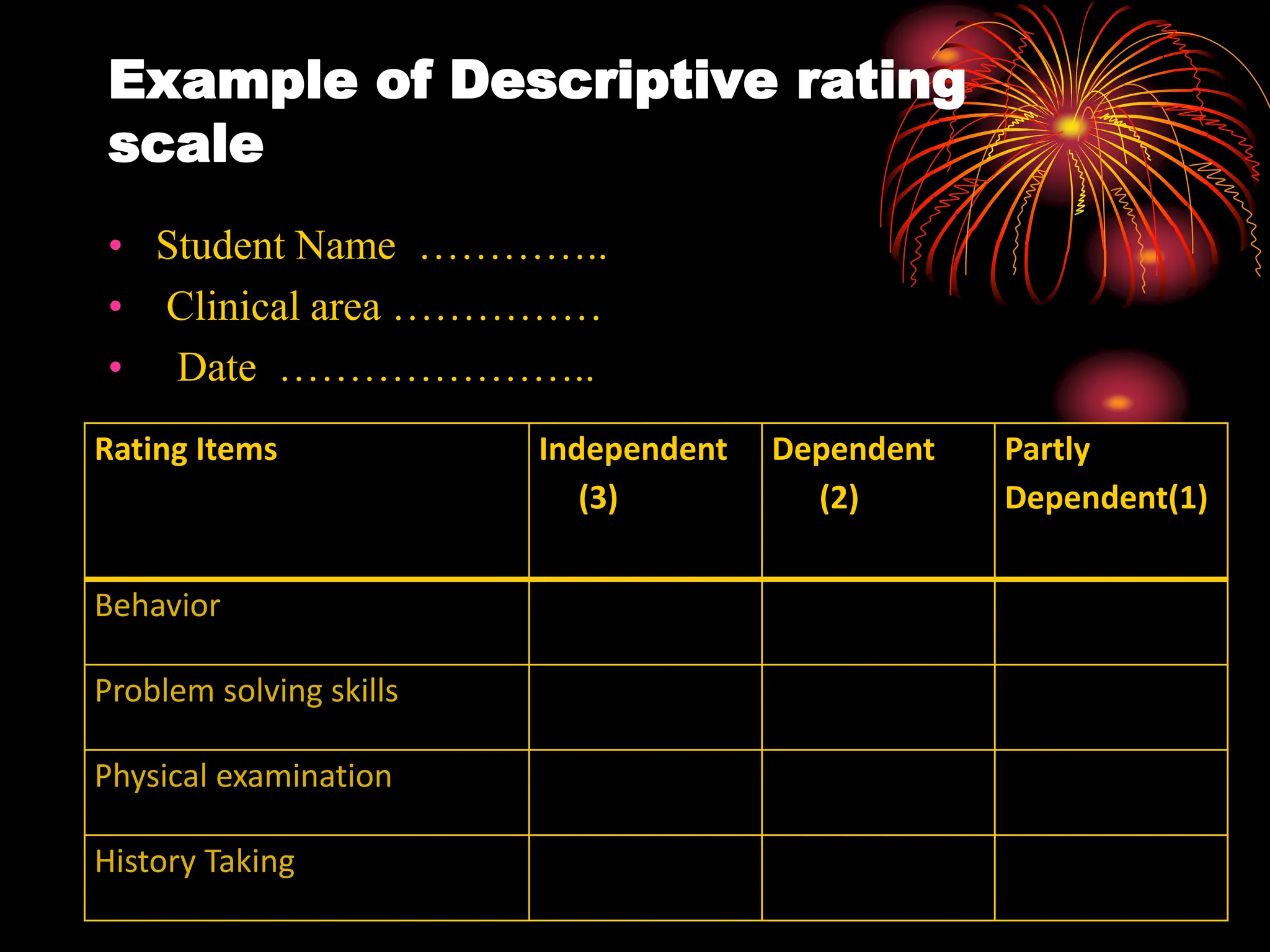
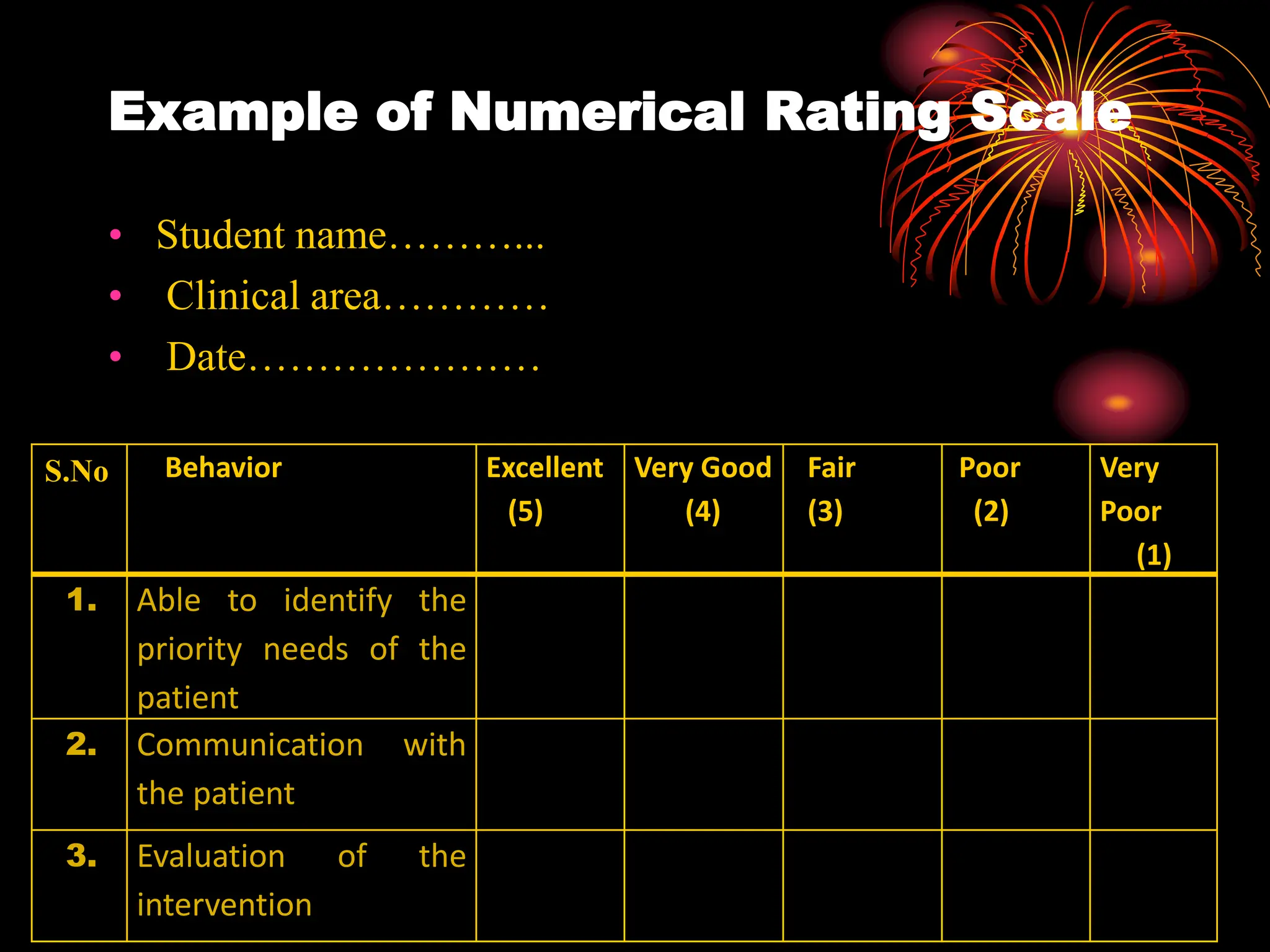
The document discusses checklist and rating scales, which are tools used to evaluate skills. It provides examples of different types of checklists and rating scales. A checklist consists of a list of steps or behaviors to record if they occur, while a rating scale involves rating individuals on a scale from low to high for a particular trait. The document outlines the key types of rating scales, including descriptive, numerical, and graphic scales. It discusses best practices for developing checklists and rating scales, such as using clear language and trained raters, and notes they can be used to evaluate skills, outcomes, activities, interests and attitudes.