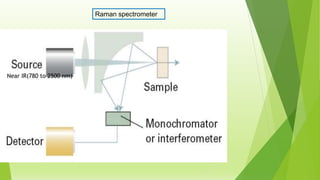
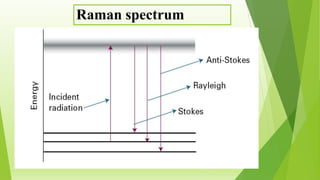
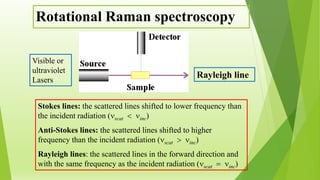
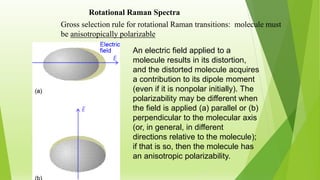
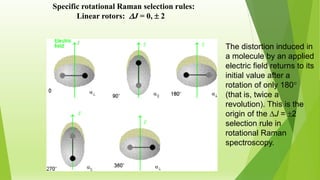
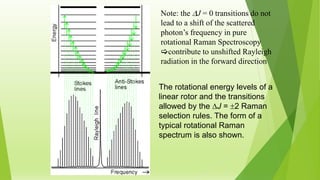
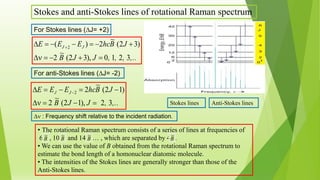
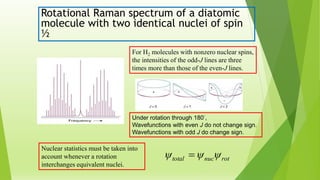
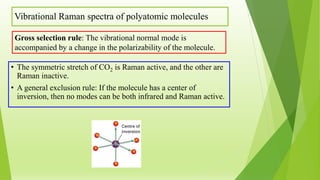
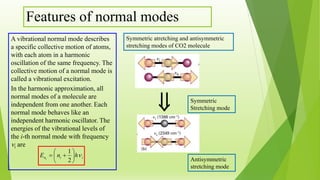
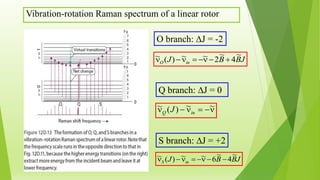
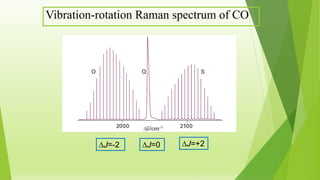
Raman spectroscopy analyzes the scattering of electromagnetic radiation by molecules and materials. It can provide information about molecular vibrations, rotations, and bond characteristics. Raman spectra contain peaks corresponding to Stokes lines at lower frequencies and anti-Stokes lines at higher frequencies relative to the incident radiation. Rotational Raman spectroscopy of linear molecules follows selection rules of ΔJ = 0, ±2. Vibrational Raman spectroscopy requires a change in molecular polarizability during vibration.