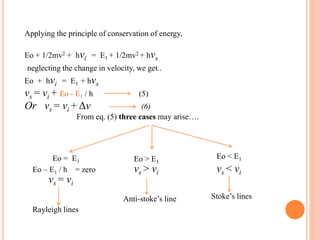
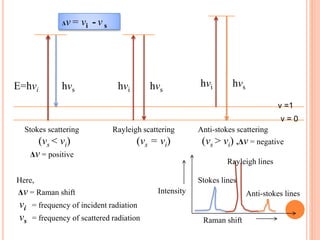
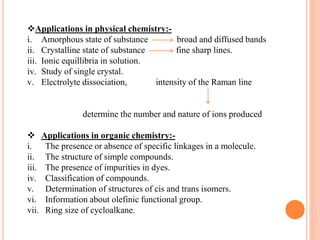
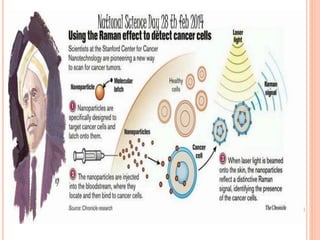
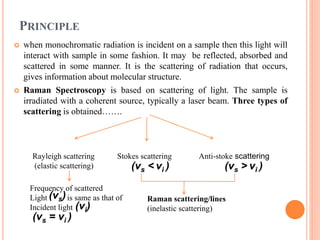
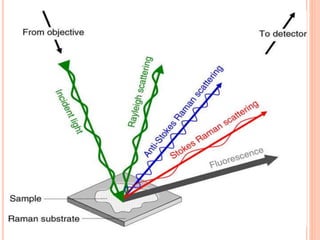
Raman spectroscopy is a technique that uses lasers to study vibrational, rotational, and other low-frequency modes in a system. When light interacts with molecules, the light may be scattered at different wavelengths than the incident laser. This shift in wavelength provides information about molecular structure and symmetry. Raman spectroscopy can be used to examine inorganic, organic, and polymeric materials, determine molecular structure and interactions, and study chemical reactions and physical transformations.






![Mechanism of Raman effect:-
Mechanism of Raman effect is explained by two theories such as,
(1) Classical Theory of Raman Effect
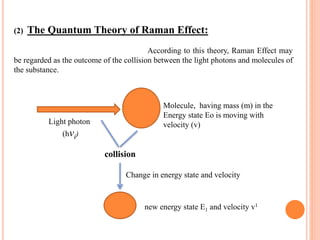
(2)Quantum Theory of Raman Effect
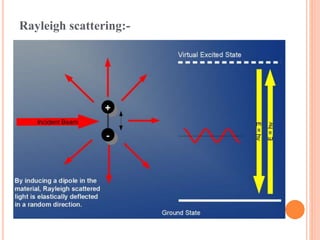
(1) The Classical Theory of Raman Effect:-
Electric field (E) is applied to a molecule
[visible light(electromagnetic light)]
( E,B) electrons and nuclei are displaced
induced dipole moment (μ) produced
polarisation
Polarizability:-
when electric field is applied to molecule,then the ease with
which molecule get polarised.
molecule under
study
get polarised](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ramanspectroscopy-190923141751/85/Raman-spectroscopy-17-320.jpg)
![μ E here, E= applied electric field
μ = α E (1) μ = induced dipole moment
α is polarizability
E = Eo Sin2 πνt (2)
μ = α Eo Sin2πνt (3)
by applying electric field ,induced dipole moment produced and as a result
polarisability produced.
α = αo+(d α/dQ) Sin2πνvt (4)
αo = constant (amplitude)
d α/dQ = change in polarizability w.r.t. Coordinanat
Substituting eq. (4) in eq. (3)….
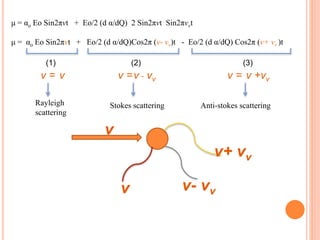
μ = [αo+(d α/dQ) Sin2πνvt ]Eo Sin2πνt
μ = αo Eo Sin2πνt + Eo/2 (d α/dQ) 2 Sin2πνt Sin2πνvt
by applying formula ( 2SinASinB = Cos(A-B) – Cos(A+B) )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ramanspectroscopy-190923141751/85/Raman-spectroscopy-18-320.jpg)