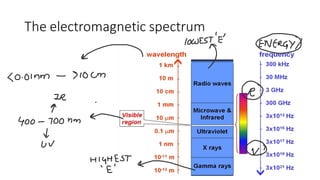
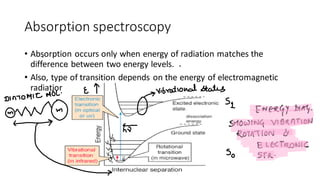
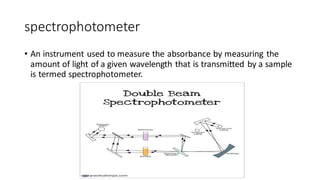
This document discusses spectroscopy techniques, specifically atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS). It begins by explaining the electromagnetic spectrum and photon interactions with matter. It then describes different types of spectroscopy including absorption, fluorescence, and phosphorescence. Beer-Lambert law is introduced which states that absorbance is directly proportional to concentration. Instrumental components of a spectrophotometer such as light sources, monochromators, sample holders, and detectors are outlined. The principles of atomic absorption spectroscopy are explained including hollow cathode lamps and atomic excitation. Advantages of AAS compared to atomic emission spectroscopy are provided.