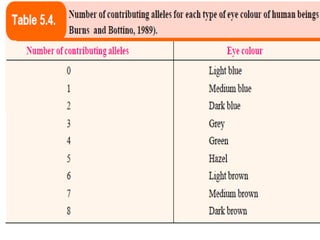
This document discusses polygenic or quantitative inheritance, where multiple genes each have a small effect on a trait, resulting in continuous variation in phenotypes. Key points:
- Traits like height, weight, eye color are polygenic, with no clear boundaries between types.
- The multiple factor hypothesis proposes that multiple genes, each with small effects, combine to produce quantitative variation in traits.
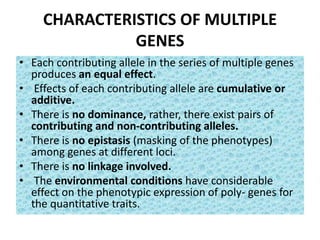
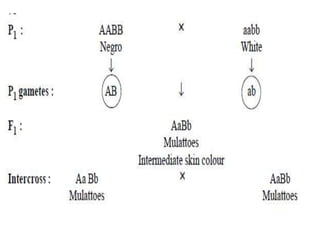
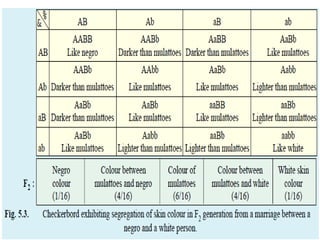
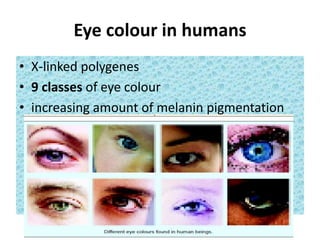
- Characteristics of polygenic traits include each gene having an additive, cumulative effect and no dominance or epistasis between genes. Environmental factors also influence phenotypic expression. Examples of polygenic traits in humans are skin and eye color.