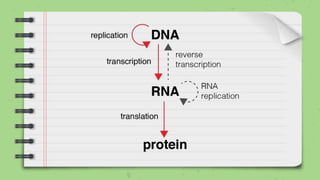
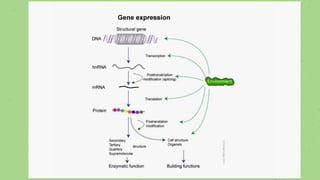
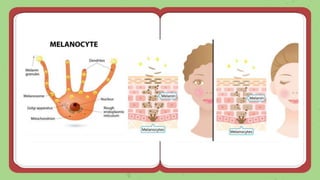
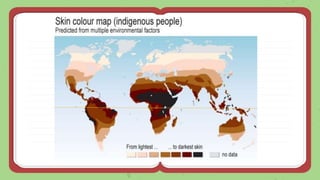
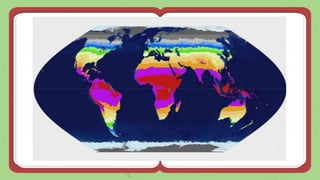
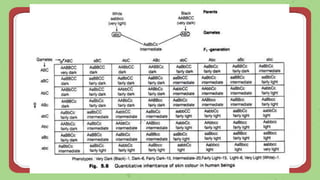
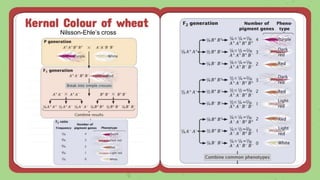
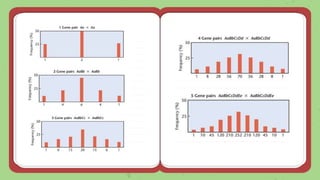
This document discusses quantitative inheritance, which refers to inheritance of traits that are influenced by multiple genes and the environment. Quantitative traits show continuous variation and are influenced by small effects from many genes. Examples discussed include human height, skin color, and kernel color in wheat. The kernel color experiment of Nilsson-Ehle is used to demonstrate quantitative inheritance. It involved crossing two wheat varieties and analyzing the ratios of kernel color phenotypes in the offspring. For the experiment to work well, the genes influencing color needed to have additive effects and the environment could not impact phenotypes. The experiment helped establish that quantitative traits are influenced by multiple independent gene loci.