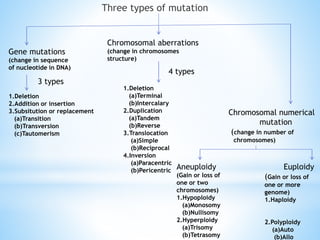
This document discusses five major factors that affect genetic equilibrium: 1) Mutations, which create genetic variations, 2) Recombinations during sexual reproduction, which reshuffle genes, 3) Genetic drift, or random changes in allele frequencies influenced by population size, 4) Gene migration between populations, and 5) Natural selection, which causes populations to adapt over generations as traits better suited to the environment are selected for. It provides details on each factor, including types of mutations, the mechanisms of recombination, how genetic drift is influenced by population bottlenecks and founder effects, and gives an example of natural selection producing giraffe's long neck.