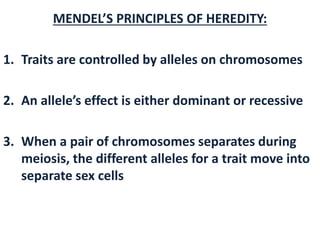
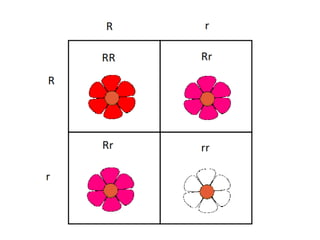
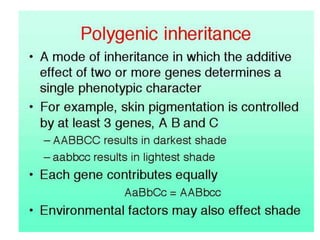
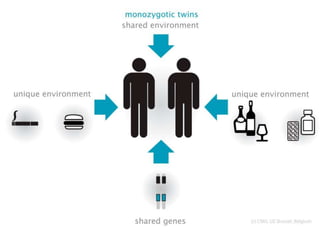
This document summarizes key concepts in heredity and genetics. It explains that heredity is the passing of traits from parents to offspring, and genetics is the study of inheritance. It describes Gregor Mendel's experiments with pea plants that laid the foundations of genetics. His principles of heredity established that traits are controlled by alleles, which can be dominant or recessive. The document also explains concepts like genotypes, phenotypes, homozygous and heterozygous traits, and how Punnett squares are used to predict inheritance patterns. It covers incomplete dominance, polygenic traits, and environmental influences on genes. Other topics include mutations, genetic disorders, sex-linked traits, and the use of pedigrees to study