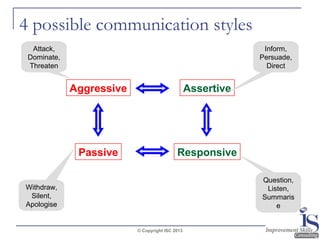
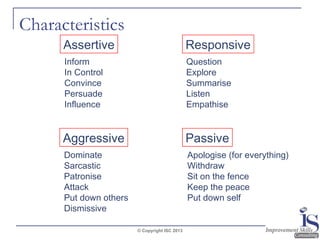
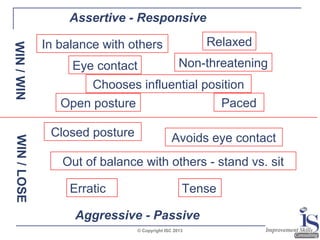
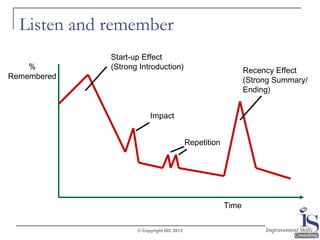
The document outlines effective questioning and listening skills, emphasizing the importance of active listening and understanding communication styles. It differentiates between listening and hearing, presents techniques for effective listening, and suggests various questioning strategies. Key skills include maintaining open body language, using verbal cues, and appropriately responding to maintain engagement during conversations.