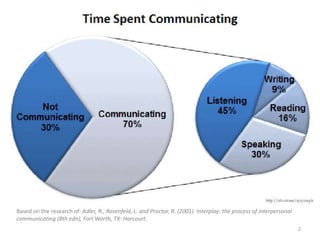
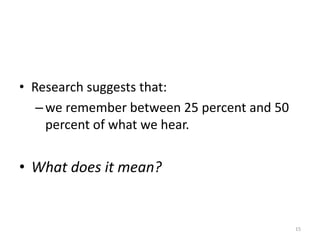The document discusses the importance of listening in communication, emphasizing that effective listening is a critical skill that significantly impacts job effectiveness and relationships. It outlines three modes of listening—competitive, passive, and active—highlighting active listening as the most beneficial, which enhances productivity, reduces misunderstandings, and fosters cooperation. Additionally, it provides practical tips for improving listening skills, such as maintaining eye contact and minimizing distractions.