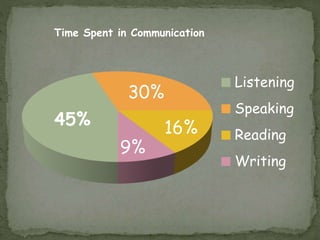
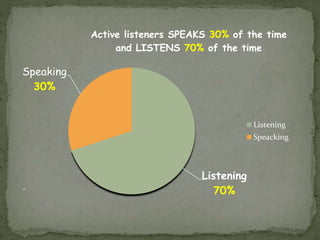
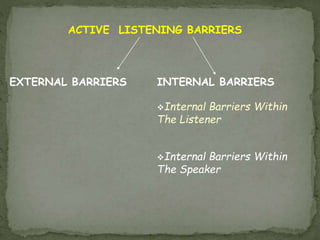
The document discusses listening as the most important communication skill. It notes that people spend 45% of communication time listening, more than any other skill. Active listening is defined as listening to understand rather than just hearing and involves paying attention, adjusting your understanding, and responding appropriately. Barriers to active listening include internal factors like preconceptions and external distractions. The document outlines steps to active listening like paraphrasing, checking understanding, and providing feedback. Overall, active listening is presented as a crucial skill for effective communication.