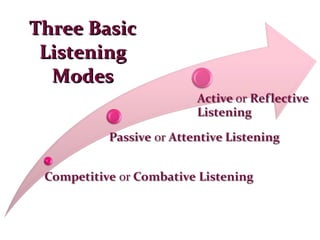
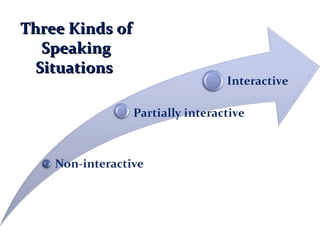
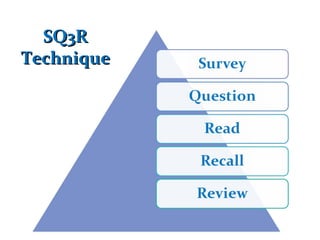
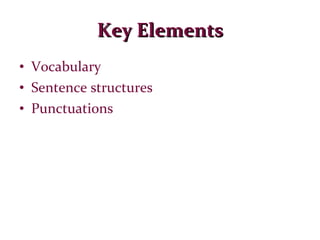
This document provides an overview of communication skills, including definitions of communication, the key elements of listening, speaking, reading and writing. It discusses active listening and its five key elements. It also outlines techniques for active reading like underlining, note-taking, and the SQ3R method. Key elements of writing like vocabulary, sentence structure and punctuation are mentioned. Finally, it discusses grammar and some common state verbs.













































![Any Queries? You can also contact me at [email_address] Visit our Department’s website: http://sites.google.com/site/englishdepartmentvoccollege/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/communication-skills1814/85/Communication-Skills-57-320.jpg)
