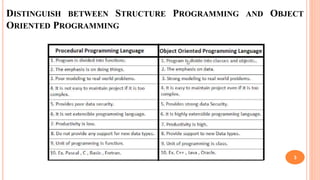
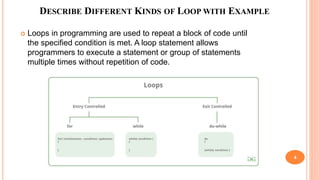
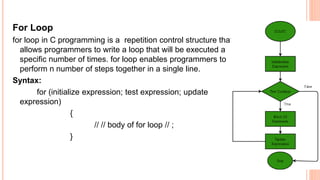
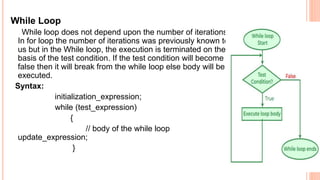
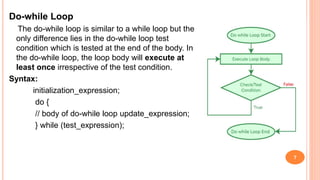
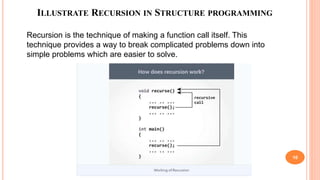
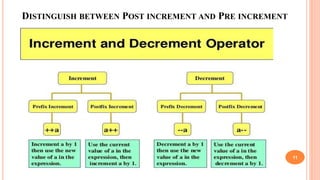
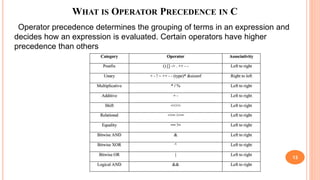
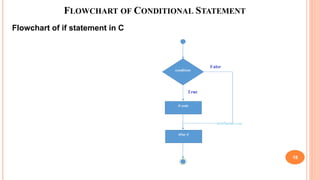
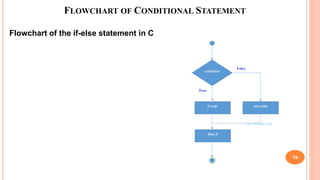
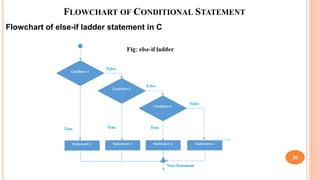
The document outlines the structure programming course at Dhaka International University, focusing on fundamental programming concepts such as structured programming, loops (for, while, do-while), recursion, and operator precedence in C. It includes examples, syntax, and error correction techniques, as well as flowcharts for conditional statements. The course aims to simplify complex programming tasks and improve functionality through structured approaches.