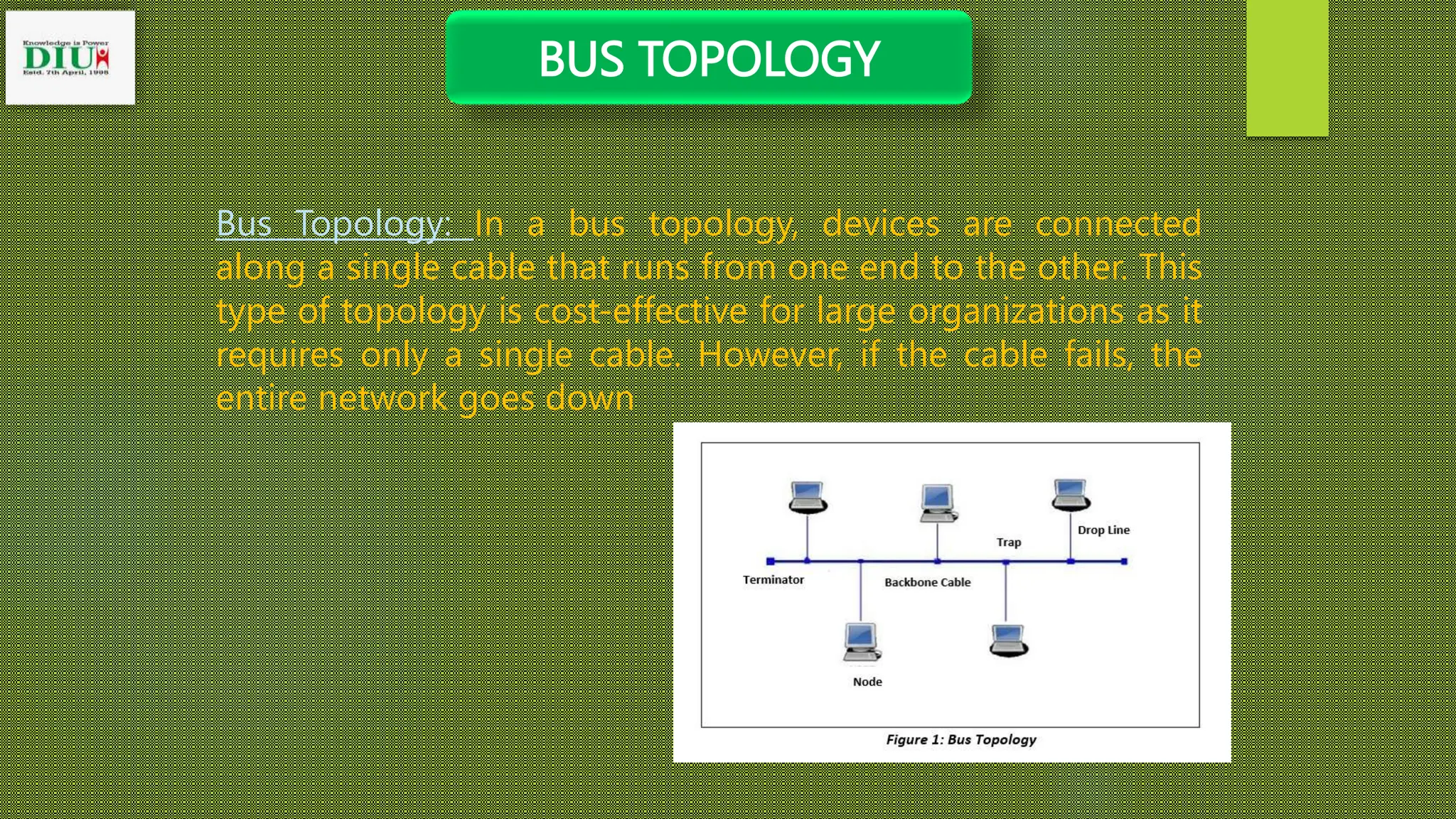
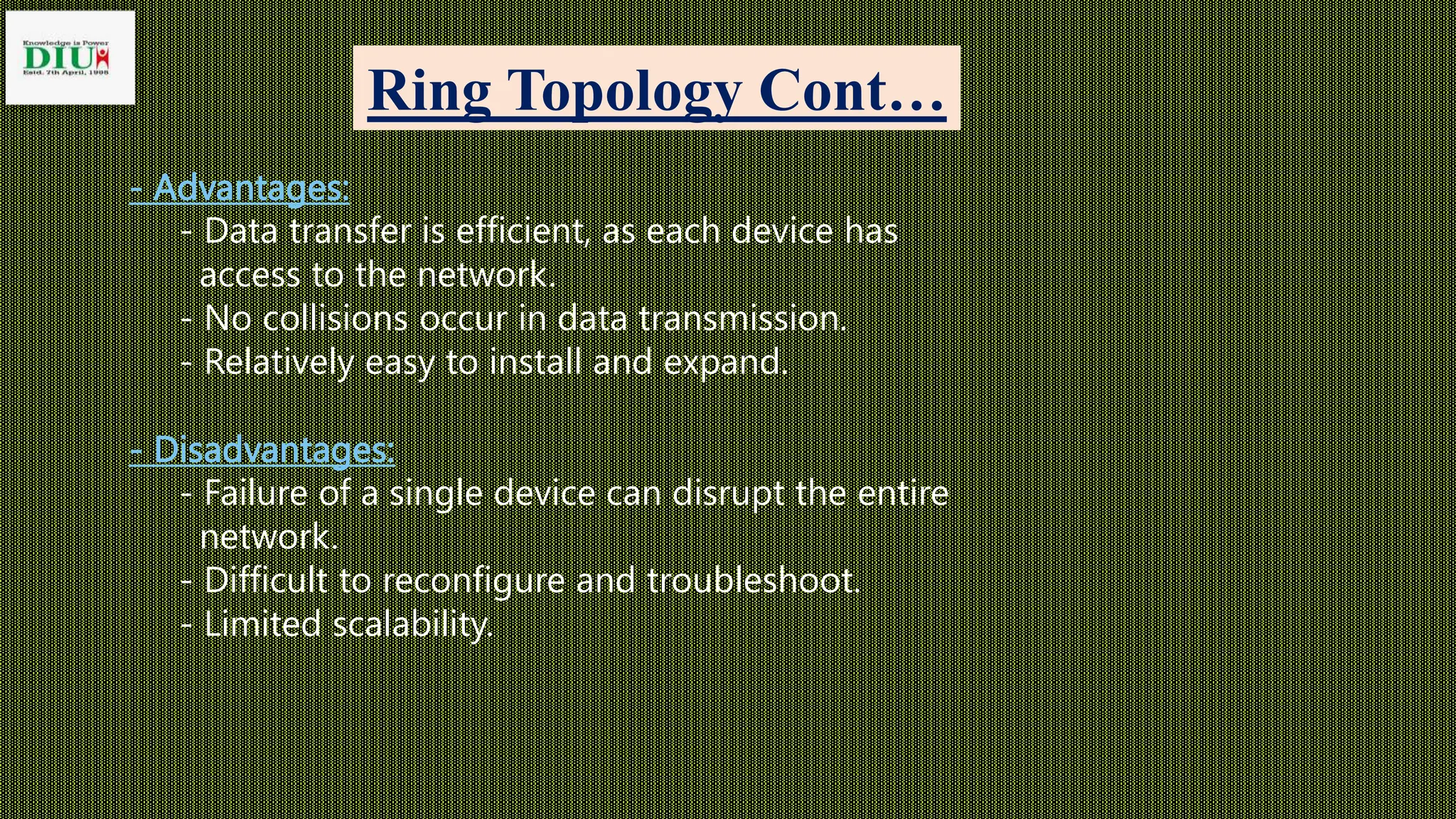
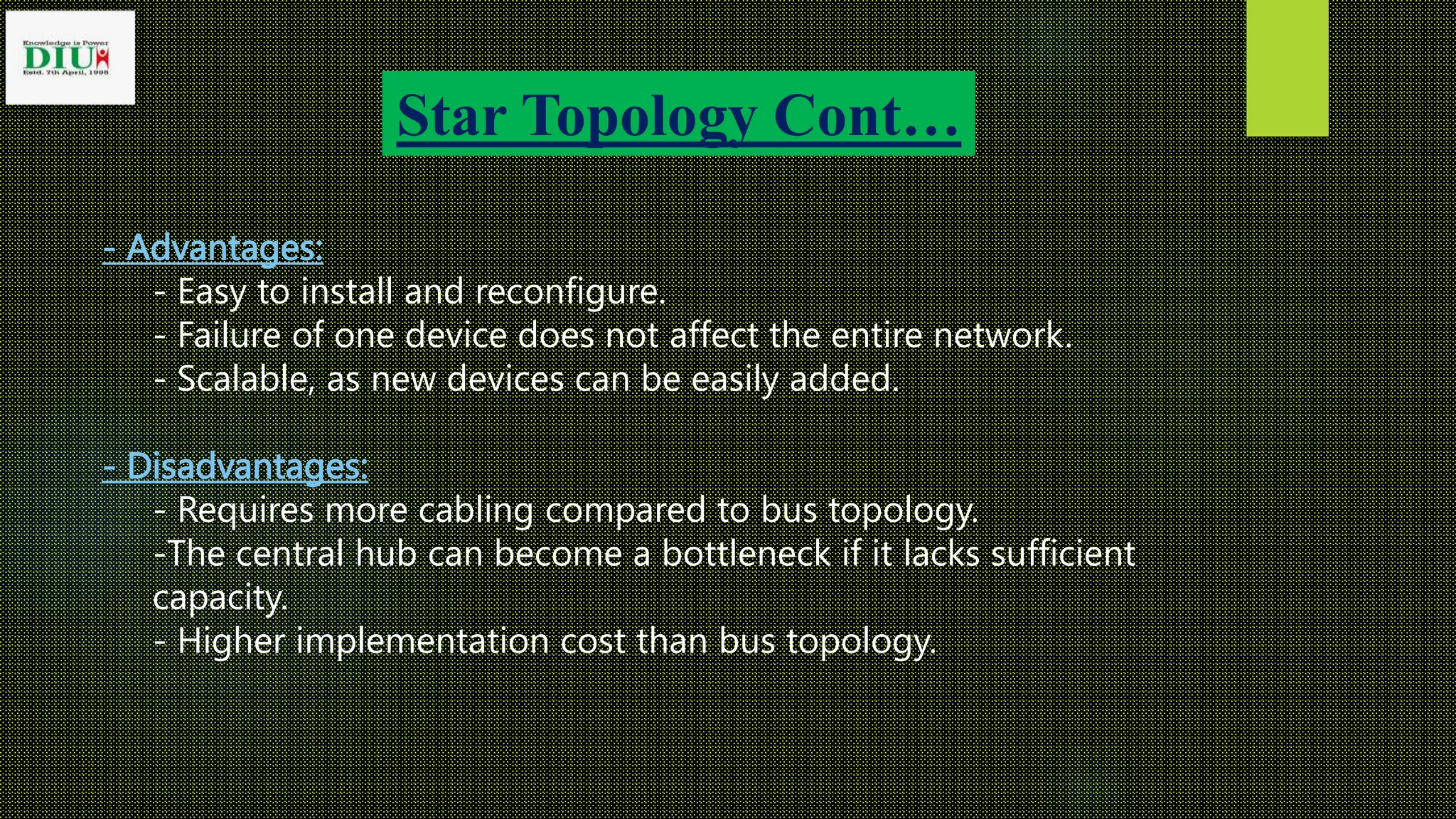
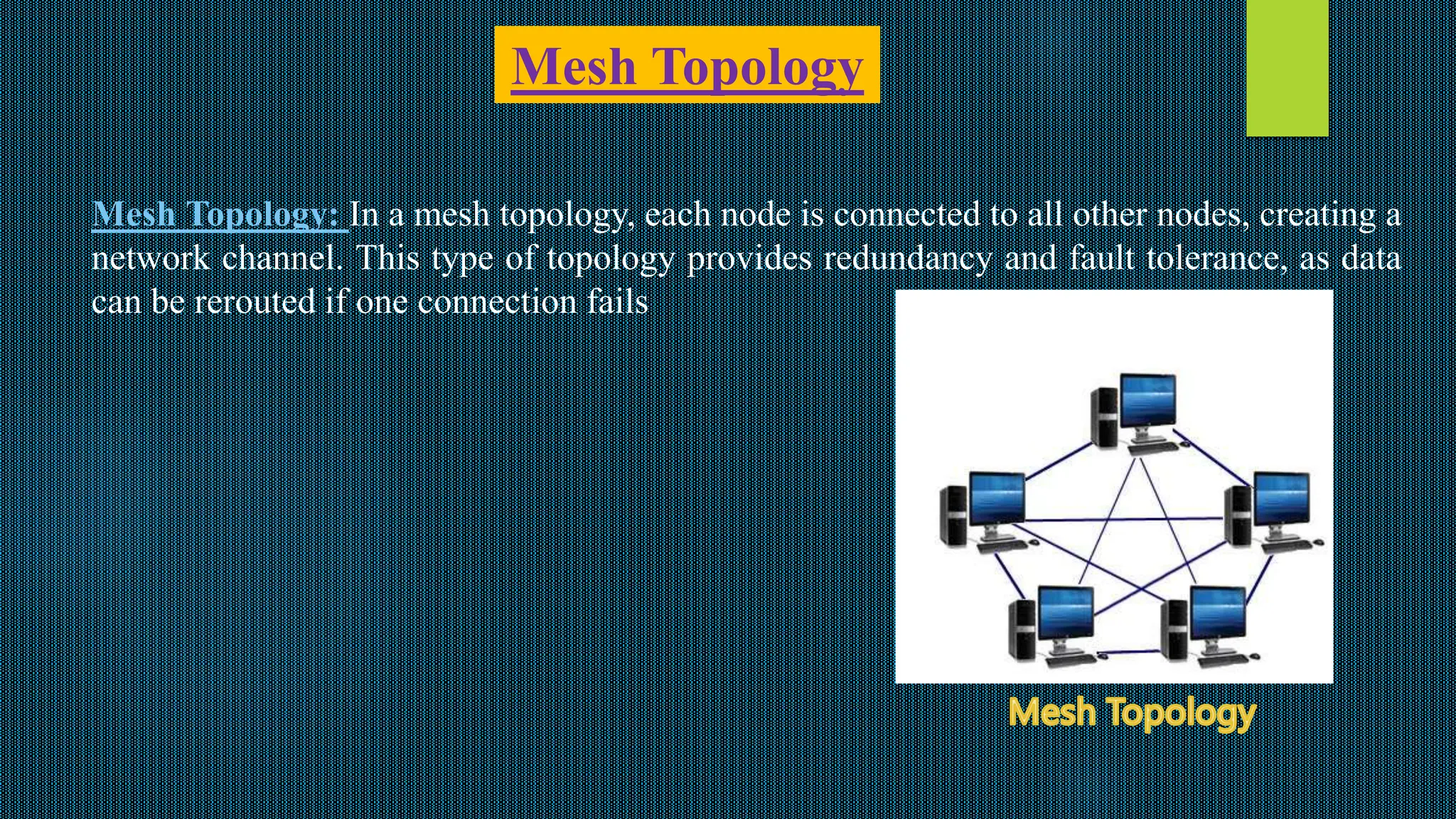
The presentation from Dhaka International University covers various types of network topology, including bus, ring, star, tree, and mesh topologies, detailing their advantages and disadvantages. It emphasizes the importance of understanding network topology for effective design, management, and troubleshooting of networks. The document serves as an educational resource for students in the Fundamentals of Computer course.