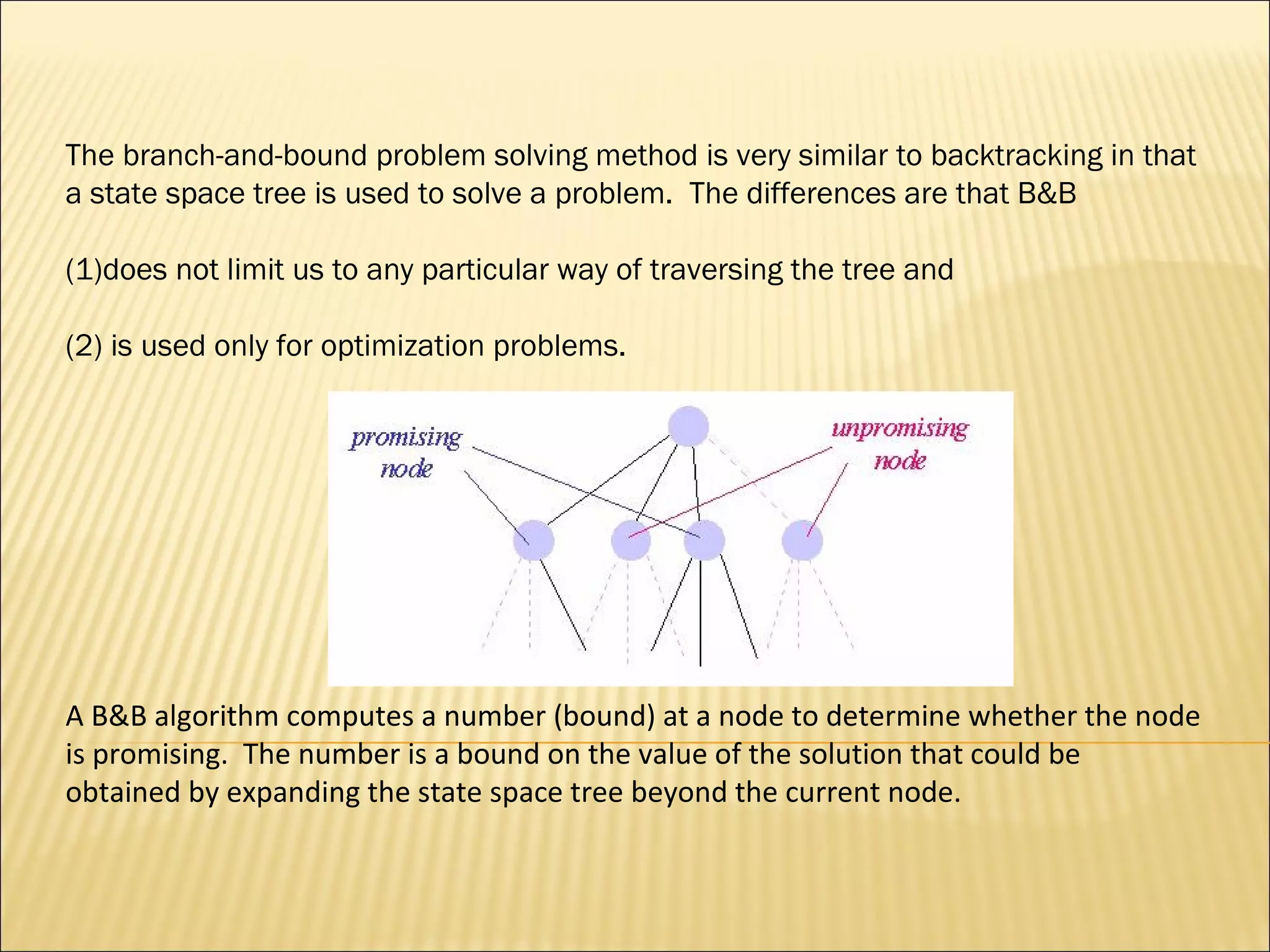
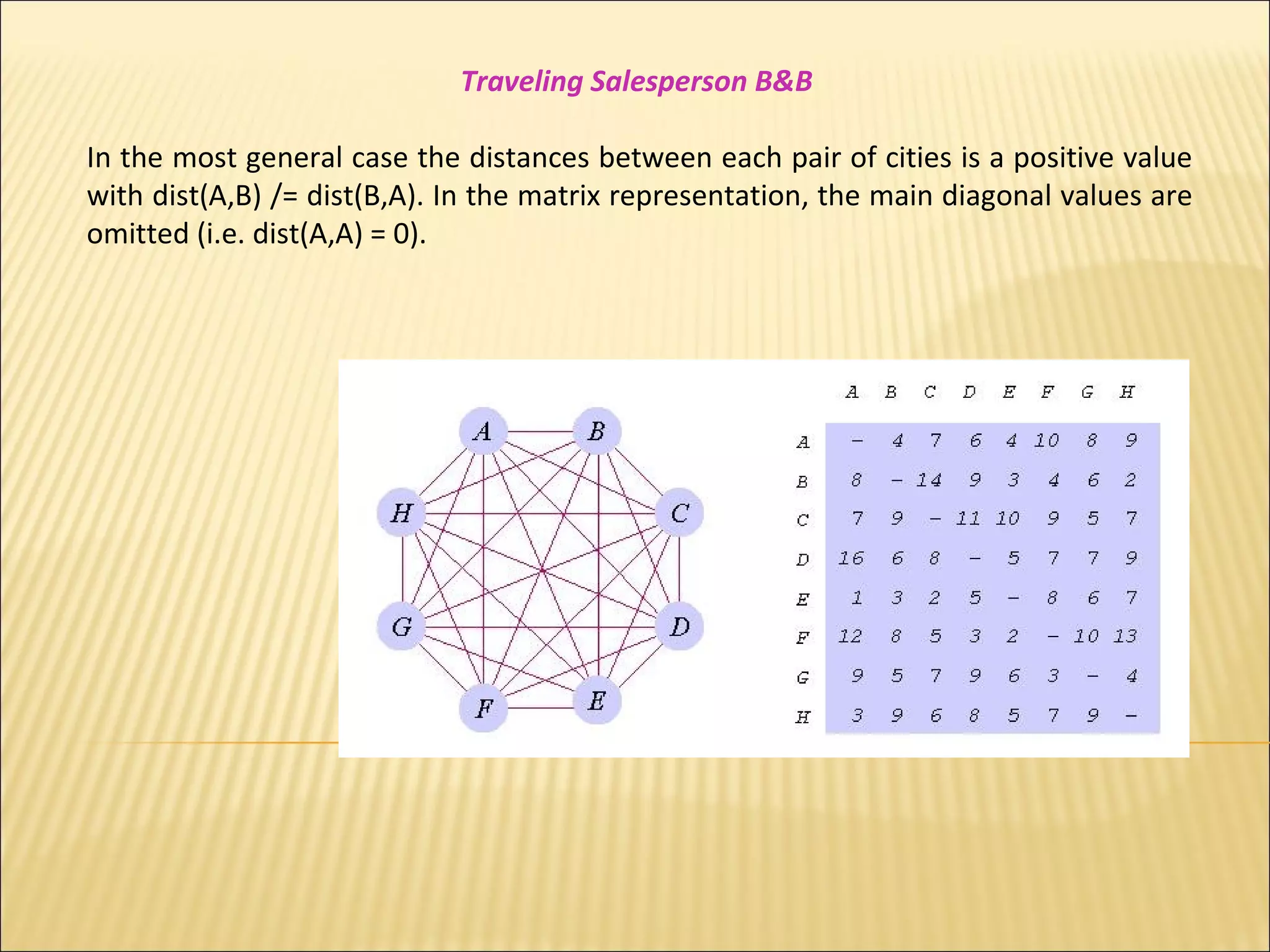
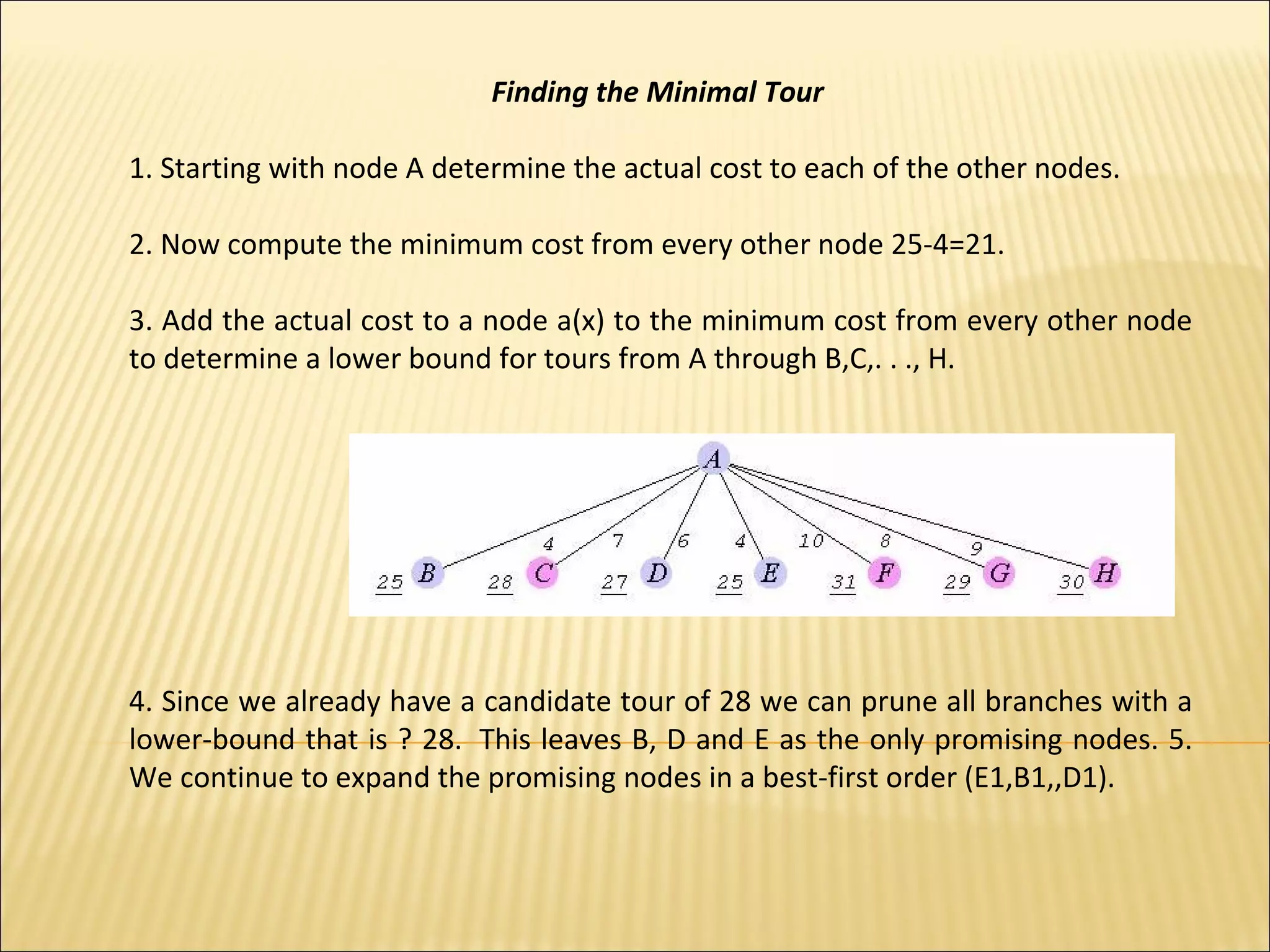
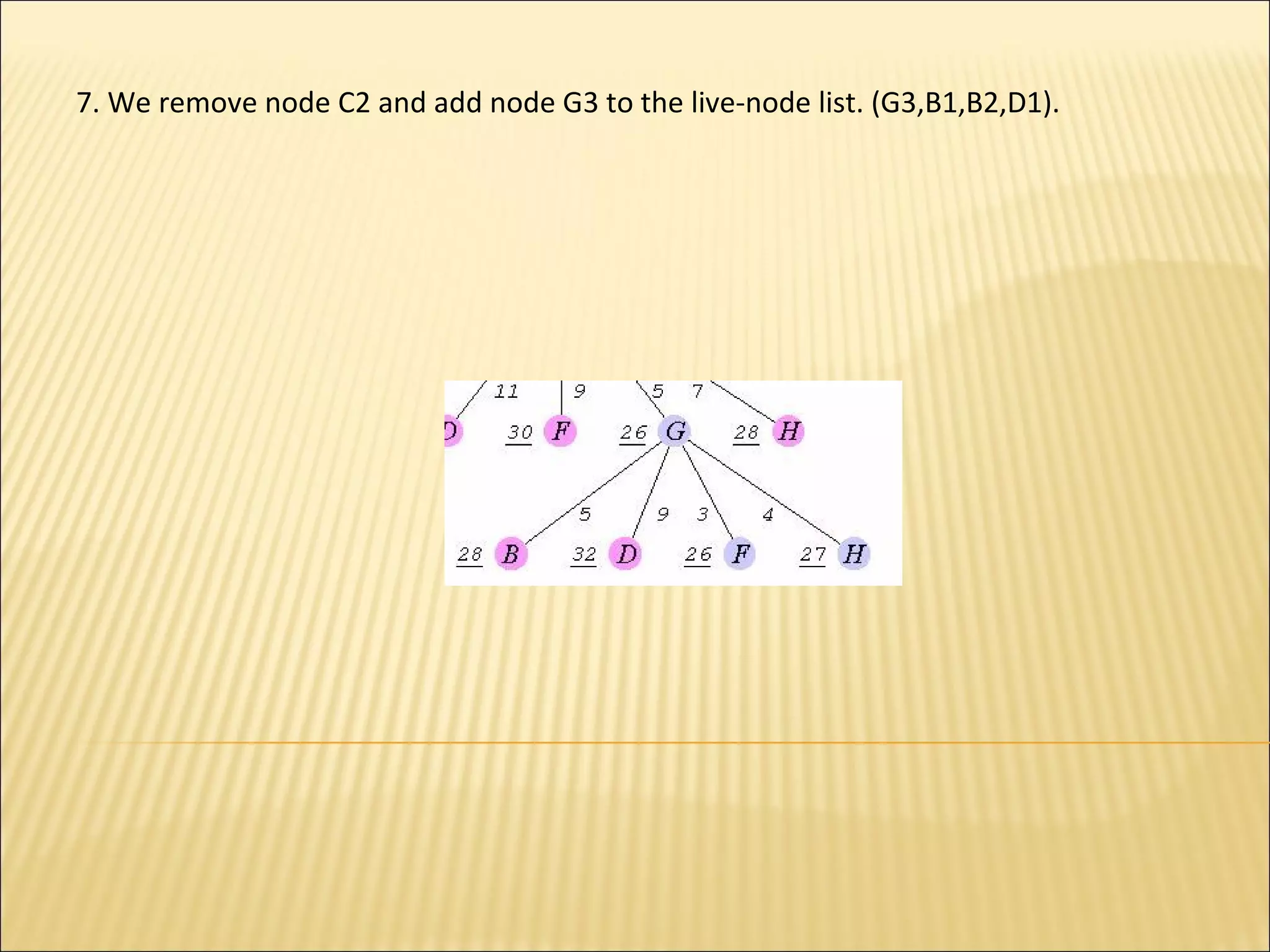
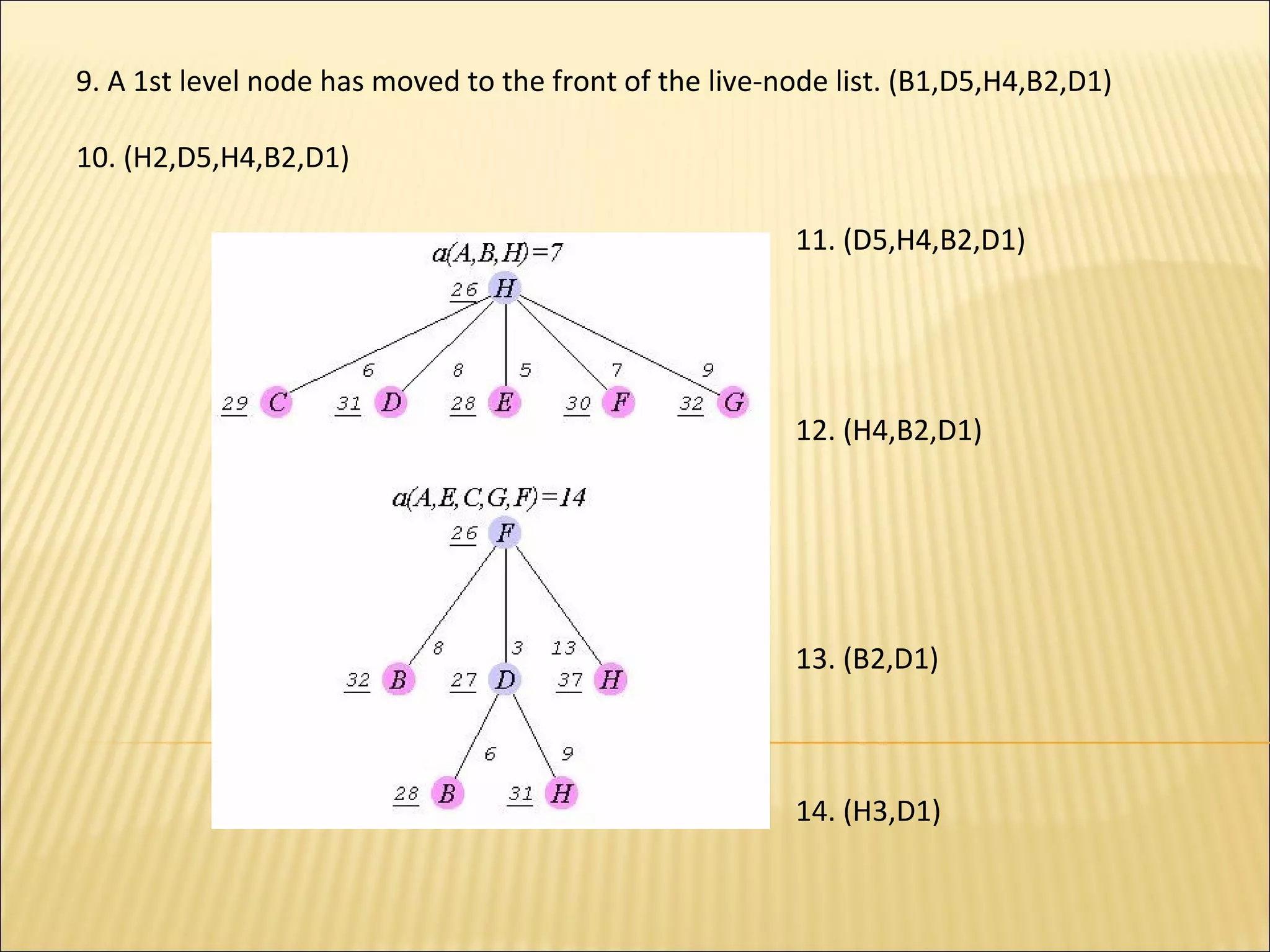
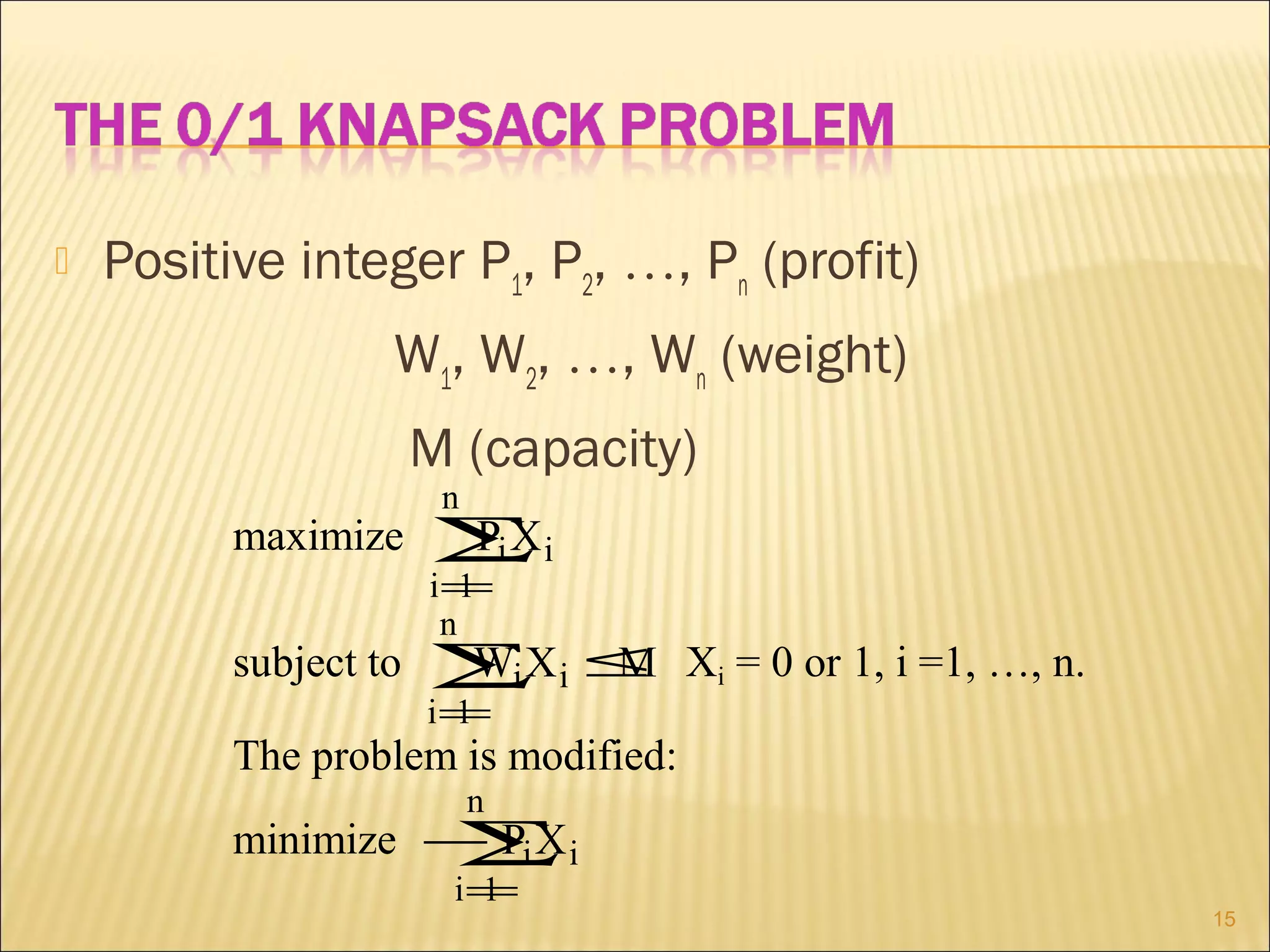
The branch-and-bound method is used to solve optimization problems by traversing a state space tree. It computes a bound at each node to determine if the node is promising. Better approaches traverse nodes breadth-first and choose the most promising node using a bounding heuristic. The traveling salesperson problem is solved using branch-and-bound by finding an initial tour, defining a bounding heuristic as the actual cost plus minimum remaining cost, and expanding promising nodes in best-first order until finding the minimal tour.