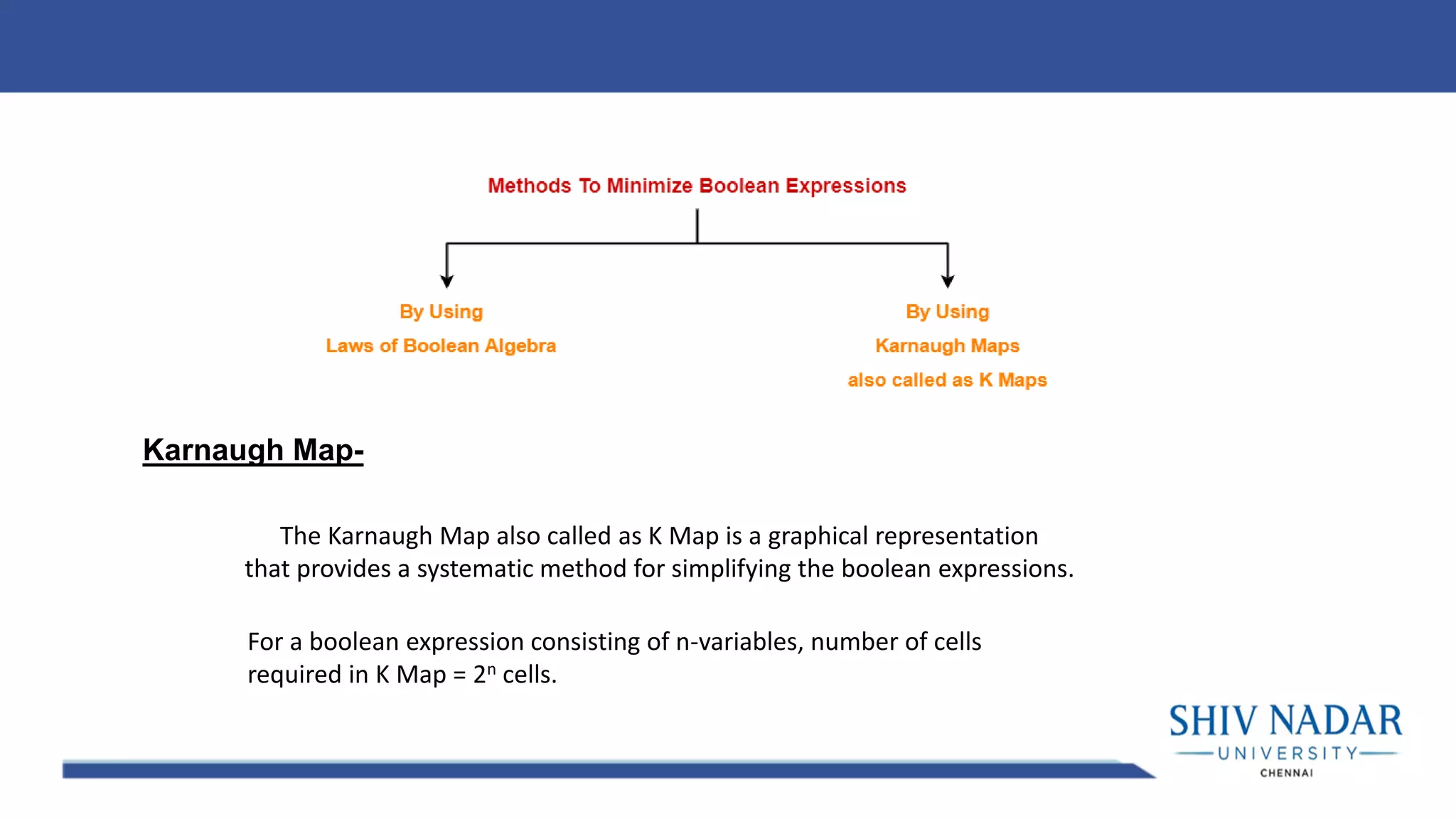
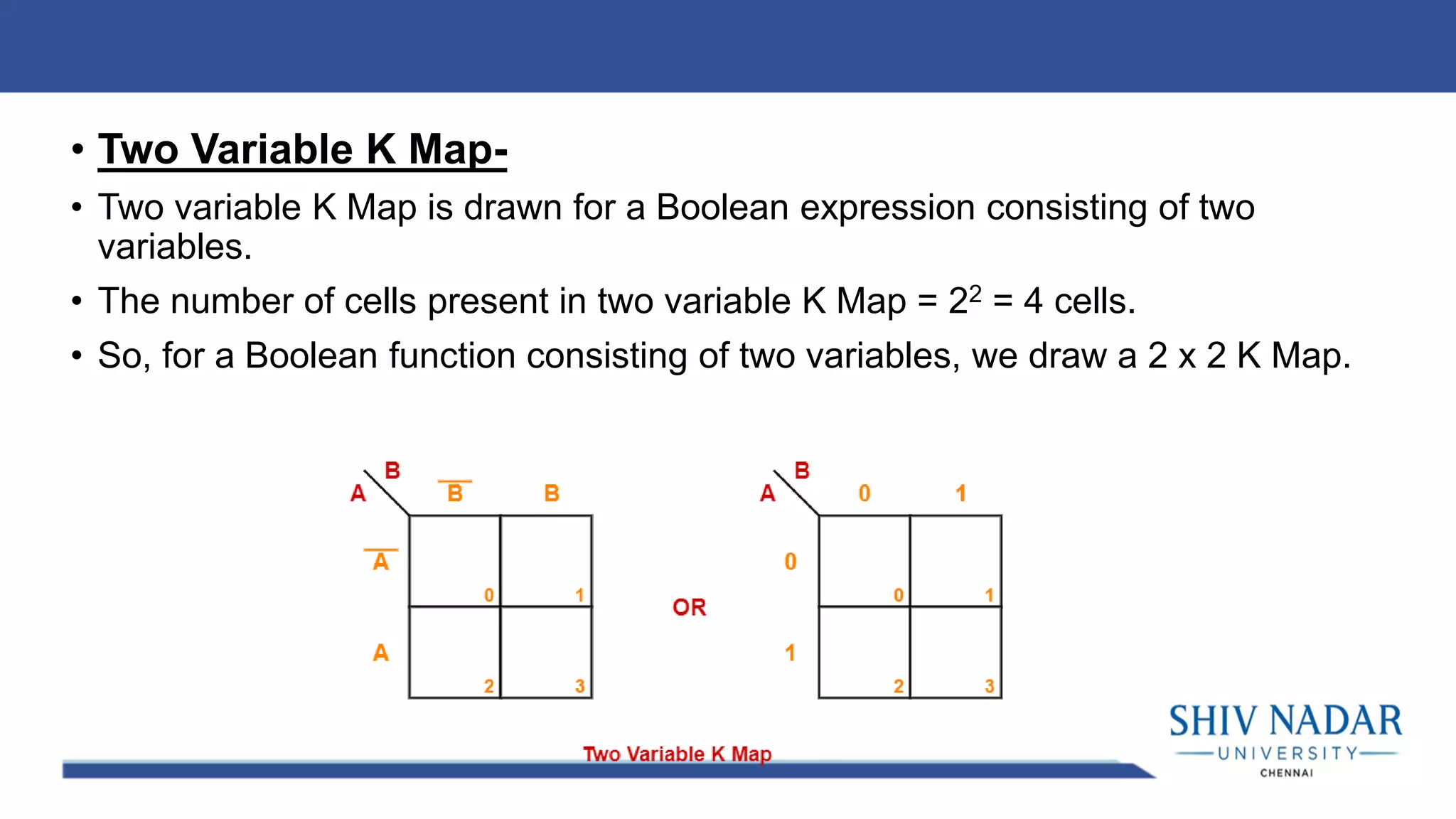
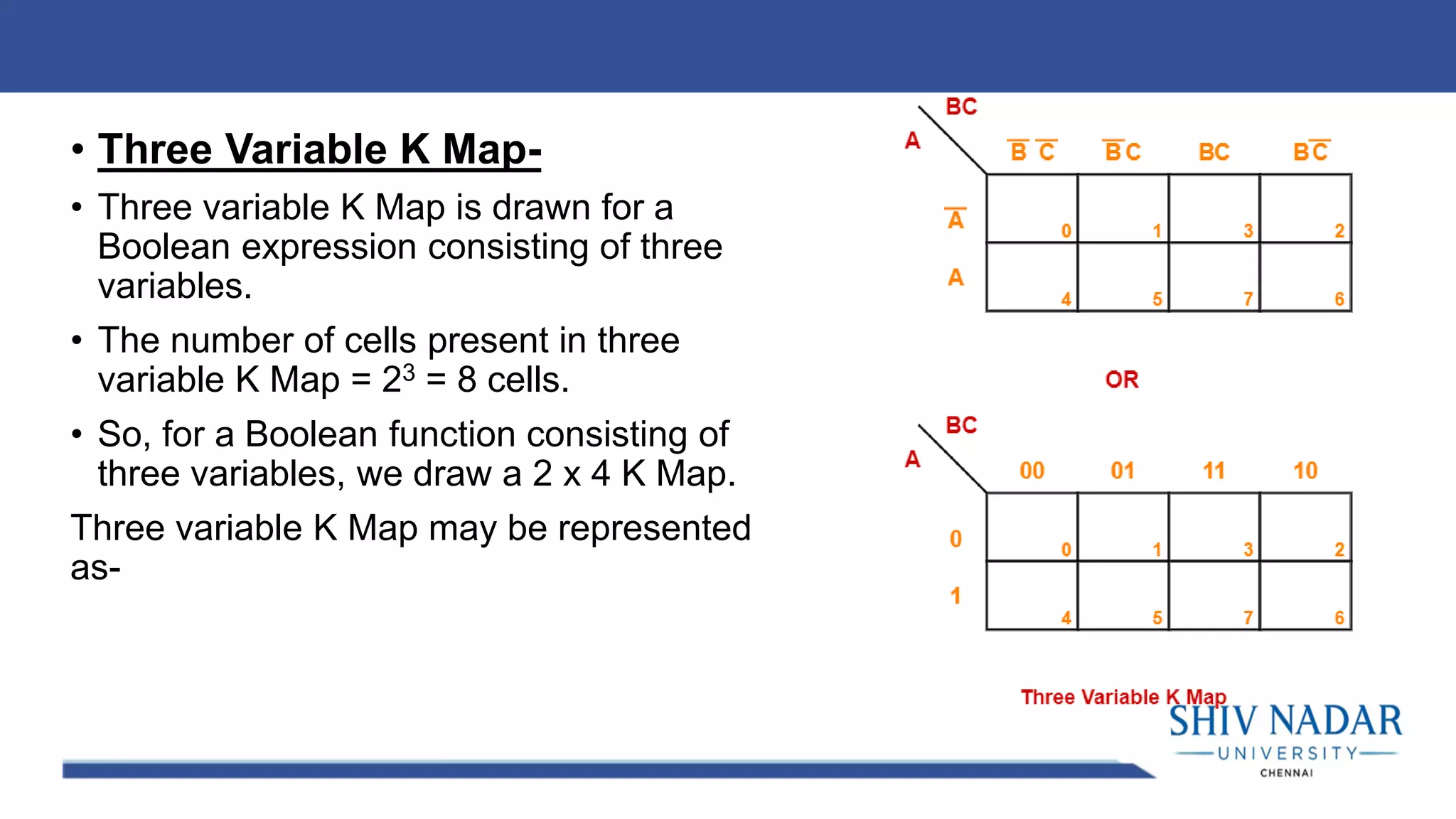
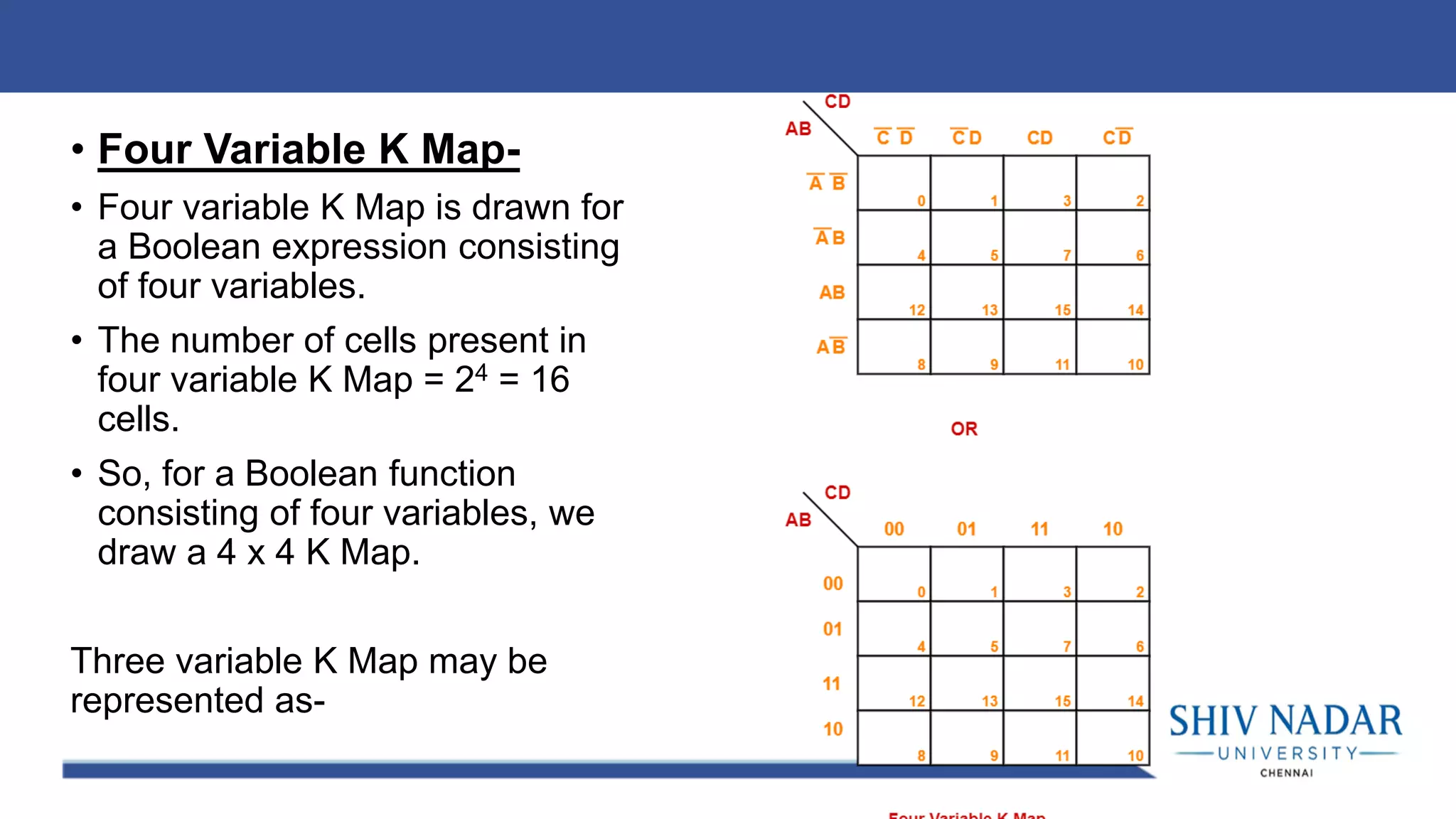
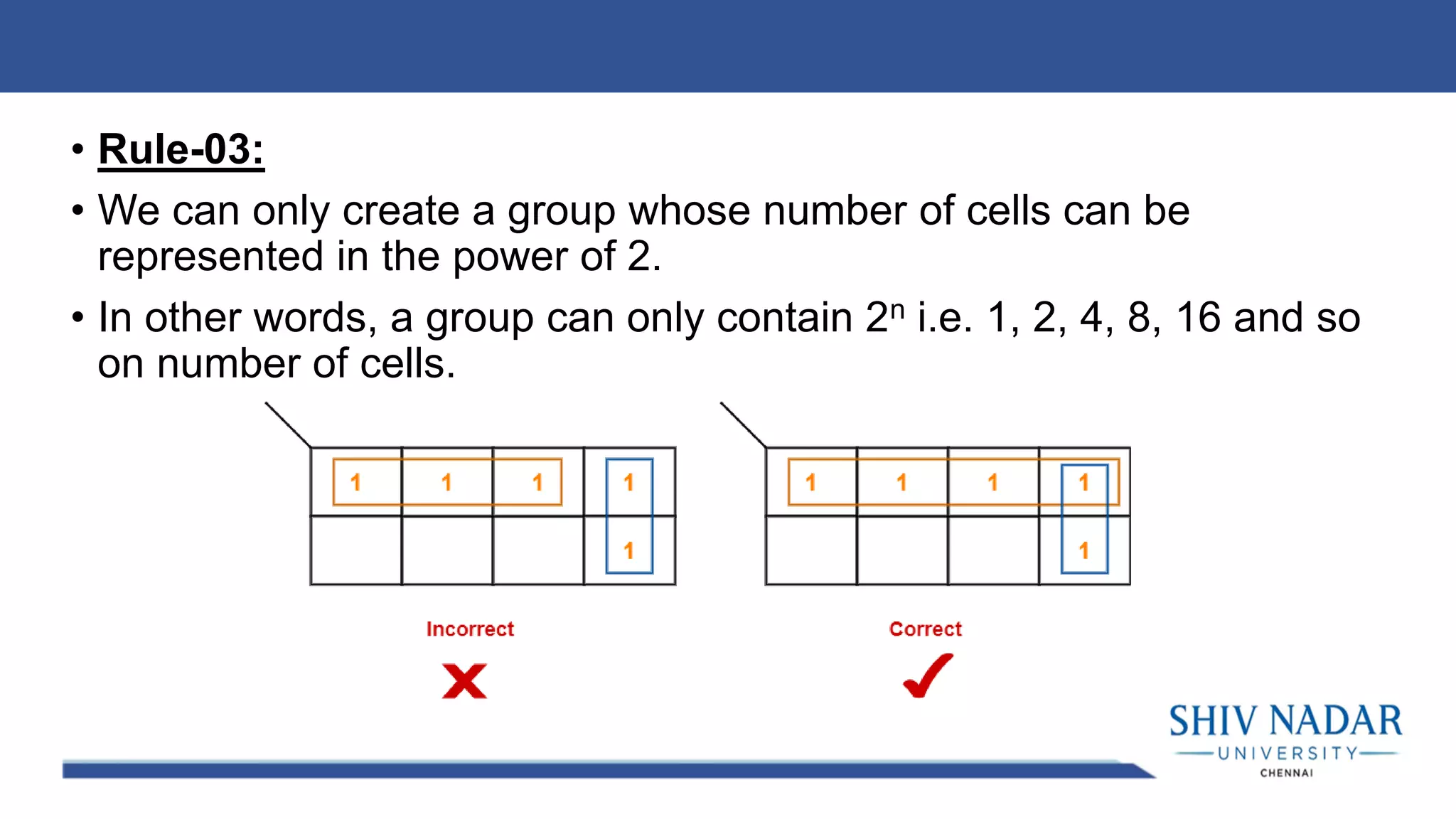
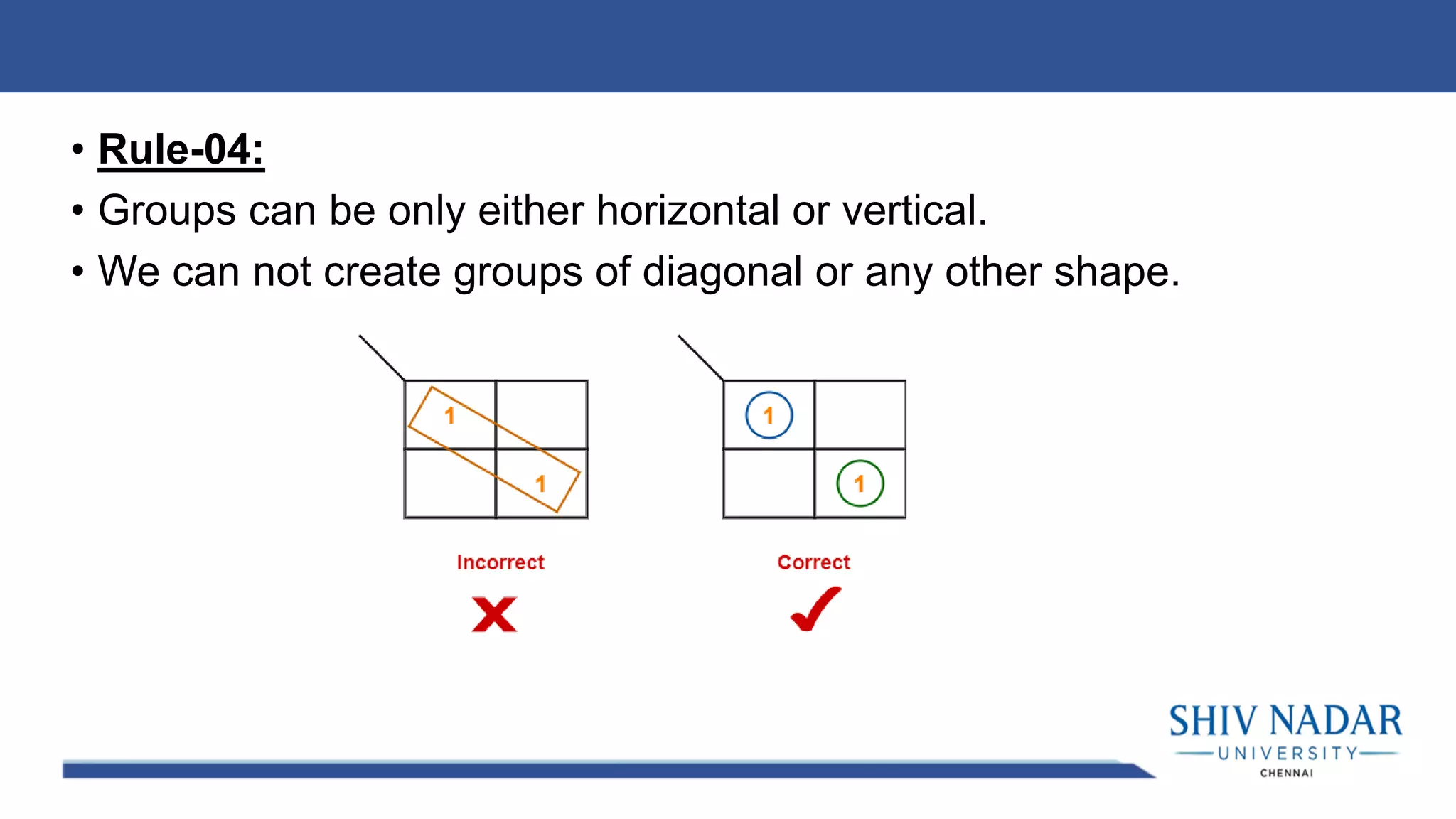
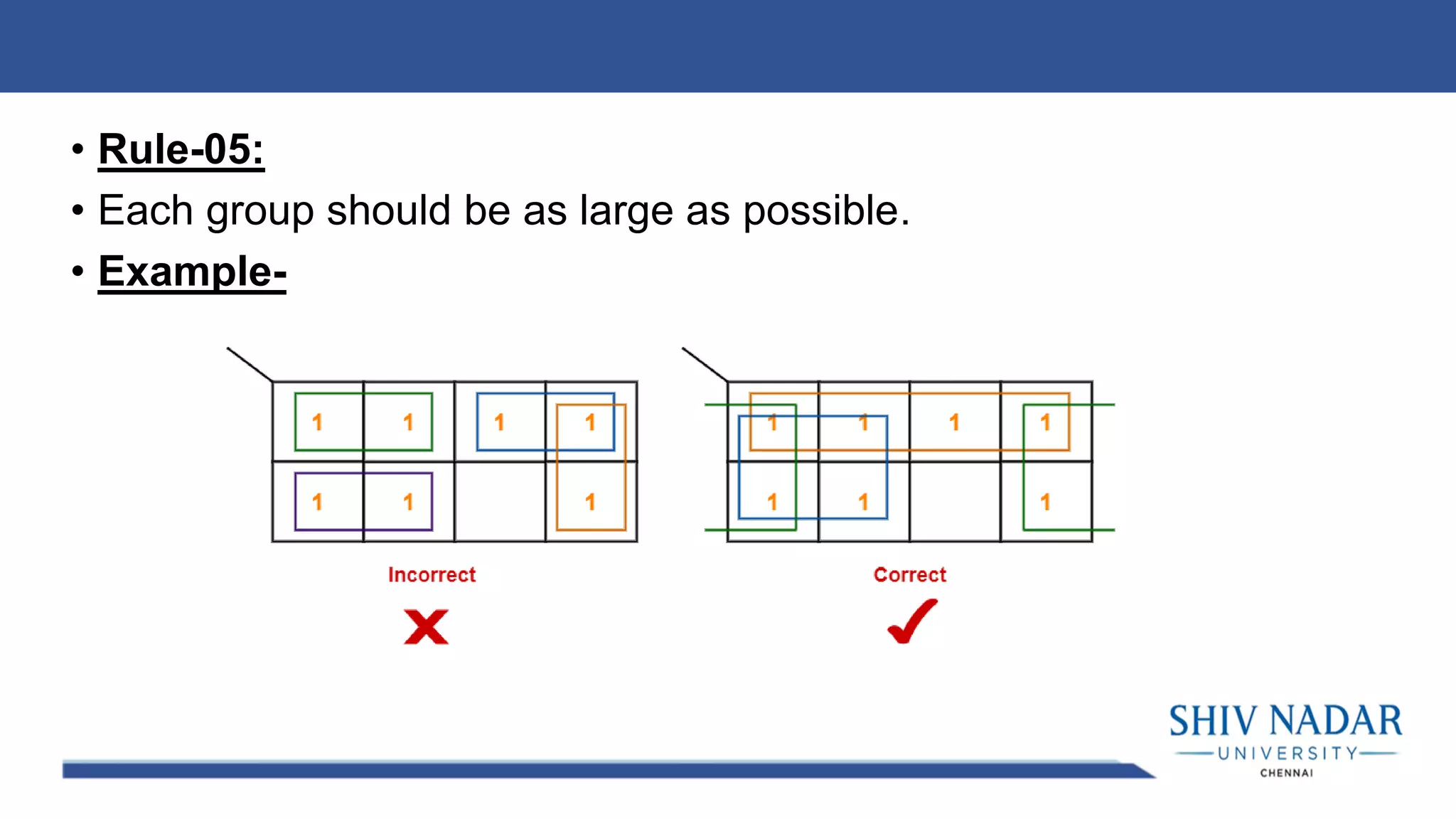
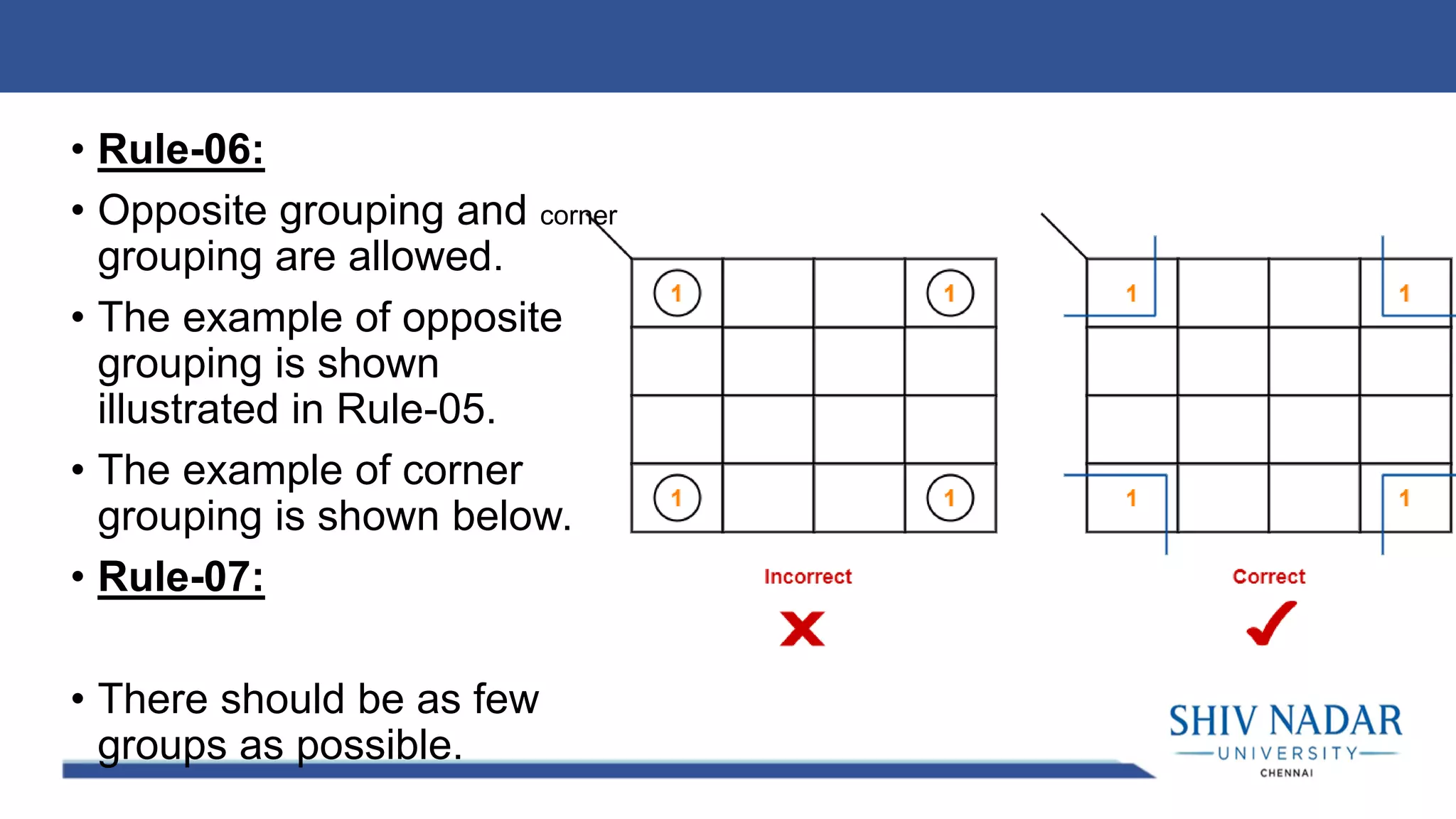
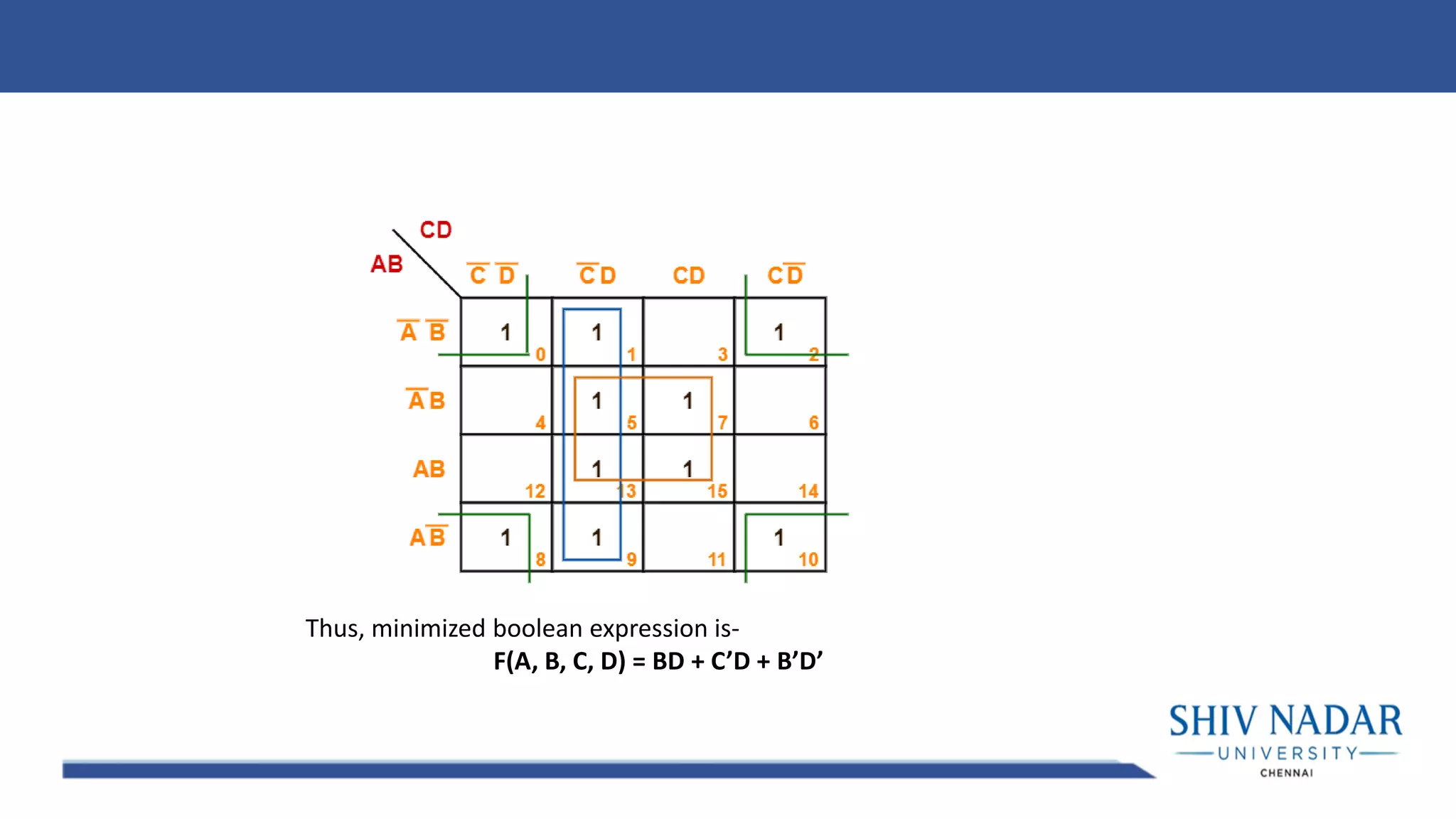
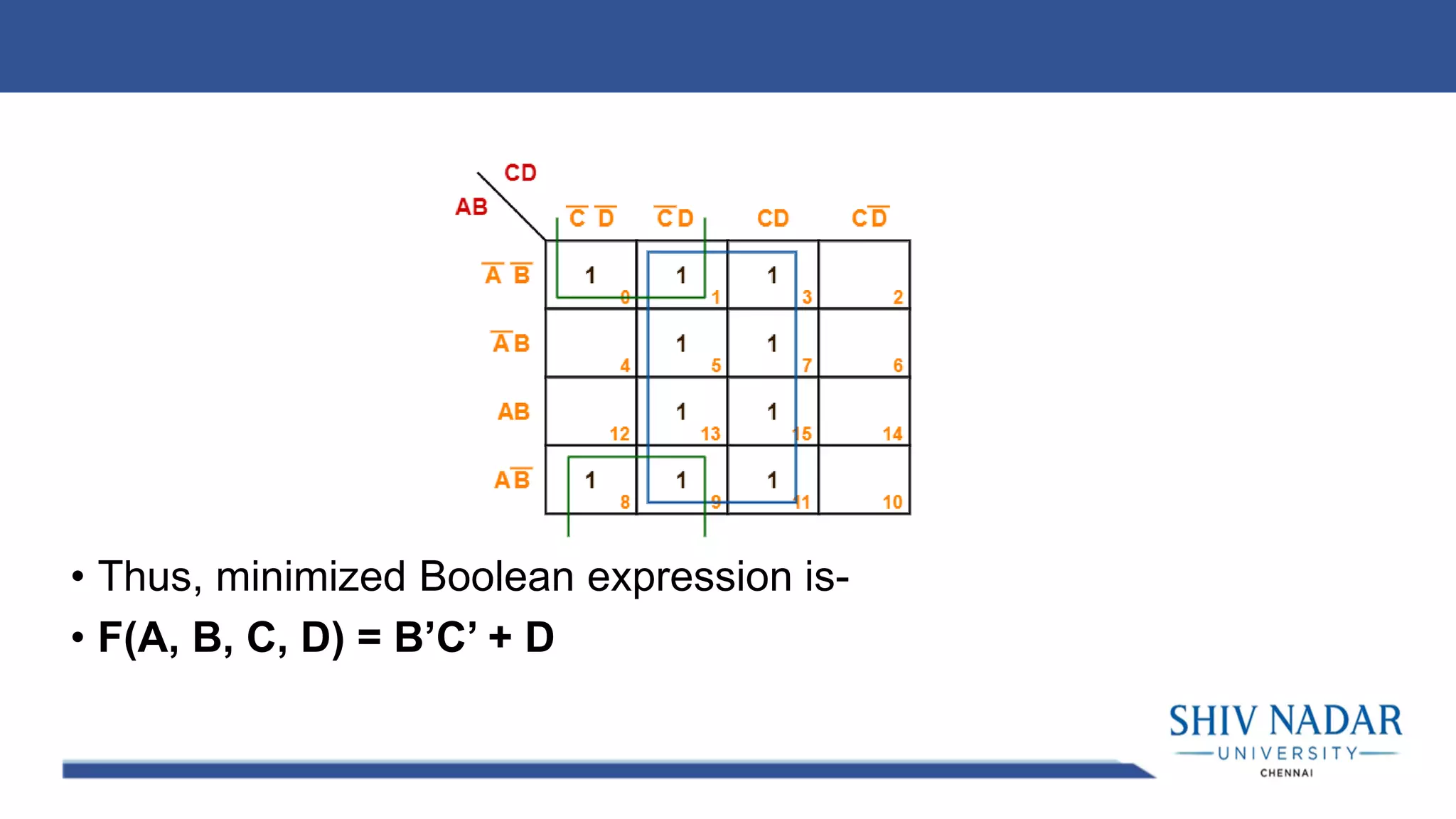
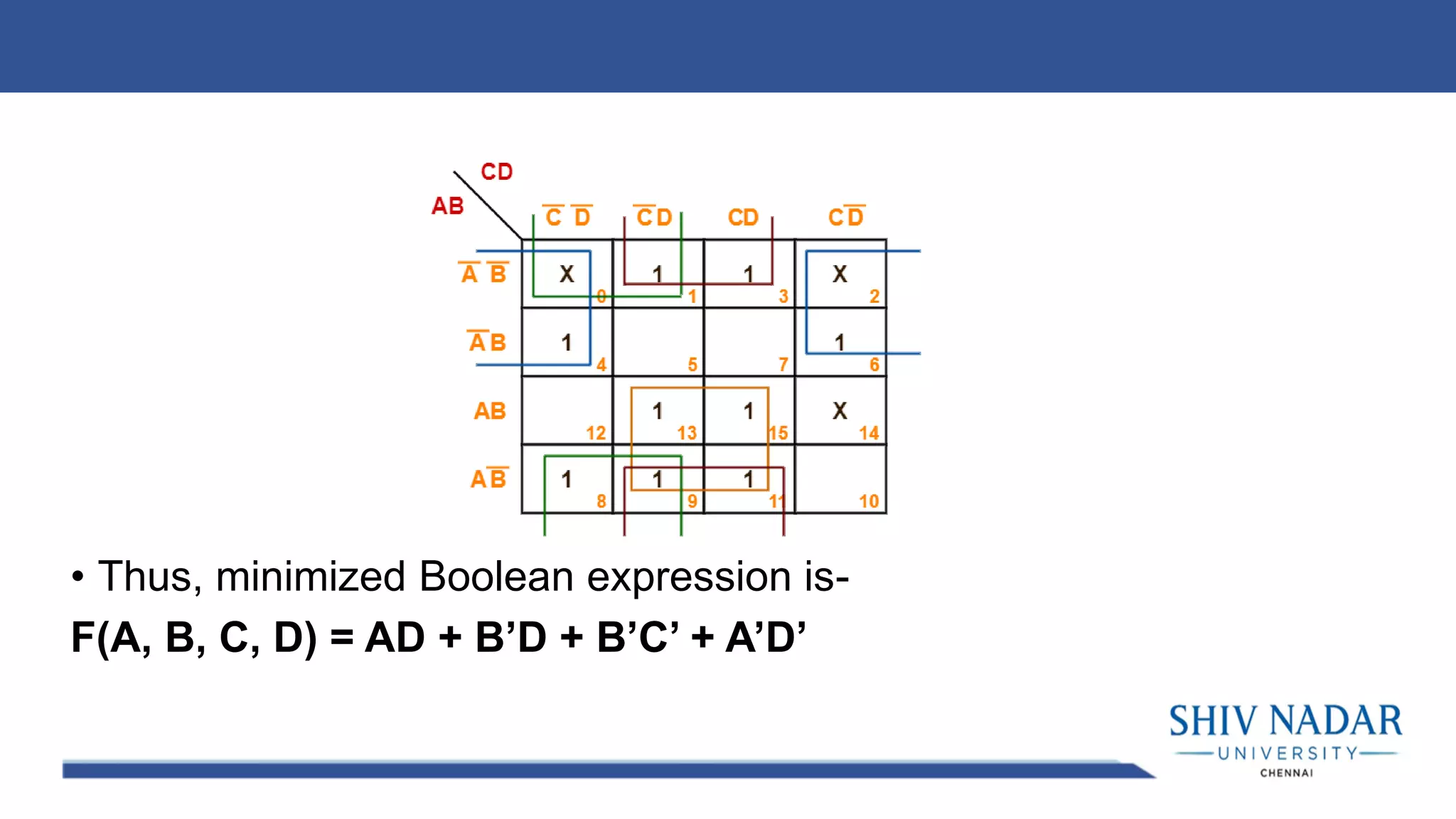
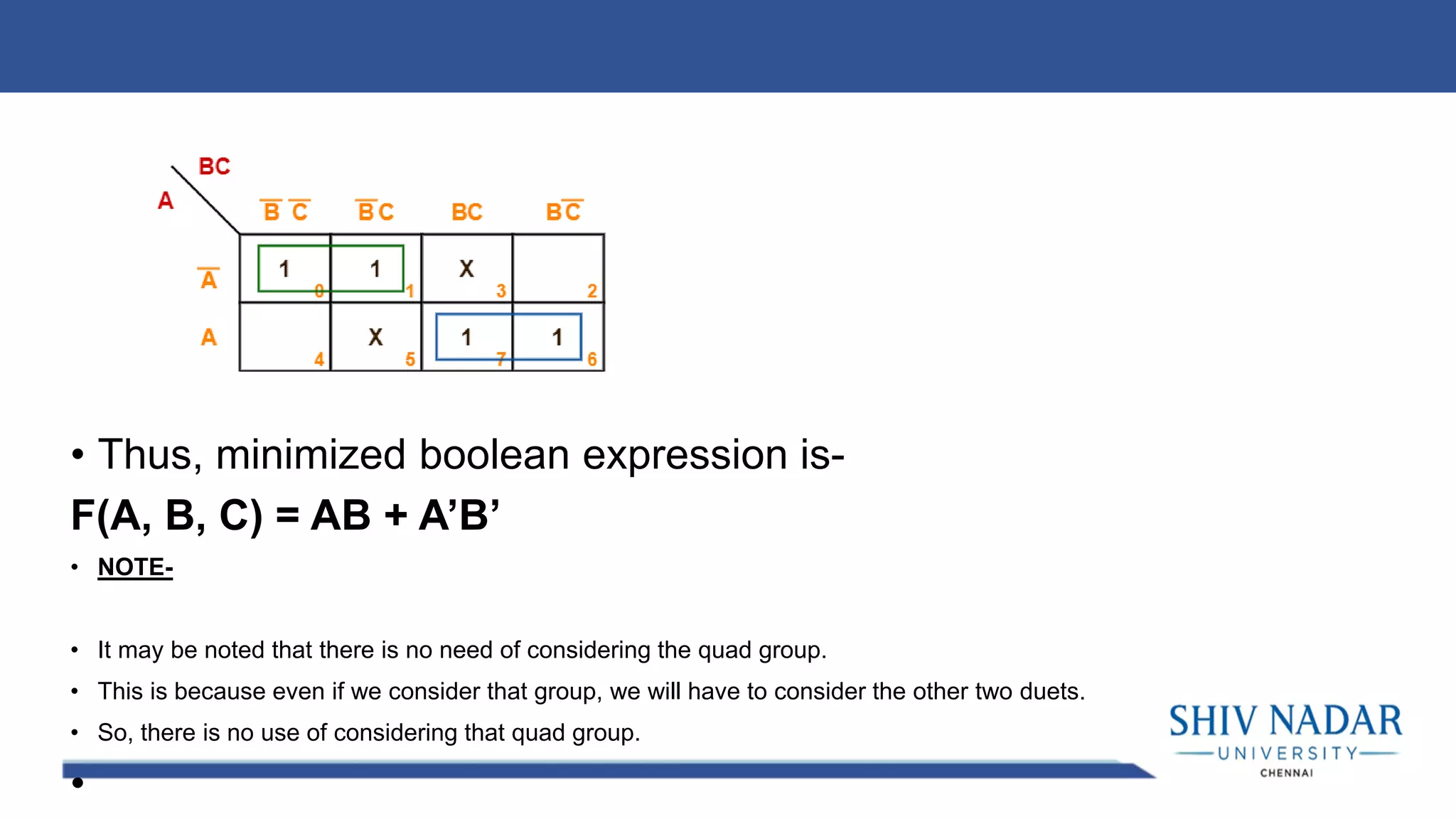
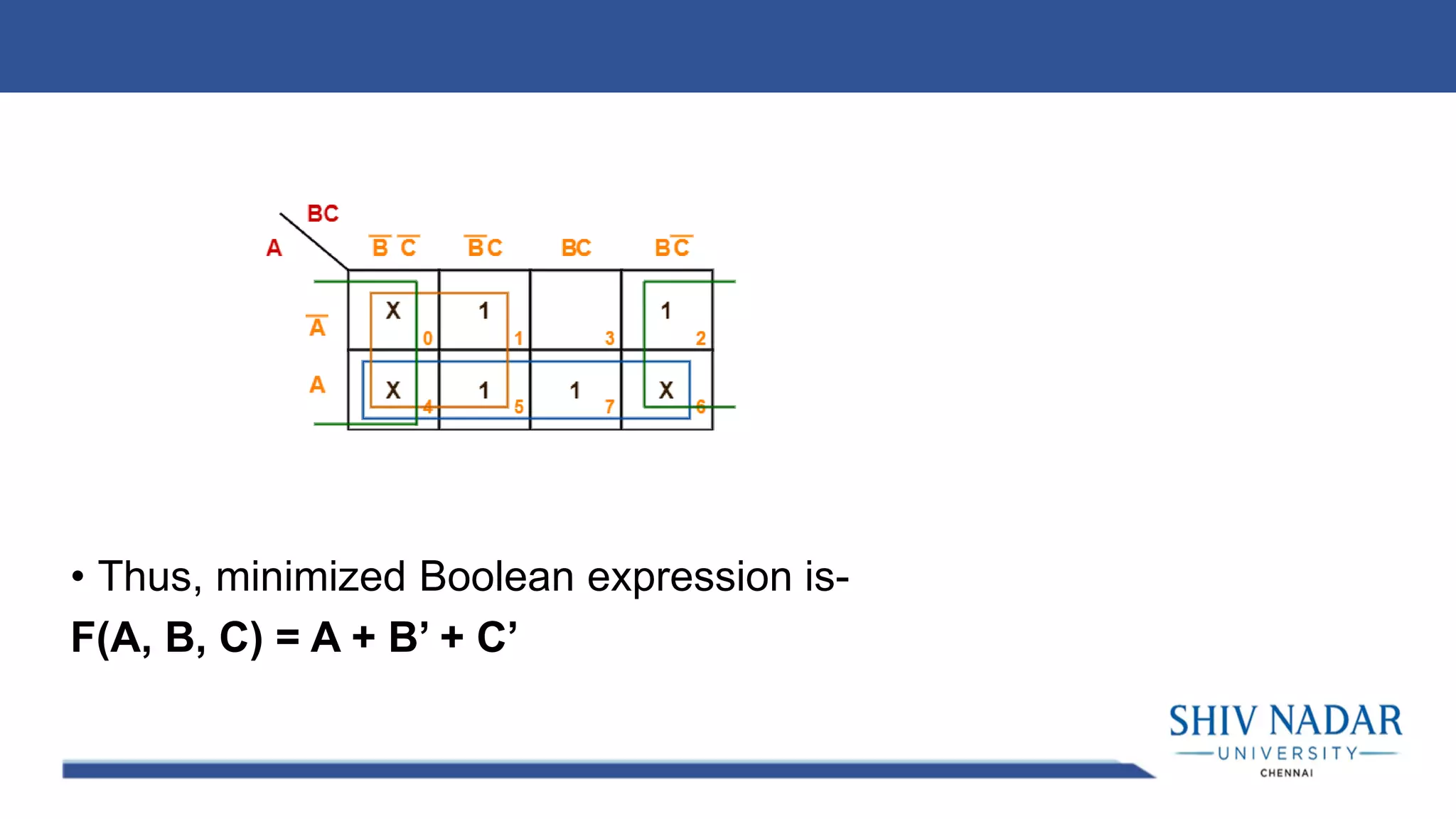
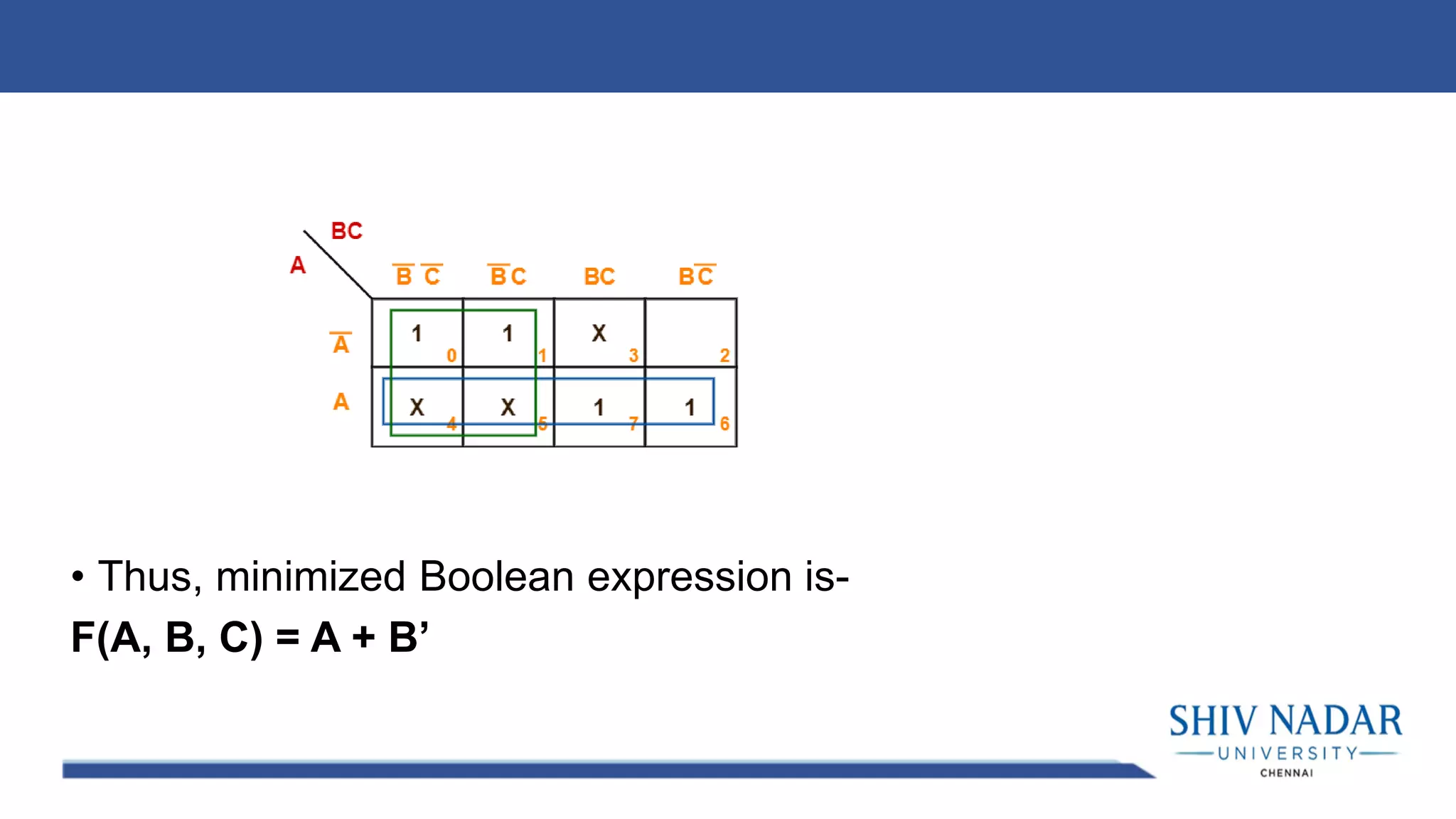
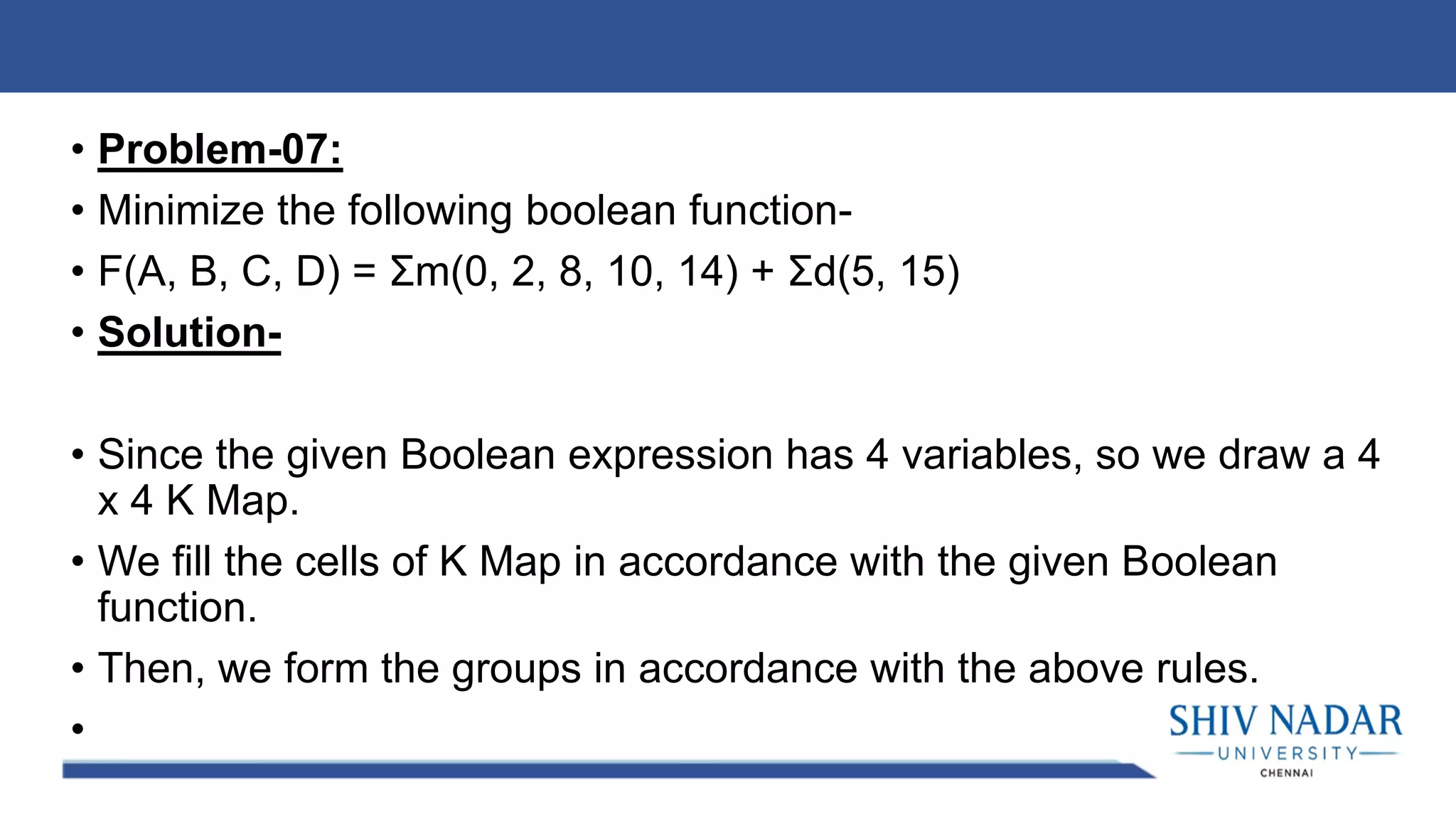
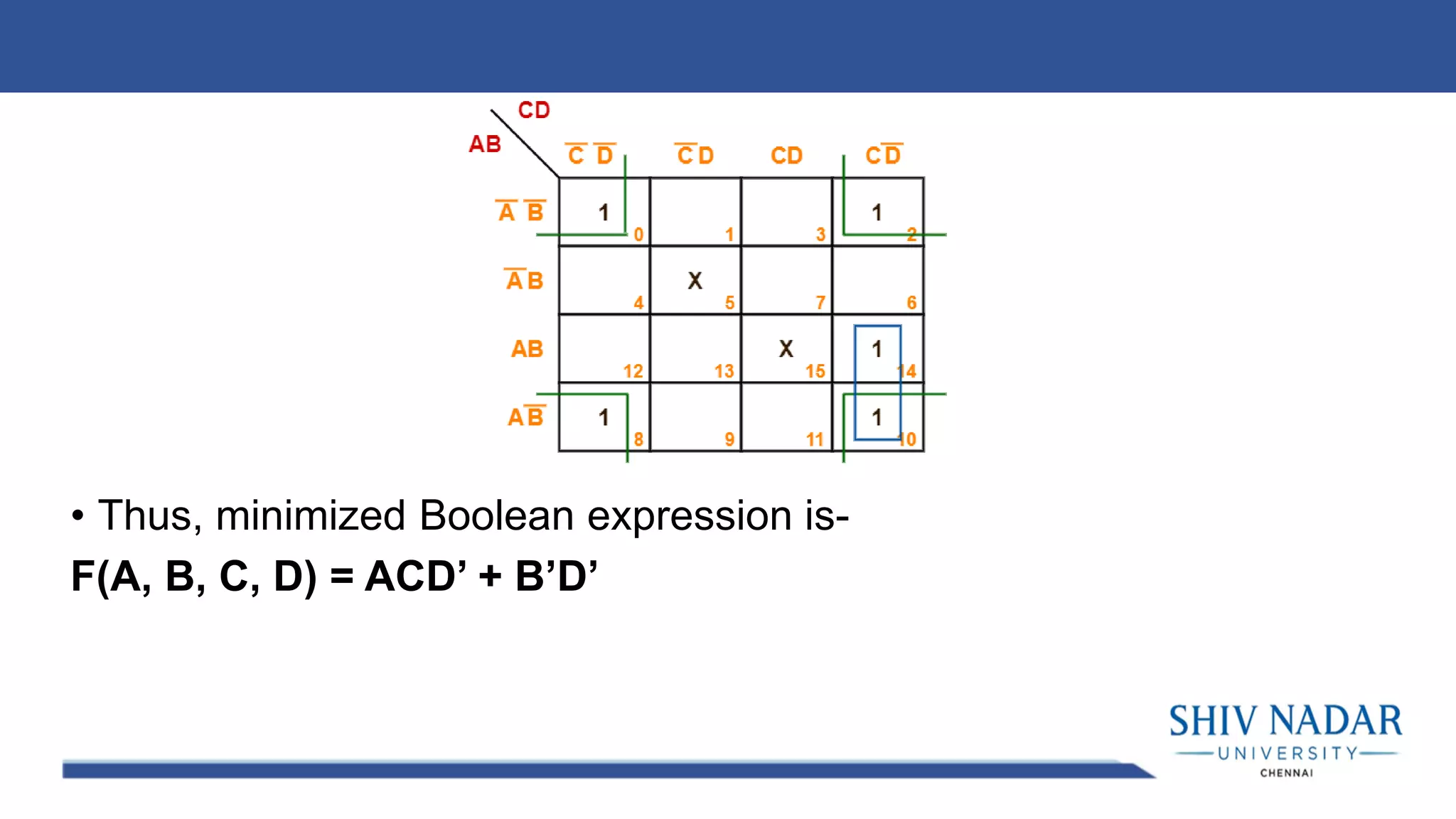
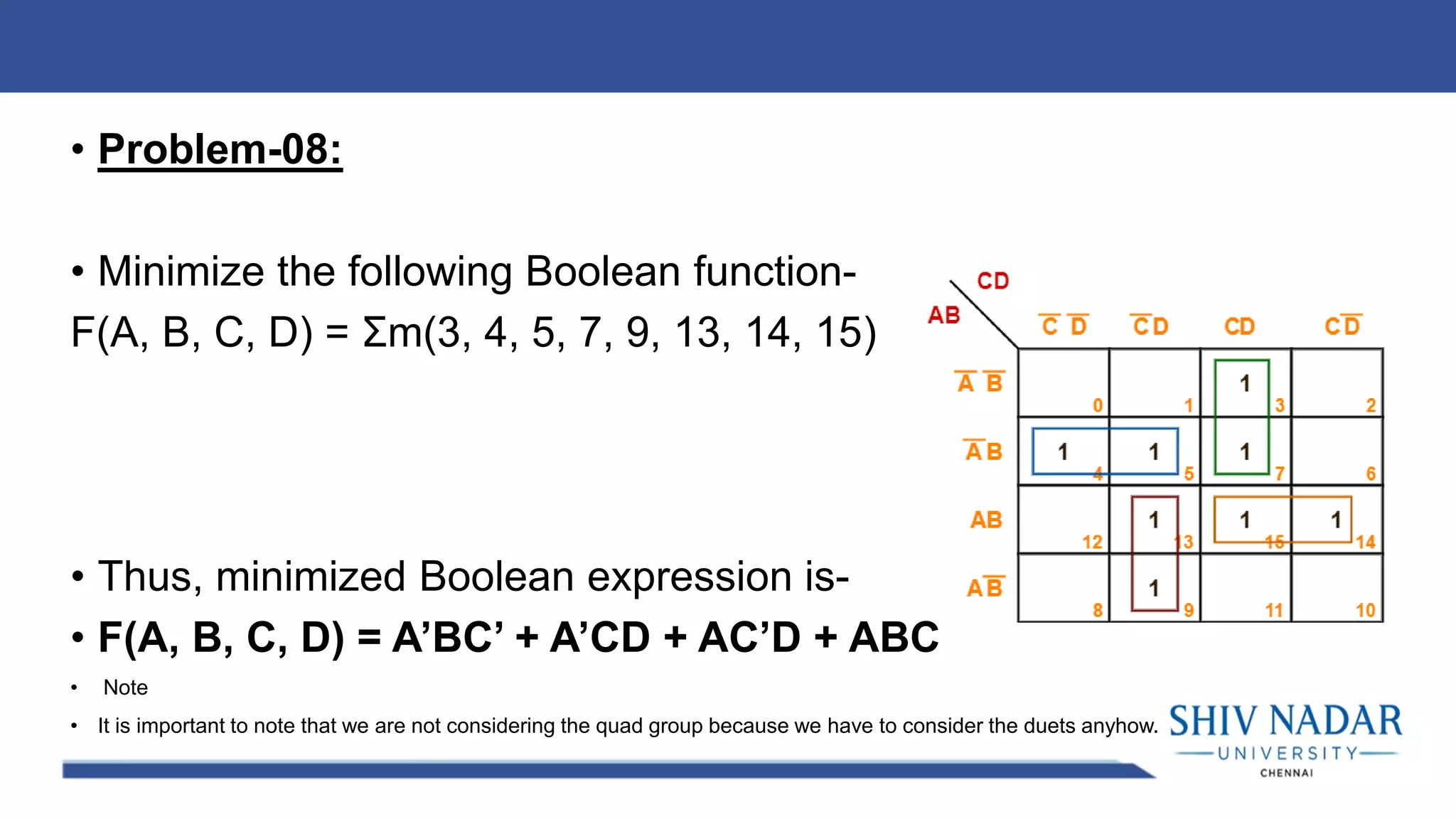
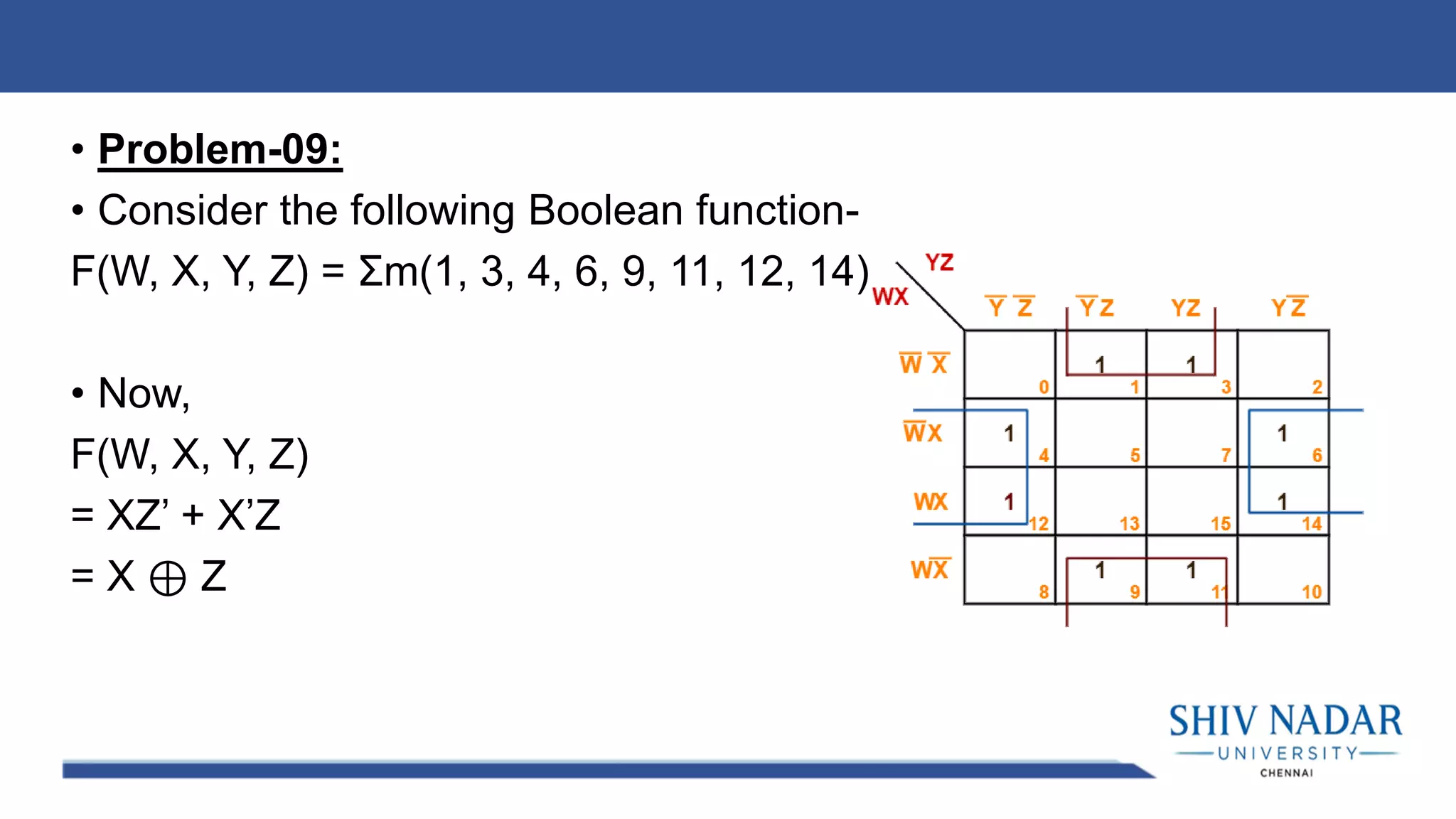
The document discusses the Karnaugh map technique for minimizing Boolean functions. It begins by explaining how to construct Karnaugh maps for functions with different numbers of variables. It then lists seven rules for grouping cells on the map to find simplified expressions. The rest of the document provides examples of applying the Karnaugh map technique to minimize various Boolean functions with 2-4 variables.