1. The agenda covers warm up activities, presentations on loops in C programming, videos on real-world applications, a game to simulate loops, practical work creating a small program in pairs using CodeBlocks, online self-learning on C programming, and a question and answer session.
2. Students will break into small groups to create a C program related to their capstone project, then discuss using loops in different programs for homework by creating an Office Mix video.
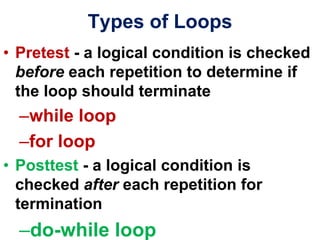
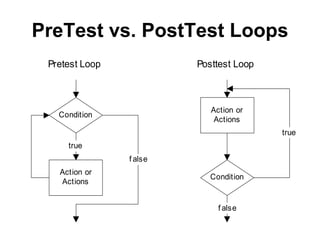
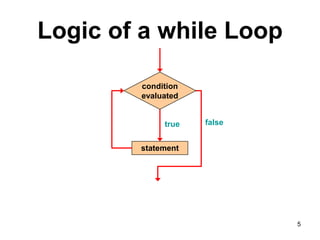
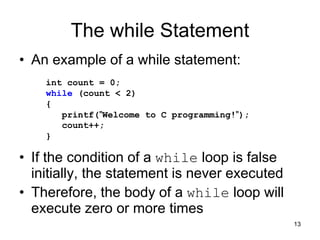
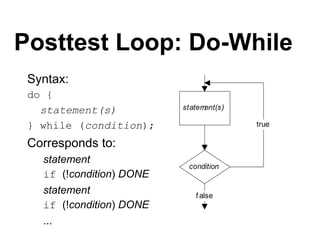
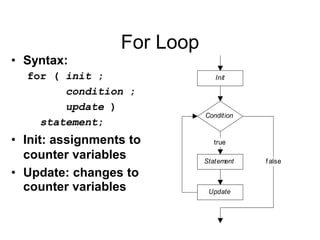
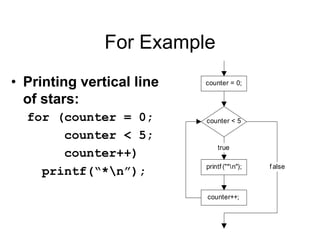
3. Resources include a video explaining for, while, and do-while loops and related reading materials.