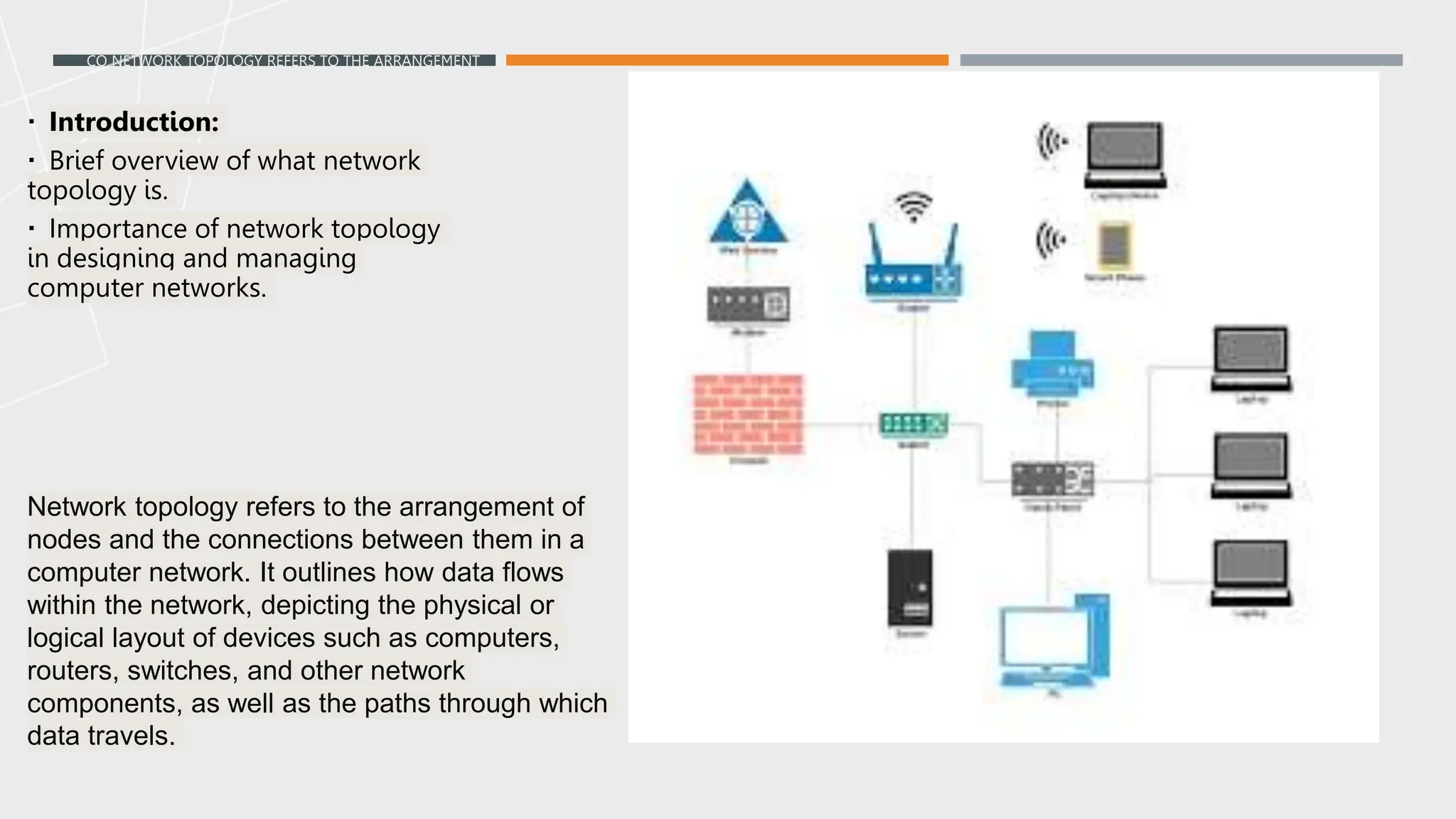
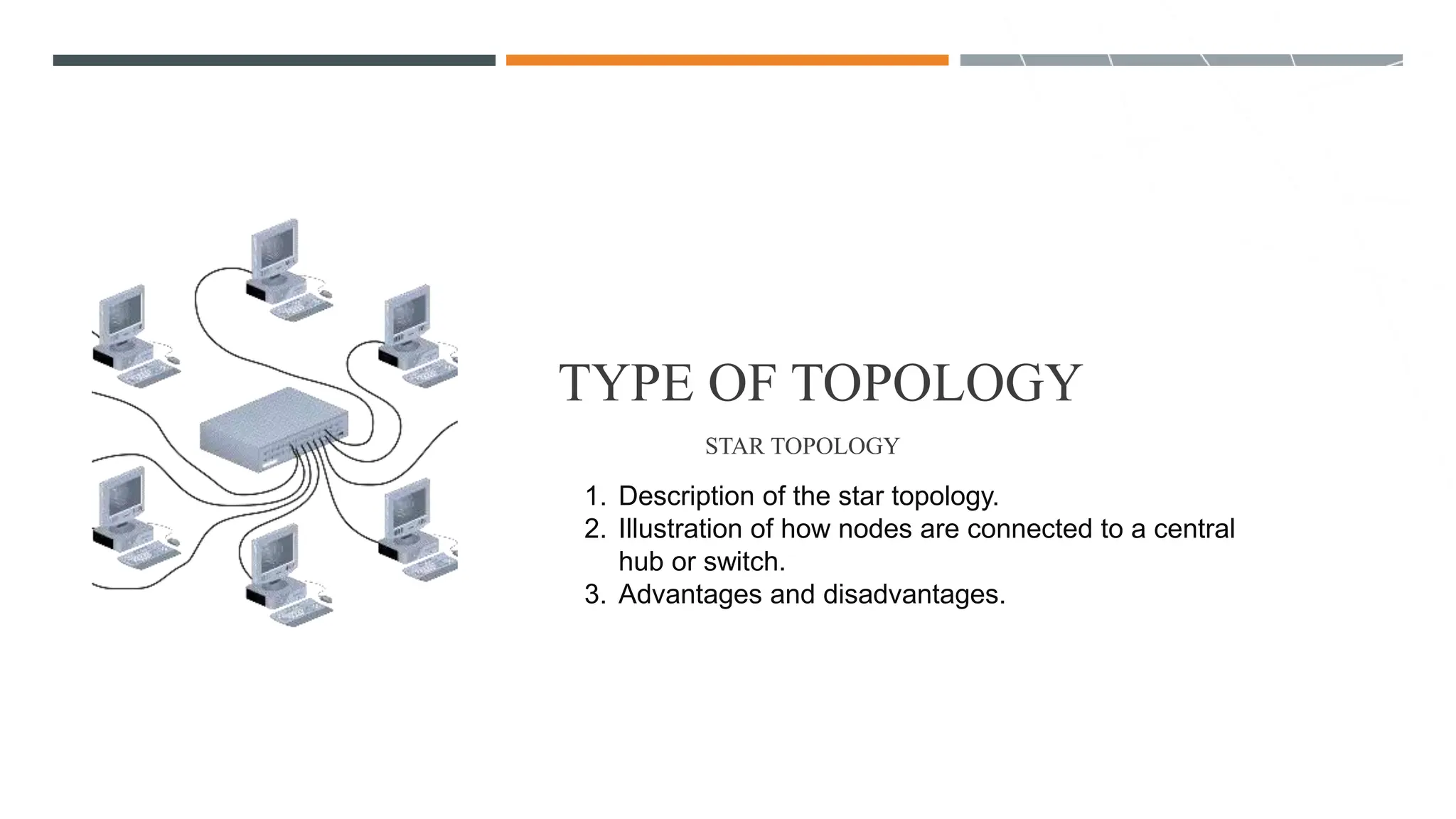
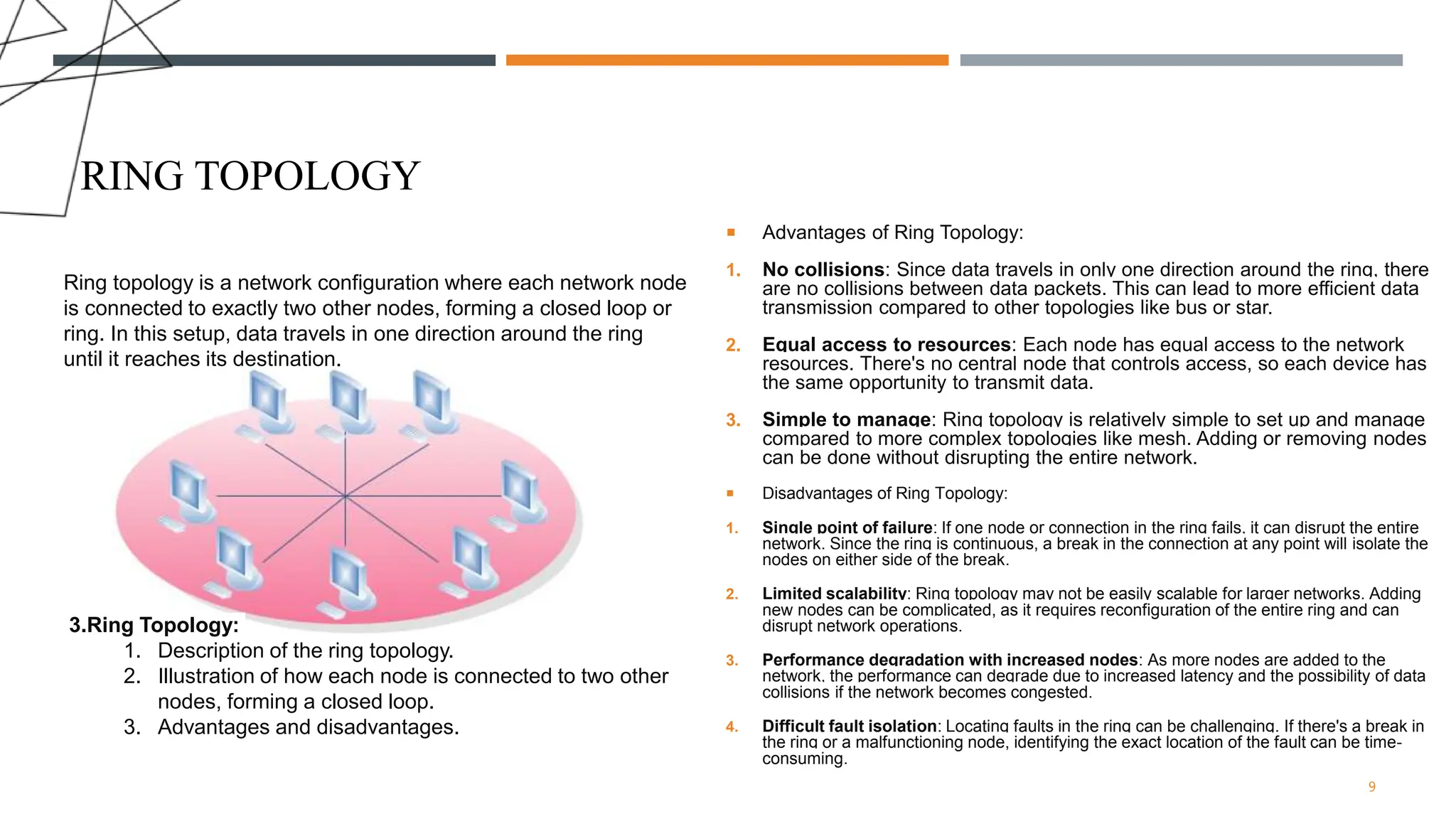
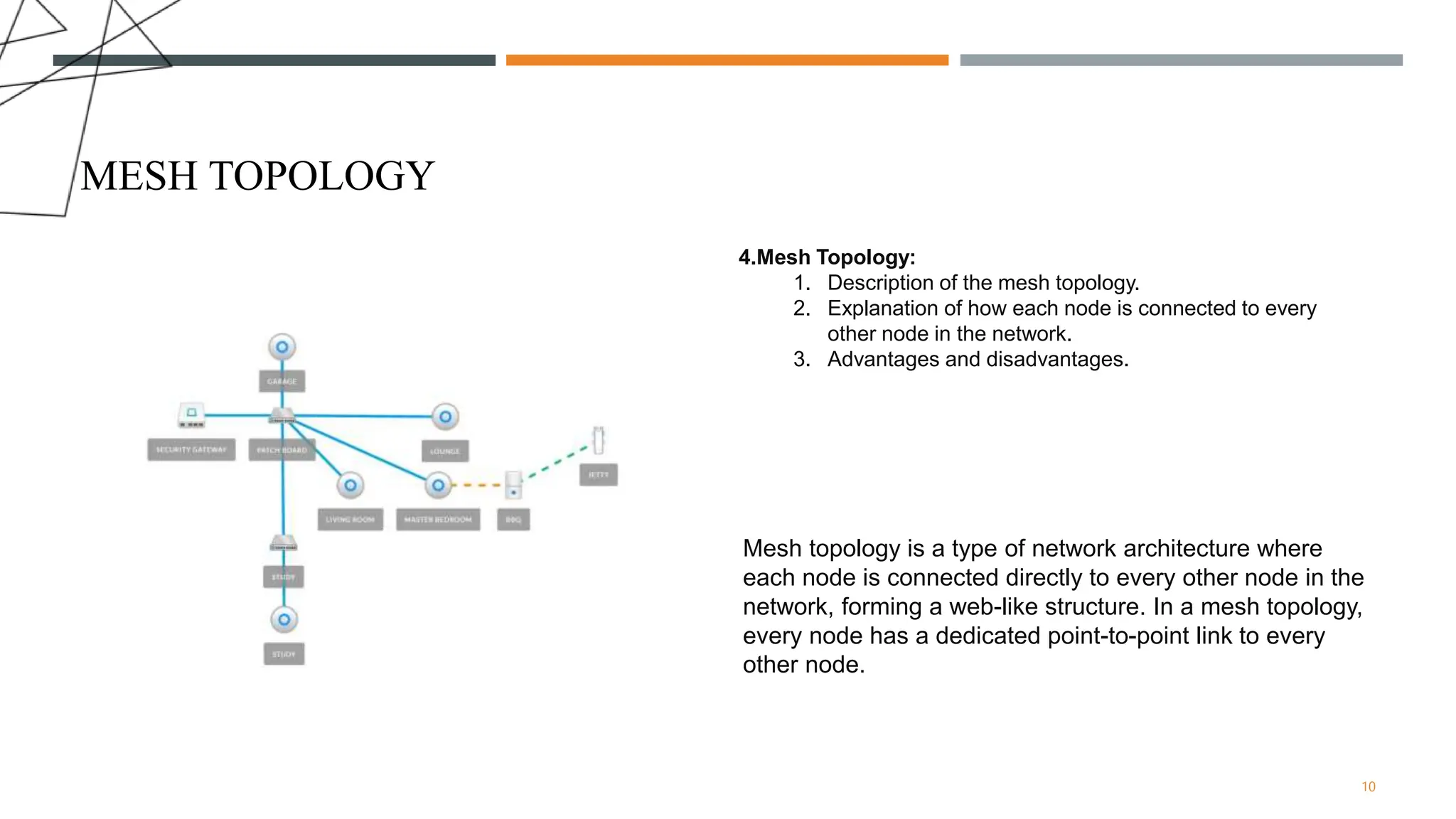
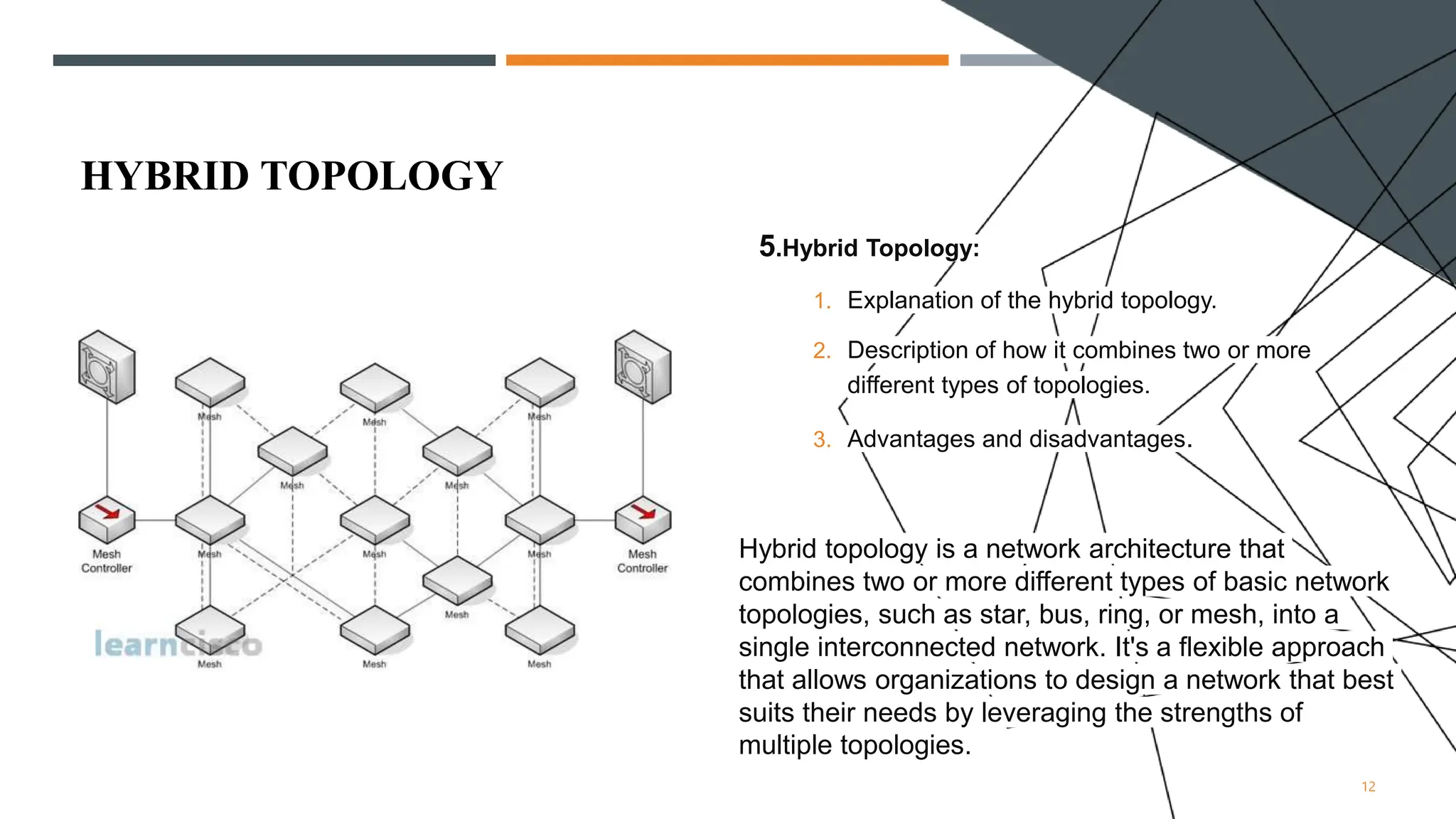
The presentation discusses various types of network topologies, including star, bus, ring, mesh, and hybrid, detailing their structures, advantages, and disadvantages. Network topology is essential for designing and managing computer networks as it defines how devices connect and communicate, influencing performance, scalability, and reliability. Additionally, factors affecting topology selection include cost, ease of management, and specific organizational needs.