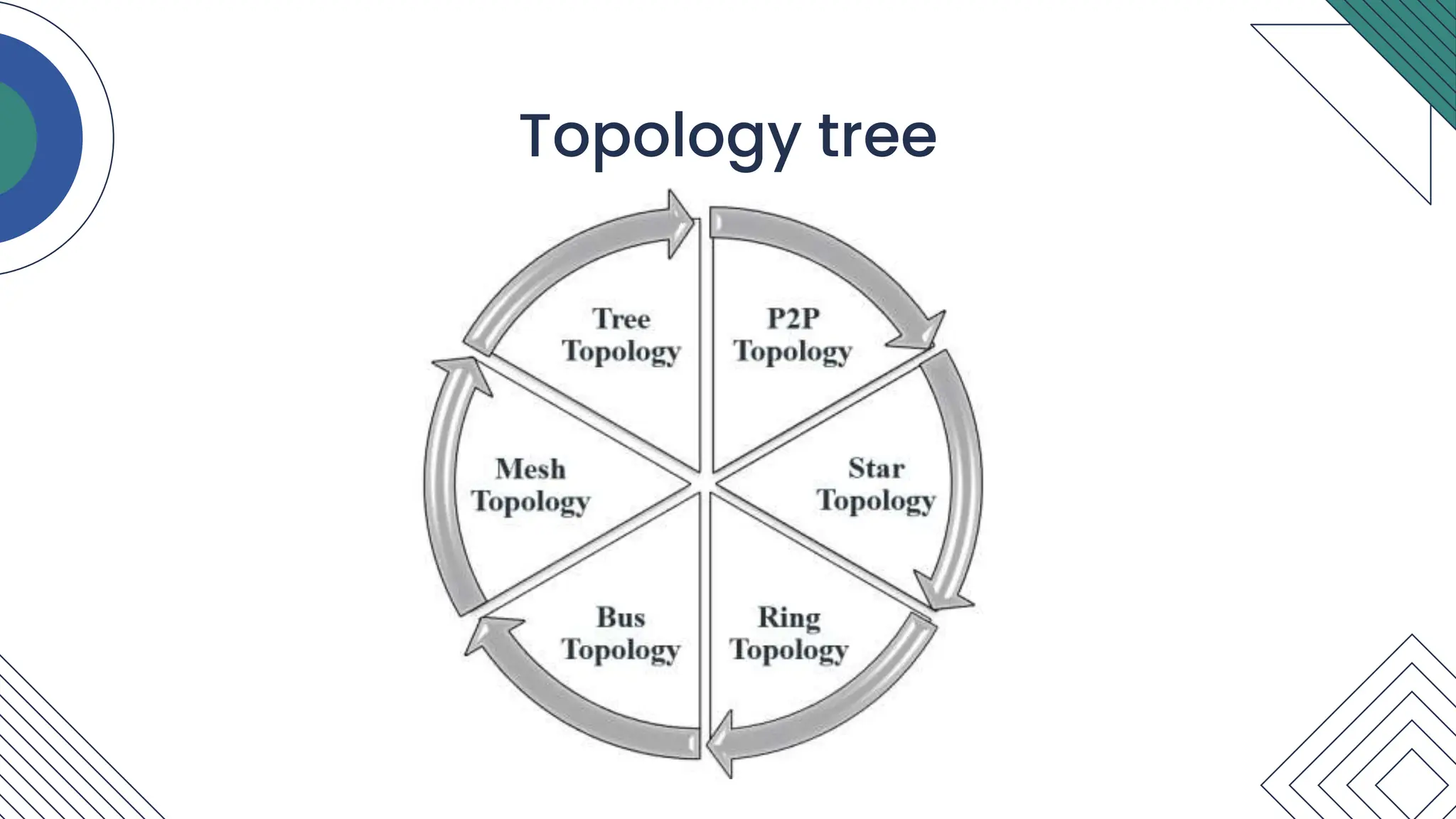
The document explores different types of network topologies including point-to-point, star, ring, bus, tree, and mesh topologies, detailing their physical and logical arrangements. Each topology is analyzed in terms of advantages and disadvantages, such as cost, installation ease, and network reliability. Overall, it provides a comprehensive overview of how data is transmitted within different network configurations.