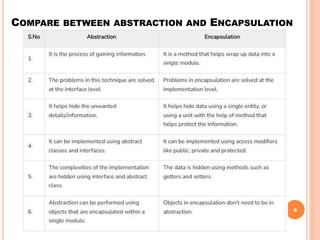
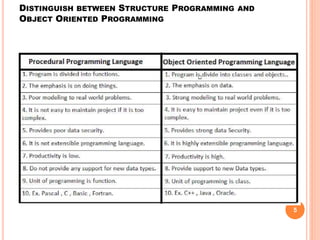
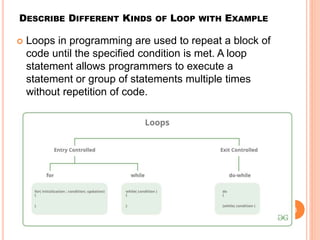
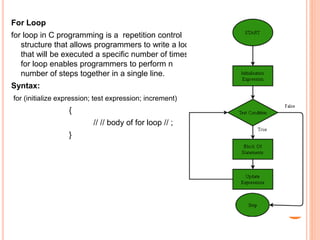
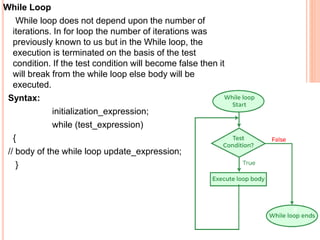
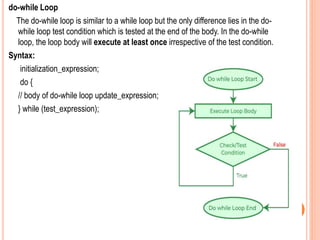
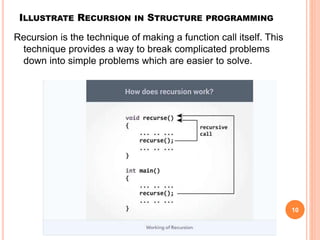
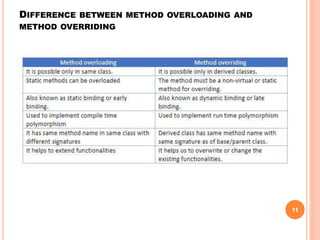
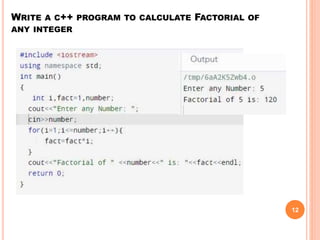
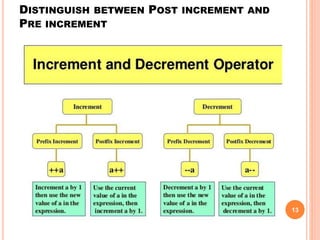
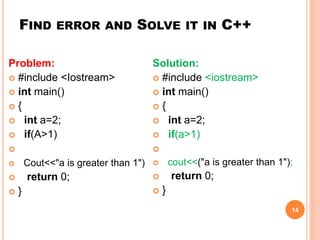
The document provides an overview of object-oriented programming (OOP), its main concepts, and features such as classes, encapsulation, and polymorphism. It explains various types of loops in programming (for, while, and do-while), recursion, and differences between certain programming concepts like method overloading and overriding. Additionally, it includes examples of C++ code with common errors and their solutions.